Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic or endoscopic limited resection is intended to be an additional therapeutic option for the treatment of early gastric cancer. However, tumorbiologic markers to predict the outcome for patients after limited resections are missing. This study therefore investigated the prognostic relevance of p53 and bcl-2 immunoreactivity as well as the percentage of apoptotic tumor cells in early invasive pT1/pT2 tumors managed with standard operations for gastric adenocarcinoma.
Methods
Histologic slides of 65 pT1/pT2 gastric carcinomas were investigated for bcl-2 and p53 immunoreactivity. For 35 patients, DNA fragmentation of tumor cell nuclei was determined by the terminal uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP) nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method. Follow-up evaluation of the patients was prospectively documented for 53.4 ± 4.1 months.
Results
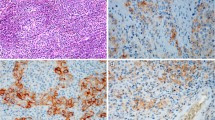
Findings showed that bcl-2 immunoreactivity was associated with tumors of the intestinal type according to Lauren´s classification (p = 0.042), and that p53 immunoreactivity was increased in more invasive tumors (pT1 vs pT2 tumors; p = 0.047). Mean survival time was significantly longer for patients with bcl-2-negative tumors (74.3 ± 6.8 months) than for patients with bcl-2-positive tumors (50.8 ± 7.6 months; p = 0.024). The percentage of apoptotic tumor cell nuclei did not have prognostic relevance in the population studied and was not associated with several histopathologic parameters or bcl-2 and p53 immunoreactivity. Subgroup analysis indicated that the survival of patients with differentiated G2 and bcl-2-negative/p53-negative tumors was significantly longer (82 ± 6 months) than the survival of patients with G2 bcl-2- and/or p53-positive tumors (41.8 ± 12.5 months; p = 0.005), with independent prognostic relevance determined by multivariate analysis (p = 0.024).
Conclusion
The data reported indicate that the analysis of bcl-2 and p53 immunoreactivity seems to have prognostic implications for early invasive (pT1/pT2) gastric adenocarcinomas and may subclassify patients for minimally invasive laparoscopic or endoscopic gastric resections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla EK, Pfister PW (2004) Staging and preoperative evaluation of upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Semin Oncol 31: 513–529
Adachi Y, Shiraishi N, Kitano S (2002) Modern treatment of early gastric cancer: review of the Japanese experience. Dig Surg 19: 333–339
Baretton GB, Diebold J, Christoforis G, Vogt M, Müller Ch, Dopfer K, Schneiderbanger K, Schmidt M, Löhrs U (1996) Apoptosis and immunohistochemical bcl-2 expression in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. Cancer 77: 255–264
Folli S, Dente M, Dell´Amore D, Gaudio M, Nanni O, Saragoni L, Vio A (1995) Early gastric cancer: prognostic factors in 223 patients. Br J Surg 82: 952–956
Fonseca L, Yonemura Y, De Arexabala X, Yamaguchi A, Miwa K, Miyazaki I (1994) p53 detection as a prognostic factor in early gastric cancer. Oncology 51: 485–490
Gabbert HE, Müller W, Schneiders A, Meier S, Hommel G (1995) The relationship of p53 expression to the prognosis of 418 patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer 76: 720–726
Harris CC, Hollstein M (1993) Clinical implications of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. N Engl J Med 329: 1318–1326
Hockenberg DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ (1991) bcl-2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88: 6961–6965
Ikeguchi M, Tatebe S, Kaibara N, Ito H (1977) Changes in levels of expression of p53 and the product of the bcl-2 in lines of gastric cancer cells during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Eur Surg Res 29: 396–402
Kerr JFR, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1994) Apoptosis: its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73: 2013–2036
Kim JP, Hur YS, Yang HK (1995) Lymph node metastasis as a significant prognostic factor in early gastric cancer: analysis of 1,136 early gastric cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 2: 308–313
Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Toga T (2004) Preclinical evaluation of antisense bcl-2 as a chemosensitizer for patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer 101: 177–2186
Kroemer G (1997) The proto-oncogene bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nature Med 3: 614–620
Lauwers GY, Scott GV, Hendricks J (1994) Immunhistochemical evidence of aberrant bcl-2 protein expression in gastric epithelial dysplasia. Cancer 73: 2900–2904
Lauwers GY, Scott GV, Karpeh MS (1995) Immunhistochemical evaluation of bcl-2 protein expression in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer 75: 2209–2213
Lin J, Beerm DG (2004) Molecular biology of upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Semin Oncol 31: 476–486
Ludwig K, Wilhelm L, Scharlau U, Amtsberg G, Berhardt J (2002) Laparoscopic–endoscopic rendezvous resection of gastric tumors. Surg Endosc 16: 1561–1565
Miwa K, Miyazaki I, Sahara H, Fujimura T, Yonemura Y, Noguchi M, Falla R (1995) Rationale for extensive lymphadenectomie in early gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer 72: 1518–1524
Rosch T (1995) Endosonographic staging of gastric cancer: a review of literature results. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 5: 549–557
Ryu KW, Lee JH, Kim HS, Kim YW, Choi IJ, Bae JM (2003). Prediction of lymph node metastasis by sentinel node biopsy in gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 29: 895–899
Scartozzi M, Galizia E, Freddari F, Berardi R, Cellerino R, Cascinu S (2004) Molecular biology of sporadic gastric cancer: prognostic indicators and novel therapeutic approaches. Cancer Treat Rev 30: 451–459
Schlag PM, Bembenek A, Schulze T (2004) Sentinel node biopsy in gastrointestinal-tract cancer. Eur J Cancer 40: 2022–2032
Selivanova G, Iotsova V, Okan I, Fritsche M, Ström M, Groner B, Grafström RC, Wiman KG (1997) Restoration of the growth suppression function of mutant p53 by a synthetic peptide derived from the 53 C-terminal domain. Nature Med 3: 632–638
Shimoyama S, Seto Y, Yasuda H, Mafune K, Kaminishi M (2005) Concepts, rationale, and current outcomes of less invasive surgical strategies for early gastric cancer: data from a quarter-century of experience in a single institution. World J Surg 29:58–65
Starzynska T, Bromley M, Gosh A, Stern PL (1992) Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in gastric and colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 66: 558–562
Tanaka K, Tonouchi H, Kobayashi M, Konishi N, Ohmori Y, Mohri Y, Kusunoki M (2004) Laparoscopically assisted total gastrectomy with sentinel node biopsy for early gastric cancer: preliminary results. Am Surg 70: 976–981
TNM classification of malignant tumors (1997) 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1992) p53: function and dysfunction. Cell 70: 523–526
Yanai H, Matsumoto Y, Harada T, Nishiaki M, Tokiyama H, Shigemitsu T, Tada M, Okita K (1997) Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in early gastric cancer: a pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc 46: 212–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopp, R., Diebold, J., Dreier, I. et al. Prognostic relevance of p53 and bcl-2 immunoreactivity for early invasive pT1/pT2 gastric carcinomas: indicators for limited gastric resections?. Surg Endosc 19, 1507–1512 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0043-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0043-7