Abstract
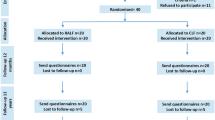
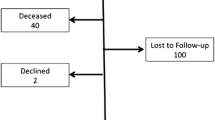
Background: Although the degree of surgical experience clearly affects early outcome of laparoscopic antireflux surgery, its influence on long-term results has not been fully evaluated. The aim of this study was to verify whether the initial experience in laparoscopic antireflux surgery could also influence the late clinical outcome. Methods: Clinical and endoscopic findings, together with quality of life, of the first 25 patients successfully submitted to laparoscopic fundoplication were compared with those of 25 matched controls operated on later. Results: At more than 2 years’, follow-up, reflux symptoms, endoscopic findings, use of antisecretory drugs, side effects, and quality of life were not significantly different in both groups, despite a high occurrence of major anatomical failures (three vs one) in the first set of patients. Conclusion: The late clinical outcome of patients with gastroesophageal disease operated on during the learning phase or after gaining experience is not different, provided the surgeon is adequately trained in laparoscopic surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G Apolone P Mosconi (1998) ArticleTitleThe Italian SF-36 survey: translation, validation and norming. J Clin Epidemiol 51 1025–1036 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0895-4356(98)00094-8 Occurrence Handle9817120
Apolone G, Mosconi P, Ware J (1997) II questionario sullo stato di salute SF-36. Manuale d’uso e quida all’interpretazione dei risultati. Guerini, Milan
A Blomqvist J Dalenback C Hagedorn H Lonroth A Hyltander L Lundell H Lonroth A Hyltander L Lundell (2000) ArticleTitleImpact of complete gastric fundus mobilization on outcome after laparoscopic total fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 4 493–500 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1091-255X(00)80092-X Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2Fjslektw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11077325
G Champault (1994) ArticleTitleReflux gastro-esophagien. Traitement par laparoscopie. 940 cas. Expérience francaise. Ann Chir 4 159–164
GG Champault C Barrat RC Rozon N Rizk JM Catheline (1999) ArticleTitleThe effect of the learning curve on the outcome of laparoscopic treatment for gastroesophageal reflux. Surg Laparosc End Percut Tech 9 375–381 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00019509-199912000-00001 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czivFSiug%3D%3D
S Contini C Scarpignato (2002) ArticleTitleEarly esophageal transit study with Gastrografin after laparoscopic fundoplication: how useful is it? Am J Surg 183 226–231 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(02)00784-5 Occurrence Handle11943116
S Contini R Zinicola A Bertelè G Nervi P Rubini C Scarpignato (2002) ArticleTitleDysphagia and clinical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen or Rossetti fundoplication: a sequential prospective study. World J Surg 26 1106–1111 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00268-002-6247-2 Occurrence Handle12045866
GL Dunnington TR De Meester (1993) ArticleTitleOutcome effect of adherence to operative principles of Nissen fundoplication by multiple surgeons. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Study Group. Am J Surg 166 654–657 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD1MbktVw%3D Occurrence Handle8273844
DC Gotley BM Smithers B Menzies FJ Branicki M Rhodes L Nathanson (1996) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and postoperative dysphagia—can it be predicted? Ann Acad Med Singapore 25 646–649 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD1c3ns1Q%3D Occurrence Handle8923996
RA Hinder JS Libbey P Gorecki T Bamner (1999) ArticleTitleAntireflux surgery: indications, preoperative evaluation and outcome. Gastronterol Clin North Am 28 987–1005 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7lvFegtA%3D%3D
GG Jamieson (1998) What are the most frequent causes of failure of antireflux operations? What is the average time for their occurrence? R Giuli JP Galmiche GG Jamieson C Scarpignato (Eds) The esophagogastric junction, Vol. 2. John Libbey Eurotext Paris 45–48
GG Jamieson DI Watson R Britten-Jones PC Mitchell M Anvari (1994) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg 220 137–145 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuA3s%2FnslY%3D Occurrence Handle8053735
T Kamolz T Bammer H Wykypiel Jr M Pasiut R Pointner M Pasiut R Pointner M Pasiut R Pointner (2000) ArticleTitleQuality of life and surgical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplication: one year follow-up. Endoscopy 32 363–368 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3nsVyksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10817172
EC Klinkenberg-Knoll F Nelis P Snel B Mitchell P Prichard D Lloyd N Havu MH Frame J Roman (2000) ArticleTitleThe Long-Term Study Group. Long-term omeprazole treatment in resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease: efficacy, safety and influence on gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 118 661–669 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXis1ens74%3D Occurrence Handle10734017
ME Luostarinen JO Isolauri (1999) ArticleTitleSurgical experience improves long-term results of Nissen fundoplication. Scand J Gastroenterol 34 117–120 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3gs1Cjtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10192186
G McLaughlan (1996) ArticleTitleEsophageal function testing and antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 83 1684–1688
H Motulsky (1995) Intuitive statistics. Oxford University Press New York
JH Peters TR De Meester P Crookes S Oberg M de Voos Shoop JA Hagen CG Bremner (1998) ArticleTitleThe treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: prospective evaluation of 100 patients with “typical” symptoms. Ann Surg 228 40–50 Occurrence Handle9671065
CE Pope II (1992) ArticleTitleThe quality of life following antireflux surgery. World J Surg 16 355–358 Occurrence Handle1561824
M Rossetti K Hell (1977) ArticleTitleFundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in hiatal hernia. World J Surg 1 439–444 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSeD3MrntlM%3D Occurrence Handle910451
DM Sataloff K Pursnani S Hoyo F Zayas C Lieber DO Castell (1997) ArticleTitleAn objective assessment of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Am J Surg 174 63–67 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(97)00026-3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA1c3ps1A%3D Occurrence Handle9240955
M Savary G Miller (1977) L’Oesophage. Manuel et Atlas d’Endoscopie. Gassmann Solaire, Switzerland
SJ Soot N Eshraghi M Farahmand BS Sheppard CW Deveney (1999) ArticleTitleTransition from open to laparoscopic fundoplication. The learning curve. Arch Surg 134 278–281 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archsurg.134.3.278 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7os1Chuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10088568
SJ Spechler E Lee D Ahnen RK Goyal I Hirano F Ramirez JP Raufman R Sampliner T Schnell S Sontag ZR Vlahcevic R Young W Williford (2001) ArticleTitleLong-term outcome of medical and surgical therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 285 2331–2338 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.285.18.2331 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvFCksbg%3D
HG Stein TR De Meester RA Hinder (1992) ArticleTitleOutpatients physiologic testing and surgical management of foregut motility disorders. Curr Probl Surg 29 415–455
TL Trus WS Laycock G Branum JP Waring S Lauren JG Hunter (1996) ArticleTitleIntermediate follow-up of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Am J Surg 171 32–35 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(99)80069-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2c3gvVY%3D Occurrence Handle8554147
V Velanovich R Karmy-Jones (1998) ArticleTitleMeasuring gastroesophageal reflux disease: relationship between the Health-Related Quality of Life score and physiologic parameters. Am Surg 64 649–653 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czhsl2rsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9655276
A Voigt J Joffre C Alvarez G Rosenthal (1999) ArticleTitleFactors contributing to laparoscopic failure during the learning curve for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in a community hospital. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Techn 9 243–248
AJ Voitk SG Tsao S Ignatius (2001) ArticleTitleThe tail of the learning curve for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am J Surg 182 250–253 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(01)00699-7 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrktV2htQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11587686
DI Watson GG Jamieson (1998) ArticleTitleAntireflux surgery in the laparoscopic era. Br J Surg 85 1173–1184 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvitlOktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9752855
DI Watson GG Jamieson RJ Baigrie G Mathew PG Devitt PA Game (1996) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic surgery for gastroesophageal reflux: beyond the learning curve. Br J Surg 83 1284–1287
DI Watson GK Pike RJ Baigrie G Mathew PG Devitt R Britten-Jones GG Jamieson (1997) ArticleTitleProspective double-blind randomized trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with division and without division of short gastric vessels. Ann Surg 226 164–652 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-199711000-00009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contini, S., Scarpignato, C. Does the learning phase influence the late outcome of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease after laparoscopic fundoplication? . Surg Endosc 18, 266–271 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9198-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9198-2