Abstract
Background
The main drawback with the laparoscopic approach is that the surgeon is unable to palpate vessels, tumors, and organs during surgery. Furthermore, the laparoscope provides only surface view of organs. There is a need for more advanced visualizations that can enhance the view to include information below the surface of the organs for planning of the procedure and for control and guidance during treatment.
Methods
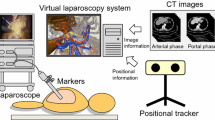
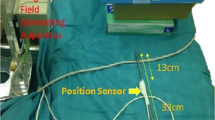
We propose three-dimensional (3D) navigation technology based on preoperatively acquired magnetic resonance or computed tomography data used in combination with a laparoscopic navigation pointer (LNP). The LNP has an attached position tracker that allows the surgeon to control the display of images interactively before and during surgery. This study evaluated the patient registration accuracy, the feasibility of image-based navigation and, qualitatively, the navigation precision in the retroperitoneum during laparoscopic surgery.
Results
This technology was used during the treatment of six patients (involving adrenalectomies and a neuroma protruding into the pelvis). An average patient registration accuracy of 6.90 mm was achieved. The precision during navigation in the retroperitoneum was, in some cases, better than the patient registration accuracy suggested. The technology helped the surgeons to understand better the anatomy and to locate blood vessels.
Conclusions
In the reported cases, the LNP was a useful tool for image guidance in laparoscopic surgery, both for planning the surgical approach in detail and for guidance. The authors believe that adominal 3D image guidance using an LNP has a large potential for improving laparoscopic surgery, especially when vessels and anatomic relations may be difficult to identify using only a laparoscope. Accordingly, they believe this new technology could increase safety and make it easier for the surgeon to perform successful laparoscopic surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Cartellieri J Kremser F Vorbeck (2001) ArticleTitleComparison of different 3D navigation systems by a clinical “user ” Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258 38–41 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004050000302 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7ntV2ksw%3D%3D
A Gronningsaeter T Lie A Kleven T Mørland T Langø G Unsgård HO Myhre R Mårvik (2000) ArticleTitleInitial experience with stereoscopic visualization of three-dimensional ultrasound data in surgery Surg Endosc 14 1074–1078 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004640000079 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FovFCjsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11116423
HK Gumprecht DC Widenka CB Lumenta (1999) ArticleTitleBrainLab Vector Vision neuronavigation system: technology and clinical experiences in 131 cases Neurosurgery 44 97–105 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7htValsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9894969
N Hata T Dohi H Iseki K Takakura (1997) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a frameless and armless stereotactic neuronavigation system with ultrasonographic registration Neurosurgery 41 608–613 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199709000-00020 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiH2MjgtlE%3D Occurrence Handle9310978
A Herline JD Stefansic J Debelak RL Galloway W Chapman (2000) ArticleTitleTechnical advances toward interactive image-guided laparoscopic surgery Surg Endosc 14 675–679 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004640000023 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7gvFWltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10948308
AJ Herline JD Stefansic JP Debelak SL Hartmann CW Pinson RL Galloway WC Chapman (1999) ArticleTitleImage-guided surgery: preliminary feasibility studies of frameless stereotactic liver surgery Arch Surg 134 644–650 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archsurg.134.6.644 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3psVaqtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10367875
TAN Hernes S Ommedal T Lie F Lindseth T Langø G Unsgaard (2002) ArticleTitleStereoscopic navigation-controlled display of preoperative MRI and intraoperative 3D ultrasound in planning and guidance of neurosurgery: new technology for minimally invasive image guided surgery approaches Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 46 129–137
L Ibanez W Schroeder L Ng J Cates (2003) The ITK Software Guide: The Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit. Edition 1.4 Kitware New York
JH Kaspersen E Sø1ie J Wesche J Åsland J Lundbom A Ødegård F Lindseth TAN Hernes (2003) ArticleTitle3D ultrasound based navigation combined with preoperative CT during abdominal interventions: a feasability study CardioVasc Intervent Radiol 26 347–356 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00270-003-2690-1 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srosFGnug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14667116
RF Labadie M Fenlon H Cevikalp S Harris R Galloway JM Fitzpatrick (2003) ArticleTitleImage-guided otologic surgery Int Congress Series 1256 627–632 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0531-5131(03)00273-5
W Lamade M Vetter P Hassenpflug M Thorn HP Meinzer C Herfarth (2002) ArticleTitleNavigation and image-guided HBP surgery: a review and preview J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 9 592–599 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s005340200079
F Lindseth JH Kaspersen S Ommedal T Langø G Unsgaard TAN Hernes (2003) ArticleTitleMultimodal image fusion in ultrasound-based neuronavigation: improving overview and interpretation by integrating preoperative MRI with intraoperative 3D ultrasound Comp Aided Surg 8 49–69
E Sjø1ie T Langø B Ystgaard G Tangen TAN Hernes R Mårvik (2002) ArticleTitle3-D ultrasound-based navigation for radiofrequency thermal ablation in treatment of liver malignancies Surg Endosc 17 933–938
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by grants from the Research Council of Norway through the Strategic University Program in Medical Technology at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, the Strategic Institute Program at SINTEF Unimed, and the Norwegian Ministry of Health and Social Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mårvik, R., Langø, T., Tangen, G.A. et al. Laparoscopic navigation pointer for three-dimensional image–guided surgery. Surg Endosc 18, 1242–1248 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-003-9190-x