Abstract
Background
The role of the human camera holder during laparoscopic surgery keeps valuable personnel from other duties. EndoAssist is a robotic cameraholding device controlled by the operator’s head movements. This study assesses its introduction into clinical practice.
Method
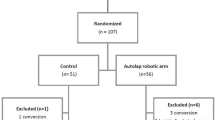
Ninety-three patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy were randomized to have either the robotic (40) or a human (46) assistant. Seven patients converted to open operation were excluded. Six surgeons were evaluated. Operating time and subjective assessments were recorded. Learning curves were constructed.
Results
The mean operating time was less using the robotic assistant (66 min) than with human assistance (74. min) (p<0.05, two-tailed t-test). The learning curves for operating time showed that within three operations surgeons were trained in using the robot. The device was safe in use.
Conclusion
The EndoAssist operating device is a significant asset in laparoscopic surgery and a suitable substitute for a human assistant. Surgeons became competent in the use of the robot within three operations. The robot offers stability and good control of the television image in laparoscopic surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baca I, Goetzen V (1998) Robotic assistance in “solo surgery” and complex laparoscopic procedures (abstract) Surg Endosc 12: 500
Begin E, Gagner M, Hurteau R, de Santis S, Pomp A (1995) A robotic camera for laparoscopic surgery: Conception and experimental results. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5: 6–11
Cadeddu J, Stoianovici D, Kavoussi LR (1998) Robotic surgery in urology. Urol Clin N Am 25: 75–85
Finlay PA (1996) Clinical experience with a goniometric headcontrolled laparoscope manipulator. Proceedings of the IARP Workshop on Medical Robotics, Vienna, Oct 1996
Gagner M, Begin E, Hurteau R, Pomp A (1994) Robotic interactive laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Lancet 343: 596–597
Geis WP (1996) Robotic arm enhancement to accommodate improved efficiency and decreased resource utilisation in complex minimally invasive procedures. Proceedings of 4th International Symposium, Medicine Meets Virtual Reality: 4, Healthcare in the Information Age: Future Tools for Transforming Medicine. San Diego, CA
Gracia C (1996) Clinical utility of a robotic assistant during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Proceedings of the Fifth Annual International Conference for Minimally Invasive Therapy, Milan, Italy, September
Kavoussi LR, Moore RG, Adams JB, Partin AW (1995) Comparison of robotic versus human laparoscopic camera control. J Urol 154: 2134–2136
Kornsuthisopon S (1999) New release of the Boonpong laparoscopic camera holder. Aust N Z J Surg 69: 141–143
Moran ME (1993) Stationary and automated laparoscopically assisted technologies. J Laparoendosc Surg 3: 221–227
Omote K, Feussner H, Ungeheuer A, Arbter K, Guo-Qing W, Siewert JR (1999) Self-guided robotic camera control for laparoscopic surgery compared with human camera control. Am J Surg 177: 321–324
Partin AW, Adams JB, Moore RG, Kavoussi LR (1995) Complete robot-assisted laparoscopic urologic surgery: a preliminary report. J Am Coll Surg 181: 552–557
Sackier JM, Wang Y (1994) Robotically assisted laparoscopic surgery. From concept to development. Surg Endosc 8: 63–66
Sackier JM, Wooters C, Jacobs L, Halversen A, Uecker D, Wang Y (1997) Voice activation of a surgical robotic assistant. Am J Surg 174: 406–409
Uggen PE, Marvik R, Myrvold HE, Finlay PA (1996) Assessment of EndoSista, a head controlled camera manipulator. Proceedings of E. A. E. S. Trondheim, Norway, June
Warden J (1996) UK waiting lists grow longer. Br Med J 316: 1627
Zweifler MJ, Leitman IM, Subramaniam VA, Turgeon R, Mitchell D (1998) Does the use of the surgical robot allow for the replacement of an assistant during laparoscopic cholecystectomy? (abstract) Surg Endosc 12: 510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Online publication: 14 June 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aiono, S., Gilbert, J.M., Soin, B. et al. Controlled trial of the introduction of a robotic camera assistant (Endo Assist) for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 16, 1267–1270 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-9174-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-9174-7