Abstract
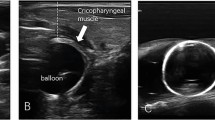
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction, especially cricopharyngeal achalasia, is a common cause of dysphagia, while patients with brainstem stroke and medullary damage have a relatively high risk of cricopharyngeal achalasia. The aim of this article was to introduce an improved method of CT-guided method of injecting botulinum toxin A into the cricopharyngeus muscle using esophageal balloon radiography, and to assess the effect of the botulinum toxin A injection on swallowing performance. Seventeen patients with cricopharyngeal dysphagia were treated with botulinum toxin A injection using esophageal balloon radiography combined with CT guidance to the cricopharyngeal muscle. Primary outcome measures, including Functional Oral Intake Scale and Deglutition Handicap Index, were performed at baseline, 1 week, and 1 month after treatment. The Levene method was used to test the homogeneity of variance, and the Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the scores between the timepoints. Botulinum toxin A injection resulted in obvious improvement in 15 patients (88.2%) and no improvement in two patients (11.8%). Compared with the scores prior to treatment, the Functional Oral Intake Scale and Deglutition Handicap Index scores were significantly improved at 1 week (P < 0.001 and P = 0.008, respectively) and 1 month after the treatment (P = 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). Thus, CT-guided percutaneous injection of botulinum toxin A is probably a relatively safe, well-tolerated, and viable technique for the treatment of cricopharyngeal dysphagia caused by brainstem injury. Localization with a balloon radiography made the needle guidance easier to visualize.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huoh KC, Messner AH. Cricopharyngeal achalasia in children: indications for treatment and management options. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;21(6):576–80.
Marchica C, Zawawi F, Daniel SJ. Management of cricopharyngeal achalasia in an 8-month child using endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;101:137–40.
Ashman A, Dale OT, Baldwin DL. Management of isolated cricopharyngeal dysfunction: systematic review. J Laryngol Otol. 2016;130(7):611–5.
Regan J, Murphy A, Chiang M, McMahon BP, Coughlan T, Walshe M: Botulinum toxin for upper oesophageal sphincter dysfunction in neurological swallowing disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 5:CD009968.
Bian RX, Choi IS, Kim JH, Han JY, Lee SG. Impaired opening of the upper esophageal sphincter in patients with medullary infarctions. Dysphagia. 2009;24(2):238–45.
Steinhagen V, Grossmann A, Benecke R, Walter U. Swallowing disturbance pattern relates to brain lesion location in acute stroke patients. Stroke. 2009;40(5):1903–6.
Yang H, Yi Y, Han Y, Kim HJ. Characteristics of cricopharyngeal dysphagia after ischemic stroke. Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(2):204–12.
Schneider I, Thumfart WF, Pototschnig C, Eckel HE. Treatment of dysfunction of the cricopharyngeal muscle with botulinum A toxin: introduction of a new, noninvasive method. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1994;103(1):31–5.
Atkinson SI, Rees J. Botulinum toxin for cricopharyngeal dysphagia: case reports of CT-guided injection. J Otolaryngol. 1997;26(4):273–6.
Woisard V, Andrieux MP, Puech M. Validation of a self-assessment questionnaire for swallowing disorders (Deglutition Handicap Index). Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2006;127(5):315–25.
Parameswaran MS, Soliman AM. Endoscopic botulinum toxin injection for cricopharyngeal dysphagia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2002;111(10):871–4.
Alberty J, Oelerich M, Ludwig K, Hartmann S, Stoll W. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A for treatment of upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(7):1151–6.
Murry T, Wasserman T, Carrau RL, Castillo B. Injection of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of dysfunction of the upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005;26(3):157–62.
Woisard-Bassols V, Alshehri S, Simonetta-Moreau M. The effects of botulinum toxin injections into the cricopharyngeus muscle of patients with cricopharyngeus dysfunction associated with pharyngo-laryngeal weakness. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270(3):805–15.
Zarate N, Mearin F, Baldovino F, Armengol JR, Malagelada JR. Achalasia treatment in the elderly: is botulinum toxin injection the best option? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14(3):285–90.
Pasricha PJ, Ravich WJ, Hendrix TR, Sostre S, Jones B, Kalloo AN. Intrasphincteric botulinum toxin for the treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(12):774–8.
Terre R, Panades A, Mearin F. Botulinum toxin treatment for oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with stroke. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(11):896–e702.
Dunne J, Hayes M, Cameron D. Botulinum toxin A for cricopharyngeal dystonia. Lancet. 1993;342(8870):559.
Jeong SH, Kim YJ, Kim YJ, Park KD, Kim EJ, Chung JW, Kwon KA, Kim KO, Park DK, Kim JH, et al. Endoscopic botulinum toxin injection for treatment of pharyngeal dysphagia in patients with cricopharyngeal dysfunction. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018;53(10–11):1201–5.
Kelly EA, Koszewski IJ, Jaradeh SS, Merati AL, Blumin JH, Bock JM. Botulinum toxin injection for the treatment of upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013;122(2):100–8.
Kocdor P, Siegel ER, Tulunay-Ugur OE. Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: A systematic review comparing outcomes of dilatation, botulinum toxin injection, and myotomy. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(1):135–41.
Moerman MB. Cricopharyngeal Botox injection: indications and technique. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;14(6):431–6.
Kim DY, Park CI, Ohn SH, Moon JY, Chang WH, Park SW. Botulinum toxin type A for poststroke cricopharyngeal muscle dysfunction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006;87(10):1346–51.
Ravich WJ. Botulinum toxin for UES dysfunction: therapy or poison? Dysphagia. 2001;16(3):168–70.
Haapaniemi JJ, Laurikainen EA, Pulkkinen J, Marttila RJ. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of cricopharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2001;16(3):171–5.
Shaw GY, Searl JP. Botulinum toxin treatment for cricopharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2001;16(3):161–7.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University and Department of Spinal Surgery, Armed Police Corps Hospital of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huai, J., Hou, Y., Guan, J. et al. Botulinum Toxin A Injection Using Esophageal Balloon Radiography Combined with CT Guidance for the Treatment of Cricopharyngeal Dysphagia. Dysphagia 35, 630–635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10070-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10070-5