Abstract
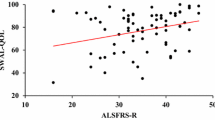
There have been no quantitative studies on dysphagia and its impact on quality of life (QOL) of adults with cerebral palsy (CP). In this cross-sectional study, we aimed to investigate the characteristics of dysphagia symptoms and their impact on QOL in adults with CP on a full oral diet compared with healthy adults. Additionally, we aimed to determine the factors affecting dysphagia-related QOL in this population. We enrolled adults with CP on full oral diet (N = 117) and healthy individuals (N = 117) and interviewed them using the swallowing-quality of life (SWAL-QOL) questionnaire which includes 14 items regarding dysphagia symptoms and 30 items regarding swallowing-related QOL. The functional status of each participant with CP was evaluated using the gross motor function classification system, the manual ability classification system (MACS), and the Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS). Among pharyngeal symptoms, choking on food was reported most frequently (sometimes or more 76.9%), followed by coughing and choking on liquid. Among oral symptoms, chewing problems were reported most frequently (sometimes or more 59.8%), followed by food dribbling from the mouth (sometimes or more 53.8%). Compared to healthy adults, those with CP reported worse QOL across all SWAL-QOL items, with the lowest scores obtained for meal duration, followed by communication, burden, fatigue, sleep, and eating desire. On multiple linear regression analysis, higher MACS level, lower FOIS level, and older age were predictors of worse SWAL-QOL score. Among adults with CP, it is necessary to evaluate swallowing function and establish an active intervention plan even if a full oral diet is established.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haak P, Lenski M, Hidecker MJC, Li M, Paneth N. Cerebral palsy and aging. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009;51:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03428.x.
Senner JE, Logemann J, Zecker S, Gaebler-Spira D. Drooling, saliva production, and swallowing in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;46:801–6.
Clancy KJ, Hustad KC. Longitudinal changes in feeding among children with cerebral palsy between the ages of 4 and 7 years. Dev Neurorehabil. 2012;14:191–8. https://doi.org/10.3109/17518423.2011.568467.
Benfer KA, Weir KA, Bell KL, Ware RS, Davies PS, Boyd RN. Longitudinal study of oropharyngeal dysphagia in preschool children with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97:552-60.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2015.11.016.
Calis EAC, Veugelers R, Sheppard JJ, Tibboel D, Evenhuis HM, Penning C. Dysphagia in children with severe generalized cerebral palsy and intellectual disability. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50:625–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03047.x.
Somerville H, Tzannes G, Wood J, Shun A, Arrowsmith F, Slater A, O’Loughlin E. Gastrointestinal and nutritional problems in severe developmental disability. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50:712–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03057.x.
Edvinsson SE, Lundqvist LO. Prevalence of orofacial dysfunction in cerebral palsy and its association with gross motor function and manual ability. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58:385–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12867.
Kaatzke-Mcdonald M. Dysphagia, disability, and icebergs: a discussion. Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2003;5:131–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/14417040510001669161.
Bae SO, Lee GP, Seo HG, Oh BM, Han TR. Clinical characteristics associated with aspiration or penetration in children with swallowing problem. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38:734–41. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.734.
Troughton KE, Hill AE. Relation between objectively measured feeding competence and nutrition in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001;43:187–90.
Samuels R, Chadwick DD. Predictors of asphyxiation risk in adults with intellectual disabilities and dysphagia. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2006;50:362–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00784.x.
Rogers B, Arvedson J, Buck G, Smart P, Msall M. Characteristics of dysphagia in children with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia. 1994;9:69–73.
Cass H, Wallis C, Ryan M, Reilly S, McHugh K. Assessing pulmonary consequences of dysphagia in children with neurological disabilities: when to intervene? Dev Med Child Neurol. 2005;47:347–52.
Benfer KA, Weir KA, Bell KL, Ware RS, Davies PS, Boyd RN. Oropharyngeal dysphagia and gross motor skills in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 2013;131:e1553–62. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-3093.
Westbom L, Bergstrand L, Wagner P, Nordmark E. Survival at 19 years of age in a total population of children and young people with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011;53:808–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04027.x.
Balandin S, Hemsley B, Hanley L, Sheppard JJ. Understanding mealtime changes for adults with cerebral palsy and the implications for support services. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2009;34:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/13668250903074489.
McHorney CA, Robbins JA, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia. 2002;17:97–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-001-0109-1.
McHorney CA, Martin-Harris B, Robbins JA, Rosenbek J. Clinical validity of the SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcome tools with respect to bolus flow measures. Dysphagia. 2006;21:141–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-005-0026-9.
Leow LP, Huckabee ML, Anderson T, Beckert L. The impact of dysphagia on quality of life in ageing and Parkinson’s disease as measured by the swallowing quality of life (SWAL-QOL) questionnaire. Dysphagia. 2010;25:216–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-009-9245-9.
Plowman-Prine EK, Sapienza CM, Okun MS, Pollock SL, Jacobson C, Wu SS, Rosenbek JC. The relationship between quality of life and swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2009;24:1352–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22617.
Carneiro D, De Sales MDGW, Belo LR, de Marcos Rabelo AR, Asano AG, Lins OG. Quality of life related to swallowing in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia. 2014;29:578–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9548-3.
Youssof S, Romero-Clark C, Warner T, Plowman E. Dysphagia-related quality of life in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy: psychometric properties of the SWAL-QOL instrument. Muscle Nerve. 2017;56:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25441.
Rinkel RN, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Doornaert P, et al. Prevalence of swallowing and speech problems in daily life after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer based on cut-off scores of the patient-reported outcome measures SWAL-QOL and SHI. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1849–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3680-z.
Cans C. Surveillance of cerebral palsy in Europe: a collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000;42:816–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2000.tb00695.x.
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997;39:214–23.
Morris C, Kurinczuk JJ, Fitzpatrick R, Rosenbaum PL. Reliability of the manual ability classification system for children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006;48:950–3. https://doi.org/10.1017/S001216220600209X.
Van Meeteren J, Nieuwenhuijsen C, De Grund A, Stam HJ, Roebroeck ME. Using the manual ability classification system in young adults with cerebral palsy and normal intelligence. Disabil Rehabil. 2010;32:1885–93. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638281003611011.
McCormick A, Brien M, Plourde J, Wood E, Rosenbaum P, McLean J. Stability of the gross motor function classification system in adults with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;49:265–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2007.00265.x.
Crary MA, Mann GD, Groher ME. Initial psychometric assessment of a Functional Oral Intake Scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86:1516–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.11.049.
Kim JY, Kim DY, Kim H, Cho SR. A validation study of the Korean version of the swallowing-quality of life scale. Commun Sci Disord. 2013;18:341–7. https://doi.org/10.12963/csd.13038.
Benfer KA, Weir KA, Bell KL, Ware RS, Davies PSW, Boyd RN. Clinical signs suggestive of pharyngeal dysphagia in preschool children with cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;38:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.12.021.
Seo HG, Yi YG, Choi YA, Leigh JH, Yi Y, Kim K, et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults with dyskinetic cerebral palsy and cervical dystonia: a preliminary study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2018.05.024.
Sellers D, Mandy A, Pennington L, Hankins M, Morris C. Development and reliability of a system to classify the eating and drinking ability of people with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014;56:245–51.
Da Costa Franceschini A, Mourão LF. Dysarthria and dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with spinal onset: a study of quality of life related to swallowing. NeuroRehabilitation. 2015;36:127–34. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-141200.
Andrén E, Grimby G. Dependence and perceived difficulty in activities of daily living in adults with cerebral palsy and spina bifida. Disabil Rehabil. 2000;22:299–307.
Benner JL, Hilberink SR, Veenis T, Stam HJ, van der Slot WM, Roebroeck ME. Long-term deterioration of perceived health and functioning in adults with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98:2196-205.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2017.03.013.
Hutzler Y, Rodríguez BL, Laiz NM, Díez I. Barak S (2013) The effects of an exercise training program on hand and wrist strength, and function, and activities of daily living, in adults with severe cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34:4343–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.09.015.
Usuba K, Oddson B, Gauthier A, Young NL. Changes in gross motor function and health-related quality of life in adults with cerebral palsy: an 8-year follow-up study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95:2071–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2014.05.018.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the Cerebral Palsy Community Center staff who helped organize the interviews. We warmly thank all study participants. We appreciate the statistical advice to Myoung-jin Jang, statistician at the Division of Medical Statistics, Medical Research Collaborating Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
Funding
The research has been carried out through contributions donated to the Seoul National University Children’s Hospital by Sir. Suhwon Suh (Seoul National University Hospital Assignment No. 3020180060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval was obtained from the Seoul National University Hospital Institutional Review Board (IRB) No. 1712-013-903.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Y.G., Oh, BM., Seo, H.G. et al. Dysphagia-Related Quality of Life in Adults with Cerebral Palsy on Full Oral Diet Without Enteral Nutrition. Dysphagia 34, 201–209 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-09972-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-09972-7