Abstract
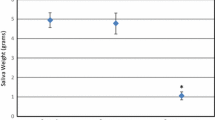
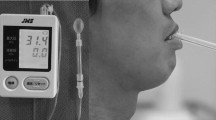
The ability to measure normality and abnormality and to accurately assess true changes in swallowing function over time, is important for the management of dysphagia. Despite this, there is a paucity of information regarding the stability and reliability of measurements tools used for dysphagia research. As both head and neck (H&N) cancer and its treatment(s) have been shown to significantly affect deglutitive tongue function, it is important that we have a reliable method to measure swallowing tongue function in this population. In this study we evaluate the reliability and stability of oro-lingual swallowing pressures captured from H&N cancer patients and from healthy, age- and gender-matched controls using the Kay Swallowing Workstation (KSW) fixed, three-transducer tongue pressure array. Significant differences between the two samples (H&N cancer and controls), with respect to mean peak oro-lingual pressures were recorded during swallowing. Furthermore, reliability of these measures was lower in H&N cancer patients. These differences highlight the importance of obtaining information about the reliability of dysphagia assessment tools with the specific population with whom they will be used.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paik NJ, Han TR. Critical review on the management of adult oropharyngeal dysphagia. Crit Rev Phys Rehabil Med. 2002;14:247–72.
Mathers-Schmidt BA, Kurlinski M. Dysphagia evaluation practices: inconsistencies in clinical assessment and instrumental examination decision-making. Dysphagia. 2003;18:114–25. doi:10.1007/s00455-002-0094-z.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 2000.
Kahrilas PJ, Lin S, Logemann JA, Ergun GA, Facchini F. Deglutitive tongue action: volume accommodation and bolus propulsion. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:152–62.
Hamlet SL. Dynamic aspects of lingual propulsive activity in swallowing. Dysphagia. 1989;4:136–45. doi:10.1007/BF02408036.
Miller JL, Watkin KL, Fong Chen M. Muscle, adipose, and connective tissue variations in intrinsic musculature of the adult human tongue. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2002;45:51–65. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2002/004).
Chi-Fishman G, Stone M, McCall GN. Lingual action in normal sequential swallow. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1998;41:771–85.
Dodds WJ. The physiology of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1989;3:171–8. doi:10.1007/BF02407219.
Kennedy JG, Kent RD. Physiological substrates of normal deglutition. Dysphagia. 1988;3:24–37. doi:10.1007/BF02406277.
Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed; 1998.
Ono T, Hori K, Nokubi T. Pattern of tongue pressure on hard palate during swallowing. Dysphagia. 2004;19:259–64.
Tasko SM, Kent RD, Westbury JR. Variability in tongue movement kinematics during normal liquid swallowing. Dysphagia. 2002;17:126–38. doi:10.1007/s00455-001-0112-6.
Hamlet S, Jones L, Mathog R, Bolton M, Patterson R. Bolus propulsive activity of the tongue in dysphagic cancer patients. Dysphagia. 1988;3:18–23. doi:10.1007/BF02406276.
Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Logemann JA, Stein D, Beery Q, Newman L, et al. Pretreatment swallowing function in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2000;22:474–82. doi:10.1002/1097-0347(200008)22:5<474::AID-HED6>3.0.CO;2-I.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Larson CR, Mittal BB, et al. Swallowing and tongue function following treatment for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43:1011–23.
Eisbruch A, Lyden T, Bradford C, Dawson L, Haxer M, Miller A, et al. Objective assessment of swallowing dysfunction and aspiration after radiation concurrent with chemotherapy for head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:23–8.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Mittal B, Vokes EE, et al. Effects of chemoradiation on tongue strength and endurance in oral cancer patients. Dysphagia. 2002;17:181. abstract.
Perlmutter MA, Johnson JT, Snyderman CH, Cano ER, Myers EN. Functional outcomes after treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the base of the tongue. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;128:887–91.
Robbins J, Kays S, Gangnon R, Hind JA, Hewitt A, Gentry L, et al. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88:150–8. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2006.11.002.
Robbins J, Gangnon R, Shannon M, Kays S, Hewitt A, Hind JA. The effects of lingual exercises on swallowing in older adults. J Appl Gerontol. 2005;53:1483–9.
Nicosia MA, Hind JA, Roecker EB, Carnes M, Doyle J, Dengel GA, et al. Age effects on the temporal evolution of isometric swallowing pressure. J Gerontol Med Sci. 2000;55A:M634–40.
Yokoyama M, Sonies BC, Michiwaki Y, Michi K. Variations in lingua-palatal pressure patterns during the oral phase of swallowing. Dysphagia. 2002;17:186. abstract.
Shaker R, Cook IJS, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ. Pressure-flow dynamics of the oral phase of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1988;3:79–84. doi:10.1007/BF02412424.
Miller JL, Watkin KL. The influence of bolus volume and viscosity on anterior lingual force during the oral stage of swallowing. Dysphagia. 1996;11:117–24. doi:10.1007/BF00417901.
Steele CM, Huckabee M. The influence of orolingual pressure on the timing of pharyngeal pressure events. Dysphagia. 2007;22:30–6. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9037-4.
Clark HM, Henson PA, Barber WD, Steirwalt JAG, Sherrill M. Relationships among subjective and objective measures of tongue strength and oral phase swallowing impairments. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2003;12:40–50. doi:10.1044/1058-0360(2003/051).
Robbins J, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol Med Sci. 1995;50A:M257–62.
Crow HC, Ship JA. Tongue strength and endurance in different aged individuals. J Gerontol Med Sci. 1996;51A:M247–50.
Pouderoux P, Kahrilas PJ. Deglutitive tongue force modulation by volition, volume, and viscosity in humans. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:1418–26. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(95)90690-8.
Solomon NP, Munson B. The effect of jaw position on measures of tongue strength. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2004;47:584–94. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2004/045).
Solomon NP, Drager KD, Luschei ES. Sustaining a constant effort by the tongue and hand: effects of acute fatigue. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2002;45:613–24. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2002/049).
Ball S, Idel O, Cotton S, Perry A. Comparison of two methods for measuring tongue pressure during swallowing in people with head and neck cancer. Dysphagia. 2006;21:1–10. doi:10.1007/s00455-005-9008-1.
Pelletier C, Dhanaraj G. The effect of taste and palatability on lingual swallowing pressure. Dysphagia. 2006;21:121–8. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9020-0.
Youmans S, Stierwalt J, Regan J, Sowman R, Walsh I. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2006;21:102–11. doi:10.1007/s00455-006-9013-z.
Yoshida M, Kikutani T, Tsuga K, Utanohara Y, Hayashi R, Akagawa Y. Decreased tongue pressure reflects symptom of dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2006;21:61–5. doi:10.1007/s00455-005-9011-6.
Hind JA, Nicosia MA, Gangnon R, Robbins J. The effects of intraoral pressure sensors on normal young and old swallowing patterns. Dysphagia. 2005;20:249–53. doi:10.1007/s00455-005-0020-2.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Larson CR, Mittal BB, et al. Swallowing and tongue function following treatment for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43:1011–23.
Goodman BM, Robbins J, Wood J, Dengel G, Luschei E, Influence of intra-oral pressure sensors on normal swallowing patterns as measured by submentally located surface electromyography. Presented at the Fifth Annual Scientific Meeting, Dysphagia Research Society, Aspen, CO, October 31–November 2, 1996.
Stachler RJ, Hamlet SL, Mathog RH, Jones L, Heilbrun LK, Manov LJ, et al. Swallowing of bolus types in post-surgical head and neck cancer patients. Head Neck. 1994;16:413–9. doi:10.1002/hed.2880160504.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Pajak T, Lazar R, et al. Effects of bolus volume, viscosity, and repeated swallows in non-stroke subjects and stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:1066–70. doi:10.1016/0003-9993(93)90063-G.
Rademaker AW, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Smith CH, Hsieh YC. Differences in normal adult swallowing by bolus type. Dysphagia. 2000;15:109. abstract.
Dantas RO, Kern MK, Massey BT, Dodds WJ, Kahrilas PJ, Brasseur JG, et al. Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:G675–81.
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;86:420–8. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.86.2.420.
Oloffson B. Study Size 2.0. Frolunda. Sweden: CreoStat HB; 2003.
Hopkins WG. Measures of reliability in sports medicine and science. Sports Med. 2000;30:1–15. doi:10.2165/00007256-200030010-00001.
Acknowledgment
GRECC Manuscript # 2007-21 (Joanne Robbins).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, R., Cotton, S.M., Hind, J. et al. A Comparison of the Reliability and Stability of Oro-lingual Swallowing Pressures in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer and Healthy Adults. Dysphagia 24, 137–144 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-008-9181-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-008-9181-0