Abstract
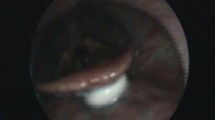
Neuroleptic medication may cause extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) that can affect swallowing as well. This report describes a case of drug-induced dysphagia in a 53-year-old man receiving haloperidol for treatment of schizophrenia. The diagnosis was established by fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. After changing medication to fluphenazin, dysphagic symptoms resolved. The literature on EPS-related dysphagia, its demographic features, typical symptoms, diagnostic modalities, clinical course, and treatment options is reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fioritti A, Giaccotto L, Melega V: Choking incidents among psychiatric patients: retrospective analysis of thirty-one cases from the west bologna psychiatric ward. Can J Psychiatry 42:515–520, 1997
Hussar AE, Bragg DG: The effect of chlorpromazine on the swallowing function in chronic schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 126:152–155, 1969
Craig TJ, Richardson MA: “Cafe coronaries” in psychiatric patients. JAMA 248:2114, 1982
Bazemore PH, Tonkonogy J, Ananth R: Dysphagia in psychiatric patients: clinical and videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia 6:2–5, 1991
Bushmann M, Dobmeyer SM, Leeker L, Perlmutter JS: Swallowing abnormalities and their responses to treatment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 39:1309–1314, 1989
Gregory RP, Smith PT, Rudge P: Tardive dyskinesia presenting as severe dysphagia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:1203–1204, 1992
Langmore SE (ed.): Endoscopic evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. New York: Thieme, 2001
Casey DE, Keepers GA: Neuroleptic side effects: acute extrapyramidal syndromes and tardive dyskinesia. In: Casey DE, Vibeke Christensen A (eds.): Psychopharmacology: current trends. Berlin: Springer, 1988, pp 74–93
Muscettola G, Barbato G, Pampallona S, Casiello M, Bollini P: Extrapyramidal syndromes in neuroloptic-treated patients: prevalence, risk factors, and association with tardive dyskinesia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19:203–208, 1999
Binder RL, Kazamatsuri H, Nishimura T, McNiel DE: Tardive dyskinesia and neuroleptic induced parkinsonism in Japan. Am J Psychiatry 144:1494–1496, 1987
Richardson MA, Craig TJ: The coexistence of parkinsonism-like symptoms and tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 139:341–343, 1982
McCreadie RG, Robertson LJ, Wiles DH: The Nithsdale schizophrenia surveys. IX: akathisia, parkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia and plasma neuroleptic level. Br J Psychiatry 161:793–799, 1992
Miller CH, Mohr F, Umbricht D, Woerner M, Fleischhacker WW, Liebermann JA: The prevalence of acute extrapyramidal signs and symptoms in patients treated with clozapine, risperidone, and conventional antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 59:69–75, 1998
Edwards LL, Pfeiffer RF, Quigyley EMM, Hofman R, Balluf M: Gastrointestinal symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 6:151–156, 1991
Sokoloff LG, Pavlakovic R: Neuroleptic-induced dysphagia. Dysphagia 12:177–179, 1997
Stewart JT: Reversible dysphagia associated with neuroleptic treatment. J Am Geriatr Soc 49:1260–1261, 2001
Stewart JT: Dysphagia associated with risperidone therapy. Dysphagia 18:274–275, 2003
Leopold NA: Dysphagia in drug-induced parkinsonism: a case report. Dysphagia 11:151–153, 1996
Hughes TAT, Shone G, Lindsay G, Wiles CM: Severe dysphagia associated with major tranquilizer treatment. Postgrad Med J 70:581–583, 1994
Bashford G, Bradd P: Drug-induced parkinsonism associated with dysphagia and aspiration: a brief report. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 9:133–135, 1996
Bulling M: Drug-induced dysphagia. Aust N Z J Med 29:748, 1999
McCarthy RH, Terkelsen KG: Esophageal dysfunction in two patients after clozapine treatment. J Clin Psychopharmacol 14:281–283, 1994
Sliwa JA, Lis S: Drug-induced dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 74:445–447, 1993
Leopold NA, Kagel MC: Pharyngo-esophageal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 12:11–18, 1997
Leopold NA, Kagel MC: Prepharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia 11:14-22, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rainer Dziewas and Tobias Warnecke contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dziewas, R., Warnecke, T., Schnabel, M. et al. Neuroleptic-Induced Dysphagia: Case Report and Literature Review. Dysphagia 22, 63–67 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-006-9032-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-006-9032-9