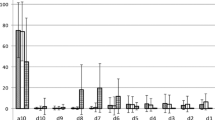
Abstract
Cervical auscultation has been proposed as a technique to augment the clinical evaluation of dysphagia to improve its accuracy in the diagnosis of dysphagia. Before using cervical auscultation to reliably diagnose disordered swallowing, it is necessary to first acoustically characterize normal swallowing for comparison with dysphagic swallowing. Ninety-seven healthy adult participants consumed teaspoon boluses of various consistencies while the sounds of swallowing were recorded. Descriptive statistics were reported for measures of duration, intensity, and frequency of the acoustic swallowing signal. Correlations between the variables and between bolus consistencies were computed. Overall, results compared favorably with previous research. Significant correlations were found among several of the variables, including an increasing duration of the acoustic swallowing signal with increasing age and decreasing intensity of the signal with increasing age. None of the variables differed significantly as a function of gender. Of potential clinical relevance, significant correlations between bolus consistencies for the duration and intensity variables indicated relative similarities across bolus consistencies. Duration and intensity of the acoustic signal appeared to be the most reliable of the variables measured. These results could serve as a reference point for future studies into normal swallowing across multiple bolus consistencies and volumes and eventually be compared with disordered swallowing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sorin R, Somers S, Austin W, Bester S: The influence of videofluoroscopy on the management of the dysphagia patient. Dysphagia 2:127–135, 1988
Splaingard ML, Hutchins B, Sulton LD, Chaudhuri G: Aspiration in rehabilitation patients: Videofluoroscopy vs bedside clinical assessment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 69:637–640, 1988
Robbins J, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster GB: Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 103:823–829, 1992
Sonies BC, Parent LJ, Morrish K, Baum BJ: Durational aspects of the oral-pharyngeal phase of swallow in normal adults. Dysphagia 3:1–10, 1988
Logemann JA: Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders, 2nd ed. Austin: Pro-ed, 1998
Langmore SE, Schatz K, Olsen N: Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: A new procedure. Dysphagia 2:216–219, 1988
Zenner PM, Losinski DS, Mills RH: Using cervical auscultation in the clinical dysphagia examination in long-term care. Dysphagia 10:27–31, 1995
Hamlet SL, Nelson RJ, Parterson RL: Interpreting the sounds of swallowing: Fluid flow through the cricopharyngeus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 99:749–752, 1990
Cichero JAY, Murdoch BE: Acoustic signature of the normal swallow: Characterization by age, gender, and bolus volume. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111:623–632, 2002
Vice FL, Heinz JM, Giuriati G, Hood M, Bosma JF: Cervical auscultation of suckle feeding in newborn infants. Dev Med Child Neurol 32:760–768, 1990
Hamlet S, Penney DG, Formolo J: Stethoscope acoustics and cervical auscultation of swallowing. Dysphagia 9:63–68, 1994
Takahashi, Groher ME, Michi K: Methodology for detecting swallowing sounds. Dysphagia 9:54–62, 1994
Takahashi K, Groher ME, Michi K: Symmetry and reproducibility of swallowing sounds. Dysphagia 9:168–173, 1994
Hamlet SL, Patterson RL, Fleming SM, Jones LA: Sounds of swallowing following total laryngectomy. Dysphagia 7:160–165, 1992
Vice FL, Bamford O, Heinz JM, Bosma JF: Correlation of cervical auscultation with physiological recording during suckle-feeding in newborn infants. Dev Med Child Neurol 37:167–179, 1995
Logan WJ, Kavanagh IF, Wornall A: Sonic correlates of human deglutition. J Appl Physiol 23:279–284, 1967
Mackowiak RC, Brenman HS, Friedman MHF: Acoustic profile of deglutition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 125:1149–1152, 1967
Cohen J, Cohen P: Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd ed. Hillside, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1983
Murry T, Carrau RL: Clinical manual for swallowing disorders. San Diego: Singular, 2001
Tracy JF, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Jacob P, Kobara M, Krugler C: Preliminary observations on the effects of age on oropharyngeal deglutition. Dysphagia 4:90–94, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youmans, S.R., Stierwalt, J.A. An Acoustic Profile of Normal Swallowing. Dysphagia 20, 195–209 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-005-0013-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-005-0013-1