Abstract
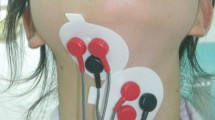
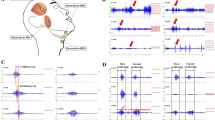
Surface electromyographic (sEMG) studies were performed on 300 normal adults to estimate normal values of sEMG records of muscle activity in the detection and evaluation of stages of normal swallowing. Our study was a prospective observational study of healthy volunteers. The parameters evaluated during swallowing include the timing, amplitude (voltage), and graphic patterns of activity of the orbicularis oris, masseter, submental, and laryngeal strap muscles covered by the platysma. Three tests were examined: voluntary single swallows of saliva (“dry” swallow), voluntary single water swallows (“normal”), and voluntary single swallows of excessive amounts of water (20 ml, “stress test”). Duration and amplitude of muscle activity in oral, pharyngeal, and initial esophageal stages of swallowing (mean + standard deviation, range + standard deviation) were measured for groups of adults of different ages (18–40, 41–70, 70+ years). Shapes of graphic records were evaluated relative to timing and voltage. The overall normal mean values for stage-by-stage duration of muscle activity during single swallowing were established for healthy adults. The duration of muscle activity in all tests showed insignificant increases with age except for the elderly group (70+) in which it was statistically significant (SPSS, χ2 criterion, 95% confidence interval, p < 0.05). There were no statistically significant gender-related differences in duration or amplitude of muscle activity during single swallowing for any age group (p ≥ 0.05). We conclude that the rectified and filtered sEMG provides a noninvasive means to assess certain aspects of complex muscle activity in deglutition. Surface EMG of swallowing is a simple and reliable noninvasive screening method for evaluating swallowing with low levels of discomfort. Stage-by-stage evaluation of duration can be very important for diagnosing the etiology of dysphagia. The combined normative timing of events, amplitude, and graphic data can be used for evaluating complaints and symptoms, as well as for comparison purposes in pre- and postoperative stages and in EMG monitoring during otolaryngological or neurological treatment. These parameters represent stages required for normal deglutition and provide a basis for the comparison of swallowing performance both within and between patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
V Gupta NP Reddy EP Canilang (1996) ArticleTitleSurface EMG measurements at the throat during dry and wet swallowing Dysphagia 11 173–179 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA2cbmt1M%3D Occurrence Handle8755460
F Magendie (1813) ArticleTitleVomissement Procès-verb Acad d Sc 5 152–159
F Magendie (1813) ArticleTitleL’epiglotte et ses usages dans le deglutition Procès-verb Acad d Sc 5 192–199
JA Logemann (1983) Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders College Hill Press San Diego, CA
PJ Kahrilas WJ Dodds J Dent JA Logemann R Shaker (1988) ArticleTitleUpper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition Gastroenterology 95 52–62 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieB38rptlY%3D Occurrence Handle3371625
P Jacob PJ Kahrilas JA Logemann V Shah T Ha (1989) ArticleTitleUpper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing Gastroenterology 97 1469–1478 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BD28%2FlvVc%3D Occurrence Handle2583413
RY Doty JF Bosma (1956) ArticleTitleAn electromyographic analysis of reflex deglutition J Neurophysiol 19 44–60 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CymD3sfpsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle13286721
AJ Miller (1982) ArticleTitleDeglutition Physiol Rev 96 129–184
R Ding CR Larson JA Logemann AW Rademaker (2002) ArticleTitleSurface electromyographic and electroglottographic studies in normal subjects under two swallow conditions: normal and during the Mendelsohn maneuver Dysphagia 17 1–12 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00455-001-0095-3 Occurrence Handle11820381
W Erb (1886) Handbuch der Electrotherapie, 2 Aufl Vogel Leipzig pp 34–45
E Remak (1909) Grundriss der Electrodiagnostik und Electrotherapie, 2 Aufl Meyer Wien 26–34
J Goodgold (1975) Anatomical Correlates of Clinical Electromyography EditionNumber1 Williams & Wilkins Baltimore 2–3
MR Isley GL Kranss KH Levin et al. (1993) Electromyography/Electroencephalography SpaceLab Medical Redford, WA
AJ Wilbourn MA Ferrante (2000) Clinical electromyography RJ Joynt RC Griggs (Eds) Baker’s clinical neurology [book on CD-ROM] WB Saunders Philadelphia
Wilbourn AJ: Nerve conduction studies: Types, components, abnormalities, and value in localization. In: Katirji B. (ed.): Clinical Electromyograply. Neurolog Clin 20, 2:310–11, 2002
FMS McConnel D Cerenko MS Mendelsohn (1988) ArticleTitleManofluorographic analysis of swallowing Otolaryngol Clin North Am 21 IssueID4 625–636 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaD2c7hs1A%3D Occurrence Handle3186255
MJ McKeown DC Torpey WC Gehm (2002) ArticleTitleNon-invasive monitoring of functionally distinct muscle activations during swallowing Clin Neurophysiol 113 354–366 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00007-X Occurrence Handle11897536
C Ertekin M Pehlivan I Aydogdu M Ertas B Uludag G Celebi Z Colakoglu A Sagduyu N Yuceyar (1995) ArticleTitleAn electrophysiological investigation of deglutition in man Muscle Nerve 18 1177–1186 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqA1cfgvVw%3D Occurrence Handle7659112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaiman, M., Eviatar, E. & Segal, S. Evaluation of Normal Deglutition with the Help of Rectified Surface Electromyography Records. Dysphagia 19, 125–132 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0504-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-003-0504-x