Abstract
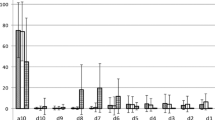
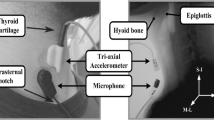
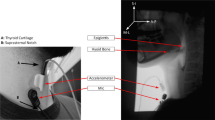
Cervical auscultation is in the process of gaining clinical credibility. In order for it to be accepted by the clinical community, the procedure and equipment used must first be standardized. Takahashi et al. [Dysphagia 9:54-62, 1994] attempted to provide benchmark methodology for administering cervical auscultation. They provided information about the acoustic detector unit best suited to picking up swallowing sounds and the best cervical site to place it. The current investigation provides contrasting results to Takahashi et al. with respect to the best type of acoustic detector unit to use for detecting swallowing sounds. Our study advocates an electret microphone as opposed to an accelerometer for recording swallowing sounds. However, we agree on the optimal placement site. We conclude that cervical auscultation is within reach of the average dysphagia clinic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cichero, J., Murdoch, B. Detection of Swallowing Sounds: Methodology Revisited. Dysphagia 17, 40–49 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-001-0100-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-001-0100-x