Abstract
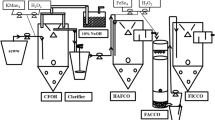
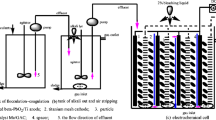
Bacillus pumilus, the thermophilic microorganism, was used to biosynthesise lipase of specific activity 5173 U. The purified lipase was highly stable in the pH range from 1 to 7 and temperature at 50 °C. The functionalized nanoporous activated carbon matrix was used for the immobilization of lipase at the optimum conditions and was used for the hydrolysis of palm oil-containing wastewater at optimum time, 3 h, pH 7, and at temperature 50 °C. The hydrolyzed palm oil wastewater was treated in an upflow anaerobic reactor for the removal of soluble COD at hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 3 days. The anaerobic-treated wastewater was applied to the fluidized immobilized carbon catalytic oxidation (FICCO) reactor at HRT of 16 h to reduce the soluble COD. The FICCO-treated wastewater was further treated in chemo-autotrophic activated carbon oxidation (CAACO) reactor to reduce the COD less than 100 mg/L.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gombert AK, Pinto AL, Castilho LR, Freire DMG (1999) Lipase production by Penicillium restrictum in solid-state fermentation using babassu oil cake as substrate. Process Biochem 35:85–90
Rupani PF, Singh RP, Ibrahim MH, Esa N (2010) Review of current palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment methods: vermi-composting as a sustainable practice. World Appl Sci J 11:70–81
Olafadehan OA, Jinadu OW (2012) Treatment of brewery wastewater effluent using activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. Int J Appl Sci Technol 2:165
Inan H, Dimoglo A, Şimşek H, Karpuzcu M (2004) Olive oil mill wastewater treatment by means of electro-coagulation. Sep Purif Technol 36:23–31
Moosai R, Dawe RA (2003) Gas attachment of oil droplets for gas flotation for oily wastewater cleanup. Sep Purif Technol 33:303–314
Ahmad AL, Sumathi S, Hameed BH (2006) Coagulation of residue oil and suspended solid in palm oil mill effluent by chitosan, alum and PAC. Chem Eng J 118:99–105
Fu Y, Chung DDL (2011) Coagulation of oil in water using sawdust, bentonite and calcium hydroxide to form floating sheets. Appl Clay Sci 53:634–641
Li L, Ding L, Tu Z, Wan Y, Clausse D, Lanoisellé JL (2009) Recovery of linseed oil dispersed within an oil-in-water emulsion using hydrophilic membrane by rotating disk filtration system. J Mem Sci 342:70–79
Srinivasan A, Viraraghavan T (2010) Oil removal from water using biomaterials. Bioresour Technol 101:6594–6600
Crine DG, Paloumet X, Bjornsson L, Alves MM, Mattiasson B (2007) Anaerobic digestion of lipid rich waste—effects of lipid concentration. Renew Energy 32:965–975
Jaeger KE, Ransac S, Dijktra BW, Colson C, Heuvel MV, Misset O (1994) Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:29–63
Mozhaev V (1993) Mechanism-based strategies for protein thermo stabilization. Trends Biotechnol 11:88–95
Adams M, Perler F, Kelly R (1995) Extremozymes: expanding the limits of biocatalysis. BioTechnol 13:662–668
Lam SY, Yeung RCY, Yu TH, Sze KH, Wong KB (2011) A rigidifying salt-bridge favors the activity of thermophilic enzyme at high temperatures at the expense of low-temperature activity. PLoSBiol 9:e1001027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001027
Schmidt-Dannert C, Sztajer H, Stocklein W, Menge U, Schmid RD (1994) Screening, purification and properties of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus. Biochem Biophys Acta 1214:43–53
Luisa RaM, Schmidt-Dannert C, Wahl S, Sprauer A, Schmid RD (1997) Thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus thermocatenulatus Large-scale production, purification and properties: aggregation behaviour and its effect on activity. J Biotechnol 56:89–102
Kim HK, Sung MH, Kim HM, Oh TK (1994) Occurrence of thermostable lipase in thermophilic Bacillus sp. strain 398. Biosci Biotech Biochem 58:961–962
Fariha H, Aamer AS, Abdul H (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microbial Technol 39:235–251
Ramani KS, Boopathy R, John Kennedy L, Mandal AB, Sekaran G (2012) Surface functionalized mesoporous activated carbon for the immobilization of acidic lipase and their application to hydrolysis of waste cooked oil: isotherm and kinetic studies. Process Biochem 47:435–445
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Angelidaki I, Kalyuzhnyi SV, Pablostathis SG, Rozzi A, Sanders WTM, Siegrist H, Vavilin VA (2002) The IWA anaerobic digestion model no.1 (ADM1). Wat Sci Tech 45:65–73
Ralf R, Matthias B, Johann H, Rainer UM, Wolfgang B et al (2016) Anaerobic Microbial Degradation of Hydrocarbons: From Enzymatic Reactions to the Environment. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 26:5–28
Labinger JA, Bercaw JE (2002) Understanding and exploiting C–H bond activation. Nature 417:507–514
Joutey NT, Bahafid W, Sayel H, El Ghachtouli N (2013) Biodegradation: involved microorganisms and genetically engineered microorganisms. In: Chamy R, Rosenkranz F (eds) Biodegradation-Life of science. IntechOpen, Rijeka. https://doi.org/10.5772/56194
Sinhal S, Chattopadhyay P, Pan I, Chatterjee S, Chandal P, Das K, Bandyopadhyay SD (2009) Microbial transformation of xenobiotics for environmental bioremediation. Afr J Biotech 8:6016
John Kennedy L, Mohan das K, Sekaran G (2004) Integrated biological and catalytic oxidation of organics/inorganics in tannery wastewater by rice husk based mesoporous activated carbon-Bacillus sp. Carbon 42:2399–2407
Saranya P, Sukanya Kumari H, Prasad Rao B, Sekaran G (2014) Lipase production from a novel thermo-tolerant and extreme acidophile Bacillus pumilus using palm oil as the substrate and treatment of palm oil-containing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:3907–3919
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal J (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ramani K, John Kennedy L, Ramakrishnan M, Sekaran G (2010) Purification, characterization and application of acidic lipase from Pseudomonas gessardii using beef tallow as a substrate for fats and oil hydrolysis. Process Biochem 45:1683–1691
Ho YS, Mckay G (1998) Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Trans Chem E 76B:183–191
Lagergren S, Svenska BK (1898) The theory of adsorption on geloester substances. Veternskapsakad Handlingar 24:1–39
Sekaran G, Karthikeyan S, Boopathy R, Mandal AB (2014) A fluidized bed reactor for treatment of waste water. Patent No: WO 2014037959 A1 (Published, International)
WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC
Ramani K, Saranya P, Chandan jain S, Sekaran G (2013) Lipase from marine strain using cooked sunflower oil waste: production optimization and application for hydrolysis and thermodynamic studies. Bioprocess Biosys Eng 36:301–315
Acknowledgements
Author Dr. P. Saranya is grateful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saranya, P., Selvi, P.K. & Sekaran, G. Integrated thermophilic enzyme-immobilized reactor and high-rate biological reactors for treatment of palm oil-containing wastewater without sludge production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 42, 1053–1064 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02104-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-019-02104-x