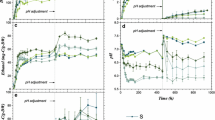
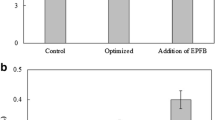
Abstract
Lignocellulose contains a large amount of cellulose but is recalcitrant to enzymatic hydrolysis, which yields sugars for fuels or chemicals. Various pretreatment methods are used to improve the enzymatic digestibility of cellulose in lignocellulose. Depending on the lignocellulose types and pretreatment methods, biomass compositions and physical properties significantly vary. Therefore, customized enzyme mixtures have to be employed for the efficient hydrolysis of pretreated lignocellulose. Here, using three recombinant model enzymes consisting of endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, and xylanase with a fixed amount of β-glucosidase, the optimal formulation of enzyme mixtures was designed for two differently pretreated rice straws (acid-pretreated or alkali-pretreated rice straw) by the mixture design methodology. As a result, different optimal compositions for the enzyme mixtures were employed depending on the type of pretreatment of rice straw. These results suggest that customized enzyme mixtures for pretreated lignocellulosic biomass are necessary to obtain increased sugar yields and should be considered in the industrial utilization of lignocellulose.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Himmel ME, Ding SY, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD (2007) Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315:804–807
Chandra RP, Bura R, Mabee WE, Berlin A, Pan X, Saddler JN (2007) Substrate pretreatment: the key to effective enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosics? Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:67–93
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch MR (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Kim IJ, Ko H-J, Kim T-W, Nam KH, Choi I-G, Kim KH (2013) Binding characteristics of a bacterial expansin (BsEXLX1) for various types of pretreated lignocellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5381–5388
Kim KH, Tucker M, Nguyen Q (2005) Conversion of bark-rich biomass mixture into fermentable sugar by two-stage dilute acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 96:1249–1255
Kim KH, Tucker MP, Nguyen QA (2002) Effects of pressing lignocellulosic biomass on sugar yield in two-stage dilute-acid hydrolysis process. Biotechnol Prog 18:489–494
Kim TH, Lee YY (2007) Pretreatment of corn stover by soaking in aqueous ammonia at moderate temperatures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137–140:81–92
Ko JK, Bak JS, Jung MW, Lee HJ, Choi I-G, Kim TH, Kim KH (2009) Ethanol production from rice straw using optimized aqueous-ammonia soaking pretreatment and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation processes. Bioresour Technol 100:4374–4380
Jalak J, Kurašin M, Teugjas H, Väljamäe P (2012) Endo-exo synergism in cellulose hydrolysis revisited. J Biol Chem 287:28802–28815
Kostylev M, Wilson D (2011) Synergistic interactions in cellulose hydrolysis. Biofuels 3:61–70
Subramaniyan S, Prema P (2002) Biotechnology of microbial xylanases: enzymology, molecular biology, and application. Cri Rev Biotechnol 22:33–64
Hong J, Ladisch MR, C-s Gong, Wankat PC, Tsao GT (1981) Combined product and substrate inhibition equation for cellobiase. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:2779–2788
Banerjee G, Car S, Scott-Craig JS, Borrusch MS, Walton JD (2010) Rapid optimization of enzyme mixtures for deconstruction of diverse pretreatment/biomass feedstock combinations. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:22
Billard H, Faraj A, Lopes Ferreira N, Menir S, Heiss-Blanquet S (2012) Optimization of a synthetic mixture composed of major Trichoderma reesei enzymes for the hydrolysis of steam-exploded wheat straw. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:9
Gao D, Chundawat SPS, Krishnan C, Balan V, Dale BE (2010) Mixture optimization of six core glycosyl hydrolases for maximizing saccharification of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreated corn stover. Bioresour Technol 101:2770–2781
Genencor (2007) Accellerase. http://www.genencor.com/cms/connect/genencor/products_and_services/agri_processing/renewable_fuels/new_products_ethanol/cellulosic_ethanol_en.htm
Watson BJ, Zhang H, Longmire AG, Moon YH, Hutcheson SW (2009) Processive endoglucanases mediate degradation of cellulose by Saccharophagus degradans. J Bacteriol 191:5697–5705
Irwin DC, Spezio M, Walker LP, Wilson DB (1993) Activity studies of eight purified cellulases: specificity, synergism, and binding domain effects. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:1002–1013
Ko JK, Jung MW, Kim KH, Choi I-G (2009) Optimal production of a novel endo-acting β-1,4-xylanase cloned from Saccharophagus degradans 2-40 into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). New Biotechnol 26:157–164
Kim Y, Ximenes E, Mosier NS, Ladisch MR (2011) Soluble inhibitors/deactivators of cellulase enzymes from lignocellulosic biomass. Enzyme Microb Technol 48:408–415
Ximenes E, Kim Y, Mosier N, Dien B, Ladisch MR (2011) Deactivation of cellulases by phenols. Enzyme Microb Technol 48:54–60
Ruiz R, Ehrman T (1996) LAP-002: Determination of carbohydrates in biomass by high performance liquid chromatography. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA
Templeton D, Ehrman T (1995) LAP-003: Determination of acid-insoluble lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2005) Determination of ash in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO, USA
Gräslund S, Nordlund P, Weigelt J, Bray J, Hallberg BM, Gileadi O, Knapp S, Oppermann U, Arrowsmith C, Hui R, Ming J, Dhe-Paganon S, Park HW, Savchenko A, Yee A, Edwards A, Vincentelli R, Cambillau C, Kim R, Kim SH, Rao Z, Shi Y, Terwilliger TC, Kim CY, Hung LW, Waldo GS, Peleg Y, Albeck S, Unger T, Dym O, Prilusky J, Sussman JL, Stevens RC, Lesley SA, Wilson IA, Joachimiak A, Collart F, Dementieva I, Donnelly MI, Eschenfeldt WH, Kim Y, Stols L, Wu R, Zhou M, Burley SK, Emtage JS, Sauder JM, Thompson D, Bain K, Luz J, Gheyi T, Zhang F, Atwell S, Almo SC, Bonanno JB, Fiser A, Swaminathan S, Studier FW, Chance MR, Sali A, Acton TB, Xiao R, Zhao L, Ma LC, Hunt JF, Tong L, Cunningham K, Inouye M, Anderson S, Janjua H, Shastry R, Ho CK, Wang DY, Wang H, Jiang M, Montelione GT, Stuart DI, Owens RJ, Daenke S, Schutz A, Heinemann U, Yokoyama S, Büssow K, Gunsalus KC (2008) Protein production and purification. Nat Methods 5:135–146
Aslanidis L, de Jong PJ (1990) Ligation-independent cloning of PCR products (LIC-PCR). Nucleic Acids Res 18:6069–6074
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Cornell JA (2002) Experiments with mixtures: designs, models, and the analysis of mixture data, 3rd edn. Wiley, USA
Dejaegher B, Vander Heyden Y (2011) Experimental designs and their recent advances in set-up, data interpretation, and analytical applications. J Pharm Biomed Anal 56:141–158
Henrissat B, Driguez H, Viet C, Schulein M (1985) Synergism of cellulases from Trichoderma reesei in the degradation of cellulose. Nat Biotech 3:722–726
Zhu L, O’Dwyer JP, Chang VS, Granda CB, Holtzapple MT (2008) Structural features affecting biomass enzymatic digestibility. Bioresour Technol 99:3817
Arantes V, Saddler J (2010) Access to cellulose limits the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis: the role of amorphogenesis. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:4
Arantes V, Saddler JN (2011) Cellulose accessibility limits the effectiveness of minimum cellulase loading on the efficient hydrolysis of pretreated lignocellulosic substrates. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:3
Rosgaard L, Pedersen S, Langston J, Akerhielm D, Cherry JR, Meyer AS (2007) Evaluation of minimal Trichoderma reesei cellulase mixtures on differently pretreated barley straw substrates. Biotechnol Prog 23:1270–1276
Hu J, Arantes V, Pribowo A, Saddler JN (2013) The synergistic action of accessory enzymes enhances the hydrolytic potential of a “cellulase mixture” but is highly substrate specific. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:112
Murnen HK, Balan V, Chundawat SPS, Bals B, da Costa Sousa L, Dale BE (2007) Optimization of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Miscanthus x giganteus to fermentable sugars. Biotechnol Prog 23:846–850
Ko JK, Ximenes E, Kim Y, Ladisch MR (2014) Adsorption of enzyme onto lignins of liquid hot water pretreated hardwoods. Biotechnol Bioeng. doi:10.1002/bit.25359
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (2013M1A2A2072597) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (10049674). Experiments were performed at the Korea University Food Safety Hall for the Institute of Biomedical Science and Food Safety.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, I.J., Jung, J.Y., Lee, H.J. et al. Customized optimization of cellulase mixtures for differently pretreated rice straw. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 929–937 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1338-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1338-7