Abstract
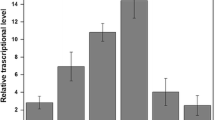
Zinc ion plays essential roles in biological chemistry. Bacteria acquire Zn2+ from the environment, and cellular concentration levels are controlled by zinc homeostasis systems. In comparison with other homeostatic systems, the ZraSR two-component system was found to be more efficient in responding to exogenous zinc concentrations. To understand the dynamic response of the bacterium ZraSR two-component system with respect to exogenous zinc concentrations, the genetic circuit of the ZraSR system was integrated with a reporter protein. This study was helpful in the construction of an E. coli system that can display selective metal binding peptides on the surface of the cell in response to exogenous zinc. The engineered bacterial system for monitoring exogenous zinc was successfully employed to detect levels of zinc as low as 0.001 mM, which directly activates the expression of chimeric ompC t —zinc binding peptide gene to remove zinc by adsorbing a maximum of 163.6 μmol of zinc per gram of dry cell weight. These results indicate that the engineered bacterial strain developed in the present study can sense the specific heavy metal and activates a cell surface display system that acts to remove the metal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg JM, Shi Y (1996) The galvanization of biology: a growing appreciation for the roles of zinc. Science 271:1081–1085
Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A (2006) Zinc through the three domains of life. J Proteome Res 5:3173–3178
Fraústo da Silva JJR WRJP (2001) The biological chemistry of the elements: the inorganic chemistry of life. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Outten CE, O’Halloran VT (2001) Femtomolar sensitivity of metalloregulatory proteins controlling zinc homeostasis. Science 292:2488–2492
Blencowe DK, Morby AP (2003) Zn(II) metabolism in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:291–311
Outten CE, Outten FW, O’Halloran TV (1999) DNA distortion mechanism for transcriptional activation by ZntR, a Zn(II)-responsive MerR homologue in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 274:37517–37524
Franke S, Grass G, Nies DH (2001) The product of the ybdE gene of the Escherichia coli chromosome is involved in detoxification of silver ions. Microbiology 147:965–972
Leonhartsberger S, Huber A, Lottspeich F, Bock A (2001) The hydH/G Genes from Escherichia coli code for a zinc and lead responsive two-component regulatory system. J Mol Biol 307:93–105
Noll M, Petrukhin K, Lutsenko S (1998) Identification of a novel transcription regulator from Proteus mirabilis, PMTR, revealed a possible role of YJAI protein in balancing zinc in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 273:21393–21401
Reitzer L, Schneider BL (2001) Metabolic context and possible physiological themes of {sigma}54-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:422–444
Beard SJ, Hashim R, Membrillo-Hernandez J, Hughes MN, Poole RK (1997) Zinc(II) tolerance in Escherichia coli K-12: evidence that the zntA gene (o732) encodes a cation transport ATPase. Mol Microbiol 25:883–891
Brocklehurst KR, Hobman JL, Lawley B, Blank L, Marshall SJ, Brown NL, Morby AP (1999) ZntR is a Zn(II)-responsive MerR-like transcriptional regulator of zntA in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 31:893–902
Rensing C, Mitra B, Rosen BP (1997) The zntA gene of Escherichia coli encodes a Zn(II)-translocating P-type ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14326–14331
Binet MRB, Poole RK (2000) Cd(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) ions regulate expression of the metal-transporting P-type ATPase ZntA in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 473:67–70
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Miller WG, Leveau JH, Lindow SE (2000) Improved gfp and inaZ broad-host-range promoter-probe vectors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:1243–1250
Blattner FR, Plunkett G III, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, Davis NW, Kirkpatrick HA, Goeden MA, Rose DJ, Mau B, Shao Y (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453–1462
Matsubara T, Hiura Y, Kawahito O, Yasuzawa M, Kawashiro K (2003) Selection of novel structural zinc sites from a random peptide library. FEBS Lett 555:317–321
Jeanteur D, Lakey JH, Pattus F (1991) The bacterial porin superfamily: sequence alignment and structure prediction. Mol Microbiol 5:2153–2164
Xu Z, Lee SY (1999) Display of polyhistidine peptides on the Escherichia coli cell surface by using outer membrane protein C as an anchoring motif. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5142–5147
Eleaume H, Jabbouri S (2004) Comparison of two standardisation methods in real-time quantitative RT-PCR to follow Staphylococcus aureus genes expression during in vitro growth. J Microbiol Methods 59:363–370
Kotrba P, Doleckova L, de Lorenzo V, Ruml T (1999) Enhanced bioaccumulation of heavy metal ions by bacterial cells due to surface display of short metal binding peptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1092–1098
Huckle JW, Morby AP, Turner JS, Robinson NJ (1993) Isolation of a prokaryotic metallothionein locus and analysis of transcriptional control by trace metal ions. Mol Microbiol 7:177–187
Ivask A, Virta M, Kahru A (2002) Construction and use of specific luminescent recombinant bacterial sensors for the assessment of bioavailable fraction of cadmium, zinc, mercury and chromium in the soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1439–1447
Riether K, Dollard MA, Billard P (2001) Assessment of heavy metal bioavailability using Escherichia coli zntAp:lux and copAp:lux-based biosensors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:712–716
Tauriainen S, Karp M, Chang W, Virta M (1998) Luminescent bacterial sensor for cadmium and lead. Biosen Bioelectron 13:931–938
Magrisso S, Erel Y, Belkin S (2008) Microbial reporters of metal bioavailability. Microb Biotechnol 1:320–330
Sousa C, Cebolla A, de Lorenzo V (1996) Enhanced metalloadsorption of bacterial cells displaying poly-His peptides. Nat Biotechnol 14:1017–1020
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the BioGreen 21 Project (PJ008057) of the Rural Development Administration of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravikumar, S., Yoo, Ik., Lee, S.Y. et al. A study on the dynamics of the zraP gene expression profile and its application to the construction of zinc adsorption bacteria. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34, 1119–1126 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0562-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0562-7