Abstract
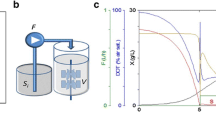
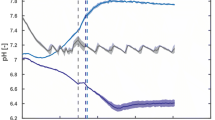
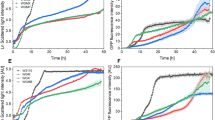
A new feeding strategy in fed-batch culture, exponential feeding combined with pH-stat is suggested to avoid the accumulation of substrate in culture broth. Exponential feeding was stopped whenever a predetermined amount of limiting substrate was supplied and then pH change was observed. When pH rose above an upper limit due to the depletion of substrate, feeding was restarted. With this feeding strategy, recombinant Escherichia coli could be grown to 101 g/l by controlling the specific growth rate at 0.1 h−1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamane T, Shimizu S (1984) Fed-batch techniques in microbial processes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 30:147–194
Lee J, Lee SY, Park S, Middelberg APJ (1999) Control of fed-batch fermentations. Biotechnol Adv 17:29–48
Johnston W, Cord-Ruwisch R, Cooney MJ (2002) Industrial control of recombinant E coli fed-batch culture: new perspectives on traditional controlled variables. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25:111–120
Yim SC, Jeong KJ, Chang HN, Lee SY (2001) High-level secretory production of human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor by fed-batch culture of recombinant Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 24:249–254
Suzuki T, Yamane T, Shimizu S (1990) Phenomenological background and some preliminary trials of automated substrate supply in pH-stat modal fed-batch culture using a setpoint high limit. J Ferment Bioeng 69:292–297
Yano T, Kobayashi T, Shimizu S (1978) Fed-batch culture of methanol-utilizing bacterium with DO-stat. J Ferment Technol 56:416–420
Kim BS, Lee SC, Lee SY, Chang HN, Chang YK, Woo SI (1994) Production of poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) by fed-batch culture of Alcaligenes eutrophus with glucose concentration control. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:892–898
Lee SY (1996) High cell-density culture of Escherichia coli. Tibtech 14:98–105
Lee SY, Yim KS, Chang HN, Chang YK (1994) Construction of plasmids, estimation of plasmid stability, and use of stable plasmids for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 32:203–211
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty RM (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:29–37
Luli GW, Strohl WR (1990) Comparison of growth, acetate production, and acetate inhibition of Escherichia coli strains in batch and fed-batch fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1004–1011
Han K, Lim HC, Hong J (1992) Acetic acid formation in Escherichia coli fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 39:663–671
Pan JG, Rhee JS, Lebeault JM (1987) Physiological constraints in increasing biomass concentration of Escherichia coli in fed-batch culture. Biotechnol Lett 2:89–94
Brown SW, Meyer HP, Fiechter A (1985) Continuous production of human leukocyte interferon with Escherichia coli and continuous cell lysis in a two-stage chemostat. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:5–9
Riesenberg D, Schulz V, Knorre WA, Pohl HD, Korz D, Sanders EA, Ro A, Deckwer WD (1991) High cell density cultivation of Escherichia coli at controlled specific growth rate. J Biotechnol 20:17–28
Slater S, Gallaher T, Dennis D (1992) Production of poly-(β-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1089–1094
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00449-004-0361-5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.S., Lee, S.C., Lee, S.Y. et al. High cell density fed-batch cultivation of Escherichia coli using exponential feeding combined with pH-stat. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26, 147–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0347-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0347-8