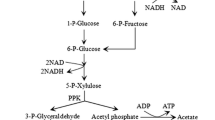
Abstract
Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B512F is the main strain used in industrial fermentations to produce dextransucrase and dextran. This process has been studied since the Second World War, when it was used as blood plasma expander. A study about the effect of phosphate concentration on cell propagation in a semicontinuous shake-flask culture is described in this work. Dextransucrase is obtained by fermentation of the Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B512F in the presence of sucrose as substrate, a nitrogen source (corn liquor or yeast extract) and minerals. Phosphate is currently used in order to buffer the culture medium. Cell propagation can be done through a repeated batch culture, where dilution in a fresh medium is made with relatively short periods. The standard medium for dextransucrase production is prepared using 0.1 M of K2HPO4. In this work the level of phosphate was increased to 0.3 M, and an increase on biomass and on the enzyme activity was found when phosphate enriched medium was used. Higher phosphate buffer concentration was also able to keep the pH values above 5.0 during the entire process, avoiding enzyme denaturation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsop L (1983) Industrial production of dextran. Progr Ind Microbiol 18:1-44
Kandarov O, Titel C, Volkova L, Nosov A, Ehwald R (2000) Additional phosphate stabilises uninterrupted growth of a Dioscorea deltoidea cell culture. Plant Sci 157:209–216
Guimarães PRB, Costa FAA, Rodrigues MI, Maugeri F (1999) Optimization of dextran synthesis and acidic hydrolysis by surface response analysis. Braz J Chem Eng 16:146
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicilic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Tsuchiya HM, Koepsell HJ, Corman J, Bryant MO, Feger VH, Jackson RW (1952) The effect of certain cultural factors on production of dextransucrase by Leuconostoc mesenteroides. J Bact 64:521–526
Kitaoka M, Robyt JF (1998) Large-scale preparation of highly purified dextransucrase form a high-producing constitutive mutant of Leuconostoc mesenteroides B-512-FMC. Enzyme Microb Technol 23:396–391
Santos M, Teixeira J, Rodrigues A (2000) Production of dextransucrose, dextran and fructose using Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B512F. Biochem Eng J 4:177–188
Robyt JF, Walseth TF (1986) Production, purification and properties of dextransucrase from Leuconosotoc mesenteroides NRRL B512 F. Carbohydr Res 147:119–133
Kobayashi M, Matsuda K (1980) Characterization of multiple forms and main component of dextransucrase form Leuconostoc mesenteroides NTTL B 512F. Biochim Biophys Acta 614:46–62
Acknowledgements
To the Brazilian Funding Angencies: CNPQ, CAPES and FAEP. This paper was accepted and presented at ESBES-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, S., Lona, L.M.F. & Franco, T.T. Effect of phosphate concentration on the production of dextransucrase by Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B512F. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 26, 57–62 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0330-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-003-0330-4