Abstract.
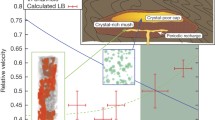
During the 1929 activity of Hokkaido-Komagatake volcano, the Plinian eruption of a phenocryst-rich andesite was preceded by a small eruption of more mafic magma formed by magma mixing. A similar eruption sequence has been reported for some other eruptions (Pallister et al. 1996; Venezky and Rutherford 1997), suggesting that eruption of a mixed magma is a precursor of phenocryst-rich magmas. For the purpose of understanding the tapping processes of the phenocryst-rich magma chamber, we investigated the temporal variation in the erupted magma and estimated the viscosity and density of the end-member and mixed magmas with constraints drawn from petrography. For the precursory mixed magma we estimate 33±4 vol.% phenocrysts, andesitic–dacitic melt composition, 3 wt.% H2O content, and temperature of 1040°C. In comparison, for the climactic, silicic end-member magma we estimate 48±3 vol.% phenocryst, high-silica rhyolitic melt, 3 wt.% H2O, and temperature of 950°C, respectively. The mafic end-member magma, which was not erupted, is thought to be an almost aphyric basaltic–andesitic magma, based on mass balance calculation of the phenocryst content. The proportion of the mafic end-member magma component in the mixed magma was calculated to be 20–40 wt.%. On the basis of these data, we estimate magma viscosities of 103.9, 106.9, and 102.0 Pa s for the mixed, silicic end-member, and mafic end-member magmas, respectively. The calculated density differences among these magmas are inconsequential when possible errors are considered. We calculate the minimum excess pressure required for dike propagation to be 31 MPa for the silicic end-member magma and 8 MPa for the mixed magma, using the estimated viscosity and dike propagation model of Rubin (1995). If we assume that excess pressure is limited by the wall rock strength of the magma chamber, excess pressure retainable in the magma chamber is less than ca. 20 MPa. This suggests that the mixed magma was able to ascend to the surface without freezing, whereas the viscous silicic end-member magma could not. The formation and precursory eruption of the mixed magma are, therefore, effective and necessary initiation processes for the phenocryst-rich, viscous magma eruption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, .S., Nakamura, .M. Role of precursory less-viscous mixed magma in the eruption of phenocryst-rich magma: evidence from the Hokkaido-Komagatake 1929 eruption. Bull Volcanol 63, 365–376 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004450100151
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004450100151