Abstract
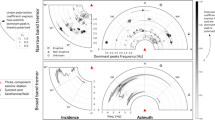
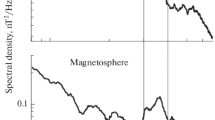
In the present paper, we analyse long-period (LP) events and seismic noise recorded at Campi Flegrei during the uplift episode of 2004–2006. The results of a detailed polarization analysis indicate that the large number of LPs detected during the seismic crisis were accompanied by a sustained activity consisting of very low-energy volcanic signals. These weak volcanic signals, which are usually absent in ambient noise recorded in the studied area, and LP events have similar properties, namely they are radially polarized towards the same LP source. The large dataset analysed allows us to study the statistics of the polarization, leading to the extraction of the average properties of the volcanic signals. An estimate of the complexity of the system can be provided by the degrees of freedom necessary to describe the asymptotic dynamics in a reconstructed phase space. This analysis shows that both LPs and low-energy signals can be described by a low-dimensional dynamical system, while ambient noise unrelated to volcanic activity is higher dimensional. Based on these observations, we interpret the phenomena observed during the seismic crisis in the framework of the theory of self-oscillating systems, in which LPs and low-energy signals represent self-oscillations generated by a persistent hydrothermal source.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarbanel HDI (1996) Analysis of observed chaotic data. Springer, New York
Acernese F, Ciaramella A, De Martino S, Falanga M, Godano C, Tagliaferri R (2004) Polarisation analysis of the independent component of low frequency events at Stromboli volcano (Eolian Islands Italy). J Volcanol Geoth Res 137:153–168. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2004.05.005
Aki K, Fehler M, Das S (1977) Source mechanism of volcanic tremor: fluid-driven crack models and their application to the 1963 Kilauea eruption. J Volcanol Geoth Res 2:259–287
Andronov AA, Vitt AA, Khaikin SE (1966) Theory of oscillators. Dover, New York
Arciniega-Ceballos A, Valdes C, Dawson P (2000) Temporal and spectral characteristics of seismicity observed at Popocatepetl volcano, central Mexico. J Volcanol Geoth Res 102:207–216
Balmforth NJ, Craster RV, Rust AC (2005) Instability in flow through elastic conduits and volcanic tremor. J Fluid Mech 527:353–377
Berens P (2009) CircStat: a Matlab toolbox for circular statistics. J Stat Softw 31(10):1–21
Bianco F, Del Pezzo E, Saccorotti G, Ventura G (2004) The role of hydrothermal fluids in triggering the July–August 2000 seismic swarm at Campi Flegrei (Italy): evidences from seismological and mesostructural data. J Volcanol Geoth Res 133:229–246
Bottiglieri M, De Martino S, Falanga M, Godano C (2008) Strombolian volcanic activity as an intermittent phenomenon. Europhys Lett 81:49001
Carniel R, Di Cecca M, Rouland D (2003) Ambrym, Vanuatu (July–August 2000): spectral and dynamical transitions on the hours-to-days timescale. J Volcanol Geoth Res 128:1–13. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(03)00243-9
Carniel R (2010) Comments on the paper “Automatic detection and discrimination of volcanic tremors and tectonic earthquakes”. J Volcanol Geoth Res 194:61–62
Chiodini G, Todesco M, Caliro S, Del Gaudio C, Macedonio G, Russo, M (2003) Magma degassing as a trigger of bradyseismic events: the case of Phlegrean Fields (Italy). Geophys Res Lett 30(8):1434–1438
Chouet BA (1988) Resonance of a fluid-driven crack: radiation properties and implications for the source of long-period events and harmonic tremor. J Geophys Res 93:4375–4400
Chouet BA (1996) Long-period volcano seismicity: its source and use in eruption forecasting. Nature 380:309–316
Chouet BA, Julian BR (1985) Dynamic of an expanding fluid-filled crack. J Geophys Res 90:11187–11198
Chouet B, Shaw HR (1991) Fractal properties of tremor and gas-piston events observed at Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. J Geophys Res 96:10177–10189
Ciaramella A, De Lauro E, Falanga M, Petrosino S (2011) Automatic detection of long-period events at Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy). Geophys Res Lett 38:L18302. doi:10.1029/2011GL049065
Cusano P, Petrosino S, Saccorotti G (2008) Hydrothermal origin for sustained long-period (LP) activity at Campi Flegrei volcanic complex, Italy. J Volcanol Geoth Res 177:1035–1044. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.07.019
De Lauro E, De Martino S, Falanga M, Esposito E, Tomasini EP (2007) Analogical model for mechanical vibrations in flue organ pipes inferred by independent component analysis. J Acoust Soc Am 122:2413–2424. doi:10.1121/1.2772225
De Lauro E, De Martino S, Del Pezzo E, Falanga M, Palo M, Scarpa R (2008) Model for high frequency Strombolian tremor inferred by wavefield decomposition and reconstruction of asymptotic dynamics. J Geophys Res 113:B02302. doi:10.1029/2006JB004838
De Lauro E, De Martino S, Falanga M, Ixaru LGr (2009a) Limit cycles in nonlinear excitation of clusters of classical oscillators. Comput Phys Commun 180:1832–1838
De Lauro E, De Martino S, Falanga M, Palo M (2009b) Modelling the macroscopic behavior of Strombolian explosions at Erebus volcano. Phys Earth Planet In 176:174–186. doi:10.1016/j.pepi.2009.05.003
Di Vito MA, Isaia R, Orsi G, Southon J, de Vita S, D’Antonio M, Pappalardo L, Piochi M (1999) Volcanism and deformation since 12,000 years at the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J Volcanol Geoth Res 91:221–246
Fabre B, Hirschberg A (2000) Physical modeling of flue instruments: a review of lumped models. Acta Acoust 86:599–610
Fraser AM, Swinney HL (1986) Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys Rev A 33:1134–1139
Fujita E, Ukawa M, Yamamoto E (2004) Subsurface cyclic magma sill expansions in the 2000 Miyakejima volcano eruption: possibility of two-phase flow oscillation. J Geophys Res 109:B04205
Godano C, Salerno M (1993) The chaoticity degree of the Campi Flegrei seismicity, southern Italy. Geophys J Int 144:392–398
Godano C, Capuano P (1999) Source characterisation of low frequency events at Stromboli and Vulcano Islands (Isole Eolie Italy). J Seismol 3:393–408
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983) Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Physica D 9:189–208
Hilborn RC (1994) Chaos and nonlinear dynamics: an introduction for scientists and engineers. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 672
Ibáñez J, Del Pezzo E, Almendros J, La Rocca M, Alguacil G, Ortiz R, García A (2000) Seismovolcanic signals at Deception Island volcano, Antarctica: wave field analysis and source modeling. J Geophys Res 105:13905–13931
Iwamura K, Kaneshima S (2005) Numerical simulation of the steam-water flow instability as a mechanism of long-period ground vibrations at geothermal areas. Geophys J Int 163:833–851
Jones J, Carniel R, Harris AJL, Malone S (2006) Seismic characteristics of variable convection at Erta ’Ale lava lake, Ethiopia. J Volcanol Geoth Res 153:64–79
Julian BR (1994) Volcanic tremor: nonlinear excitation by fluid flow. J Geophys Res 99:11859–11877
Kawakatsu H, Yamamoto M (2007) Volcano seismology. In: Schubert G (ed) Treatise on geophysics, vol 4. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 389–420
Kennel MB, Brown R, Abarbanel HDI (1992) Determining embedding dimension for phase space-reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys Rev A 45:3403–3411
Konstantinou KI (2002) Deterministic nonlinear source processes of volcanic tremor signals accompanying the 1996 Vatnajokull eruption, Central Iceland. Geophys J Int 148:663–675
Konstantinou KI, Schlindwein V (2002) Nature, wavefield properties and source mechanism of volcanic tremor: a review. J Volcanol Geoth Res 119:161–187
Konstantinou KI, Lin CH (2004) Nonlinear time series analysis of volcanic tremor events recorded at Sangay volcano, Ecuador. Pure Appl Geophys 161:145–163
Kumagai H, Chouet BA, Nakano M (2002) Waveform inversion of oscillatory signatures in long-period events beneath volcanoes. J Geophys Res 107:2301. doi:10.1029/2001JB001704
Kumagai H, Chouet B, Dawson PB (2005) Source process of a long-period event at Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. Geophys J Int 161:243–254
Kumazawa M, Imanishi Y, Fukao Y, Furmoto M, Yamamoto A (1990) A theory of spectral analysis based on the characteristic property of a linear dynamic system. Geophys J Int 101:613–630
Lesage Ph, Mora M, Alvarado G, Pacheco J, Métaxian JPh (2006) Complex behavior and source model of the volcanic tremor at Arenal volcano, Costa Rica. J Volcanol Geoth Res 157:49–59
Matsubara W, Yomogida K (2004) Source process of low-frequency earthquakes associated with the 2000 eruption of Mt. Usu. J Volcanol Geoth Res 134:223–240
Maurel A, Ern P, Zielinska BJA, Wesfreid JE (1996) Experimental study of self-sustained oscillations in a confined jet. Phys Rev E 54:3643–3651
Montalbetti JR, Kanasevich ER (1970) Enhancement of teleseismic body phase with a polarization filter. Geophys J Roy Astr S 21:119–129
Nakano M, Kumagai H, Chouet BA (2003) Source mechanism of long-period events at Kusatsu-Shirane Volcano, Japan, inferred from waveform inversion of the effective excitation functions. J Volcanol Geoth Res 122:149–164
Neuberg J, Luckett R, Baptie B, Olsen K (2000) Models of tremor and low-frequency earthquake swarms on Montserrat. J Volcanol Geoth Res 122:83–104
Orsi G, De Vita S, Di Vito MA (1996) The restless resurgent Campi Flegrei nested caldera (Italy): constraints on its evolution and configuration. J Volcanol Geoth Res 74:179–214
Orsi G, Civetta L, Del Gaudio C, De Vita S, Di Vito M, Isaia R, Petrazzuoli SM, Ricciardi GP, Ricco C (1999) Short term ground deformations and seismicity in the resurgent Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy): an example of active block-resurgence in a densely populated area. J Volcanol Geoth Res 91:415–451
Petrosino S, De Siena L, Del Pezzo E (2008) Recalibration of the magnitude scales at Campi Flegrei, Italy, on the basis of measured path and site and transfer functions. B Seismol Soc Am 98(4):1964–1974
Rigano R, Cara F, Lombardo G, Rovelli A (2008) Evidence for ground motion polarization on fault zones of Mount Etna volcano. J Geophys Res 113:B10306. doi:10.1029/2007JB005574
Ripepe M, Gordeev E (1999) Gas bubble dynamics model for shallow volcanic tremor at Stromboli. J Geophys Res 104:10639–10654
Ripepe M, Harris AJL, Carniel R (2002) Thermal, seismic and infrasonic evidences of variable degassing rates at Stromboli volcano. J Volcanol Geoth Res 118:285–297
Saccorotti G, Chouet BA, Dawson PB (2001a) Wavefield properties of shallow long-period event and tremor at Kilauea volcano, Italy. J Volcanol Geoth Res 109:163–189
Saccorotti G, Bianco F, Castellano M, Del Pezzo E (2001b) The July–August 2000 seismic swarms at Campi Flegrei volcanic complex, Italy. Geophys Res Lett 28:2525–2528
Saccorotti G, Petrosino S, Bianco F, Castellano M, Galluzzo D, La Rocca M, Del Pezzo E, Zaccarelli L, Cusano P (2007) Seismicity associated with the 2004–2006 renewed ground uplift at Campi Flegrei Caldera, Italy. Phys Earth Planet In 165:14–24
Takens F (1981) Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In: Rand DA, Young LS (eds) Dynamical systems and turbulence, Warwick. Lectures notes in mathematics, vol 898. Springer, Berlin, pp 366–381
Seidl D, Schick R, Riuscetti M (1981) Volcanic tremor at Etna: a model for hydraulic origin. B Volcanol 44:43–55
Vidale JE (1986) Complex polarization analysis of particle motion. B Seismol Soc Am 76:1393–1405
Villermaux E, Hopfinger EJ (1994) Self-sustained oscillations of a confined jet: a case study for non-linear delayed saturation model. Physica D 72:230–243
Woodhouse J (1996) Self-sustained musical oscillators. In: Mechanics of musical instruments. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
We are sincerely grateful to Francesca Bianco, Enza De Lauro, Salvatore De Martino, Edoardo Del Pezzo, Margaret Hellweg and an anonymous referee for their useful comments and suggestions that improved this manuscript. The Mobile Seismic Network team of the INGV-OV is acknowledged for having provided the data. The CircStat package (Berens 2009) has been used for the circular statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: T. Ohminato
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falanga, M., Petrosino, S. Inferences on the source of long-period seismicity at Campi Flegrei from polarization analysis and reconstruction of the asymptotic dynamics. Bull Volcanol 74, 1537–1551 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-012-0612-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-012-0612-2