Abstract
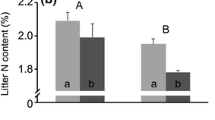
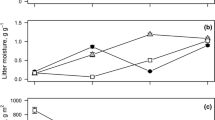
The effects of forest fragmentation on leaf-litter decomposition rates were investigated for the first time in an experimentally fragmented tropical forest landscape in Central Amazonia. Leaf-litter decomposition rates were measured at seven distances (0–420 m) along forest edge-to-interior transects in two 100-ha fragments, two continuous forest edges, and at an identical series of distances along two deep continuous forest transects, as well as at the centers of two 1-ha and two 10-ha fragments. Decomposition rates increased significantly towards the edge of 100-ha forest fragments. Litter turnover times were 3–4 times faster within 50 m of the edge of 100-ha fragments than normally found in deep continuous forest. In contrast, there was no significant change in the rate of leaf-litter decomposition from the interior to the edge of continuous forest. It is difficult to account for these very different edge responses. Decomposition rates were not correlated with air temperature differentials, evaporative drying rates, litter depth, biomass or moisture content, or with total invertebrate densities, either within individual edge transects or across all sites. The difference in edge response may be due to chance, particularly the patchy removal of vast quantities of litter by litter-feeding termites, or may be a real, area-dependent phenomenon. Clearly, however, forest fragmentation increases the variability and unpredictability of litter decomposition rates near forest edges. In addition to edge effects, decomposition rates were strongly affected by decreasing fragment area. While sites at the centers of 10-ha and 100-ha forest fragments and continuous forest had equivalent decomposition rates, rates were markedly lower at the centers of 1-ha fragments. Litter turnover times were 2–3 times slower in 1-ha fragments than in continuous forest, and up to 13 times slower than at 100-ha edges. Litter structure and nutrient cycling dynamics are inevitably altered by forest fragmentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 October 1997 / Accepted: 14 April 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Didham, R. Altered leaf-litter decomposition rates in tropical forest fragments. Oecologia 116, 397–406 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050603
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050603