Abstract.
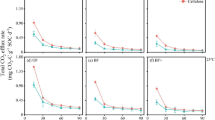
The Arctic contains extensive soil carbon reserves that could provide a substantial positive feedback to atmospheric CO2 concentrations and global warming. Evaluation of this hypothesis requires a mechanistic understanding of the in situ responses of individual components of tundra net ecosystem CO2 exchange (NEE) to warming. In this study, we measured NEE, total ecosystem respiration and respiration from below ground in experimentally warmed plots within Alaskan acidic tussock tundra. Soil warming of 2–4°C during a single growing season caused strong increases in total ecosystem respiration and belowground respiration from moss-dominated inter-tussock areas, and similar trends from sedge-dominated tussocks. Consequently, the overall effect of the manipulation was to substantially enhance net ecosystem carbon loss during mid-summer. Components of vascular plant biomass were closely correlated with total ecosystem respiration and belowground respiration in control plots of both microsites, but not in warmed plots. By contrast, in the warmed inter-tussock areas, belowground respiration was most closely correlated with organic-layer depth. Warming in tussock areas was associated with increased leaf nutrient pools, indicating enhanced rates of soil nutrient mineralisation. Together, these results suggest that warming enhanced net ecosystem CO2 efflux primarily by stimulating decomposition of soil organic matter, rather than by increasing plant-associated respiration. Our short-term experiment provides field evidence to support previous growth chamber and modelling studies indicating that arctic soil C reserves are relatively sensitive to warming and could supply an initial positive feedback to rising atmospheric CO2 concentrations/changing climate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grogan, P., Chapin III, F. Initial effects of experimental warming on above- and belowground components of net ecosystem CO2 exchange in arctic tundra. Oecologia 125, 512–520 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000490
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000490