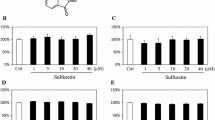
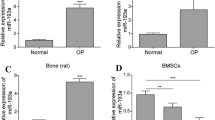
Abstract
It has been established that inflammation plays an important role in bone formation and bone loss. Although a lot is known about the role of TNF-α in bone health, very little is understood about TNF-β, also called lymphotoxin. In this report, we examine the effect of TNF-β on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and its modulation by resveratrol. Monolayer and high-density cultures of MSCs were treated with osteogenic induction medium with/without TNF-β, Sirt1 inhibitor nicotinamide (NAM), antisense oligonucleotides against Sirt1 (ASO) and/or Sirt1 stimulator resveratrol. We found that TNF-β inhibits, in a similar way to NAM or Sirt1-ASO, the early stage of osteogenic differentiation of MSCs and this was accompanied with downregulation of bone-specific matrix, β1-integrin, Runx2 and with upregulation of NF-κB phosphorylation and NF-κB-regulated gene products involved in the inflammatory, degradative processes and apoptosis. However, resveratrol reversed TNF-β- and NAM-suppressed MSCs osteogenesis by activation of Sirt1 and Runx2 that led to osteoblast differentiation. Furthermore, downregulation of Sirt1 by mRNA inhibited the effect of resveratrol, highlighting the important impact of this enzyme in the TNF-β signaling pathway. Finally, resveratrol was able to manifest its effect both by suppression of TNF-β-induced NF-κB and through direct activation of the Sirt1 and Runx2 pathway. Thus, through these studies, we present a mechanism by which a T cell-derived cytokine, TNF-β can affect bone formation through modulation of MSCs differentiation that involves NF-κB, Sirt1, Runx2 and resveratrol reversed TNF-β-promoted impairments in MSCs osteogenesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756
Aggarwal BB, Moffat B, Harkins RN (1984) Human lymphotoxin. Production by a lymphoblastoid cell line, purification, and initial characterization. J Biol Chem 259:686–691
Aggarwal BB, Eessalu TE, Hass PE (1985a) Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature 318:665–667
Aggarwal BB, Kohr WJ, Hass PE, Moffat B, Spencer SA, Henzel WJ, Bringman TS, Nedwin GE, Goeddel DV, Harkins RN (1985b) Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem 260:2345–2354
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Kim JH (2012) Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 119:651–665
Armiento AR, Alini M, Stoddart MJ (2018) Articular fibrocartilage-why does hyaline cartilage fail to repair? Adv Drug Deliv Rev
Backesjo CM, Li Y, Lindgren U, Haldosen LA (2006) Activation of Sirt1 decreases adipocyte formation during osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Mineral Res 21:993–1002
Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, Buchan I, Matteson EL, Montori V (2006) Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials. Jama 295:2275–2285
Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A, Matis U, Shakibaei M (2010) Curcumin mediated suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB promotes chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a high-density co-culture microenvironment. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R127
Buhrmann C, Shayan P, Aggarwal BB, Shakibaei M (2013) Evidence that TNF-beta (lymphotoxin alpha) can activate the inflammatory environment in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 15:R202
Buhrmann C, Busch F, Shayan P, Shakibaei M (2014) Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) is required for promoting chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem 289:22048–22062
Buhrmann C, Popper B, Aggarwal BB, Shakibaei M (2017) Resveratrol downregulates inflammatory pathway activated by lymphotoxin alpha (TNF-beta) in articular chondrocytes: comparison with TNF-alpha. PLoS One 12:e0186993
Busch F, Mobasheri A, Shayan P, Lueders C, Stahlmann R, Shakibaei M (2012a) Resveratrol modulates interleukin-1beta-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB signaling pathways in human tenocytes. J Biol Chem 287:38050–38063
Busch F, Mobasheri A, Shayan P, Stahlmann R, Shakibaei M (2012b) Sirt-1 is required for the inhibition of apoptosis and inflammatory responses in human tenocytes. J Biol Chem 287:25770–25781
Calmon-Hamaty F, Combe B, Hahne M, Morel J (2011a) Lymphotoxin alpha revisited: general features and implications in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 13:232
Calmon-Hamaty F, Combe B, Hahne M, Morel J (2011b) Lymphotoxin alpha stimulates proliferation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Cytokine 53:207–214
Cao L, Lee V, Adams ME, Kiani C, Zhang Y, Hu W, Yang BB (1999) Beta-integrin-collagen interaction reduces chondrocyte apoptosis. Matrix Biol 18:343–355
Corrado A, Maruotti N, Cantatore FP (2017) Osteoblast role in rheumatic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 18
Csaki C, Matis U, Mobasheri A, Ye H, Shakibaei M (2007) Chondrogenesis, osteogenesis and adipogenesis of canine mesenchymal stem cells: a biochemical, morphological and ultrastructural study. Histochem Cell Biol 128:507–520
Csaki C, Matis U, Mobasheri A, Shakibaei M (2009) Co-culture of canine mesenchymal stem cells with primary bone-derived osteoblasts promotes osteogenic differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol 131:251–266
De Bari C, Roelofs AJ (2018) Stem cell-based therapeutic strategies for cartilage defects and osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 40:74–80
Dinarello CA, Kim SH (2006) IL-32, a novel cytokine with a possible role in disease. Ann Rheum Dis 65(Suppl 3):iii61–iii64
Dixon WG, Symmons DP, Lunt M, Watson KD, Hyrich KL, Silman AJ (2007) Serious infection following anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: lessons from interpreting data from observational studies. Arthritis Rheum 56:2896–2904
Dosier CR, Erdman CP, Park JH, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD, Guldberg RE (2012) Resveratrol effect on osteogenic differentiation of rat and human adipose derived stem cells in a 3-D culture environment. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 11:112–122
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL, Karsenty G (1997) Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell 89:747–754
Edwards JR, Perrien DS, Fleming N, Nyman JS, Ono K, Connelly L, Moore MM, Lwin ST, Yull FE, Mundy GR et al (2013) Silent information regulator (Sir)T1 inhibits NF-kappaB signaling to maintain normal skeletal remodeling. J Bone Mineral Res 28:960–969
Erdman CP, Dosier CR, Olivares-Navarrete R, Baile C, Guldberg RE, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2012) Effects of resveratrol on enrichment of adipose-derived stem cells and their differentiation to osteoblasts in two-and three-dimensional cultures. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 6(Suppl 3):s34–s46
Estrov Z, Shishodia S, Faderl S, Harris D, Van Q, Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Aggarwal BB (2003) Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1beta-induced activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappaB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase arrest, and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 102:987–995
Ferreira SA, Motwani MS, Faull PA, Seymour AJ, Yu TTL, Enayati M, Taheem DK, Salzlechner C, Haghighi T, Kania EM et al (2018) Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate. Nat Commun 9:4049
Frith JE, Mills RJ, Hudson JE, Cooper-White JJ (2012) Tailored integrin-extracellular matrix interactions to direct human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells Dev 21:2442–2456
Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Jonas BL, Thieda P, Lohr KN (2006) The comparative efficacy and safety of biologics for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheumatol 33:2398–2408
Gilbert L, He X, Farmer P, Rubin J, Drissi H, van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Stein GS, Nanes MS (2002) Expression of the osteoblast differentiation factor RUNX2 (Cbfa1/AML3/Pebp2alphaA) is inhibited by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem 277:2695–2701
Gimble J, Guilak F (2003) Adipose-derived adult stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy 5:362–369
Gramaglia I, Mauri DN, Miner KT, Ware CF, Croft M (1999) Lymphotoxin alphabeta is expressed on recently activated naive and Th1-like CD4 cells but is down-regulated by IL-4 during Th2 differentiation. J Immunol 162:1333–1338
Gronthos S, Simmons PJ, Graves SE, Robey PG (2001) Integrin-mediated interactions between human bone marrow stromal precursor cells and the extracellular matrix. Bone 28:174–181
Gupta SC, Sundaram C, Reuter S, Aggarwal BB (2010) Inhibiting NF-kappaB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:775–787
Harth, M., and Nielson, W.R. (2019). Pain and affective distress in arthritis: relationship to immunity and inflammation. Expert review of clinical immunology
Hirose, T., Fukuma, Y., Takeshita, A., and Nishida, K. (2018). The role of lymphotoxin-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res ... [et al.] 67, 495–501
Hochberg MC, Lebwohl MG, Plevy SE, Hobbs KF, Yocum DE (2005) The benefit/risk profile of TNF-blocking agents: findings of a consensus panel. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34:819–836
Jue DM, Jeon KI, Jeong JY (1999) Nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway as a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci 14:231–238
Kamath MS, Ahmed SS, Dhanasekaran M, Santosh SW (2014) Polycaprolactone scaffold engineered for sustained release of resveratrol: therapeutic enhancement in bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine 9:183–195
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H (2011) Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7:33–42
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J, Kaarniranta K, Salminen A (2013) Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-kappaB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell Signal 25:1939–1948
Komori T (2008) Regulation of bone development and maintenance by Runx2. Front Biosci 13:898–903
Komori T (2010) Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. Cell Tissue Res 339:189–195
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M et al (1997) Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 89:755–764
Kotake S, Nanke Y (2014) Effect of TNFalpha on osteoblastogenesis from mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:1209–1213
Lei M, Liu SQ, Liu YL (2008) Resveratrol protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell derived chondrocytes cultured on chitosan-gelatin scaffolds from the inhibitory effect of interleukin-1beta. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:1350–1356
Leombruno JP, Einarson TR, Keystone EC (2009) The safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor treatments in rheumatoid arthritis: meta and exposure-adjusted pooled analyses of serious adverse events. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1136–1145
Lepage S, Robson N, Gilmore H, Davis O, Hooper A, St John S, Kamesan V, Gelis P, Carvajal D, Hurtig M et al. (2019) Beyond cartilage repair: the role of the osteochondral unit in joint health and disease. Tissue engineering. Part B, Reviews
Liu Y, Wang L, Kikuiri T, Akiyama K, Chen C, Xu X, Yang R, Chen W, Wang S, Shi S (2011) Mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T lymphocytes via IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. Nat Med 17:1594–1601
Liu C, Zhang H, Tang X, Feng R, Yao G, Chen W, Li W, Liang J, Feng X, Sun L (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells promote the osteogenesis in collagen-induced arthritic mice through the inhibition of TNF-alpha. Stem Cells Int 2018:4069032
Luo K, Gao X, Gao Y, Li Y, Deng M, Tan J, Gou J, Liu C, Dou C, Li Z et al (2019) Multiple integrin ligands provide a highly adhesive and osteoinductive surface that improves selective cell retention technology. Acta Biomater 85:106–116
Manna SK, Mukhopadhyay A, Aggarwal BB (2000) Resveratrol suppresses TNF-induced activation of nuclear transcription factors NF-kappa B, activator protein-1, and apoptosis: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. J Immunol 164:6509–6519
Matsuda Y, Minagawa T, Okui T, Yamazaki K (2018) Resveratrol suppresses the alveolar bone resorption induced by artificial trauma from occlusion in mice. Oral Dis 24:412–421
Mendes KL, Lelis DF, Santos SHS (2017) Nuclear sirtuins and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 38:98–105
Okay E, Simsek T, Subasi C, Gunes A, Duruksu G, Gurbuz Y, Gacar G, Karaoz E (2015) Cross effects of resveratrol and mesenchymal stem cells on liver regeneration and homing in partially hepatectomized rats. Stem Cell Rev 11:322–331
O'Rourke KP, O'Donoghue G, Adams C, Mulcahy H, Molloy C, Silke C, Molloy M, Shanahan F, O'Gara F (2008) High levels of Lymphotoxin-Beta (LT-Beta) gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovium: clinical and cytokine correlations. Rheumatol Int 28:979–986
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A, Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen BR et al (1997) Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell 89:765–771
Pfeilschifter J, Koditz R, Pfohl M, Schatz H (2002) Changes in proinflammatory cytokine activity after menopause. Endocr Rev 23:90–119
Pillarisetti S (2008) A review of Sirt1 and Sirt1 modulators in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov 3:156–164
Pinarli FA, Turan NN, Pinarli FG, Okur A, Sonmez D, Ulus T, Oguz A, Karadeniz C, Delibasi T (2013) Resveratrol and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are effective in the prevention and treatment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30:226–238
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Rajshankar D, Wang Y, McCulloch CA (2017) Osteogenesis requires FAK-dependent collagen synthesis by fibroblasts and osteoblasts. FASEB J 31:937–953
Ramiro S, Radner H, van der Heijde D, van Tubergen A, Buchbinder R, Aletaha D, Landewe RB (2011) Combination therapy for pain management in inflammatory arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, other spondyloarthritis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev:Cd008886
Ren Z, Wang L, Cui J, Huoc Z, Xue J, Cui H, Mao Q, Yang R (2013) Resveratrol inhibits NF-kB signaling through suppression of p65 and IkappaB kinase activities. Die Pharmazie 68:689–694
Rutledge KE, Cheng Q, Jabbarzadeh E (2016) Modulation of Inflammatory Response and Induction of Bone Formation Based on Combinatorial Effects of Resveratrol. J Nanomedicine Nanotechnol:7
Safaeinejad Z, Kazeminasab F, Kiani-Esfahani A, Ghaedi K, Nasr-Esfahani MH (2018) Multi-effects of resveratrol on stem cell characteristics: effective dose, time, cell culture conditions and cell type-specific responses of stem cells to resveratrol. Eur J Med Chem 155:651–657
Salliot C, Dougados M, Gossec L (2009) Risk of serious infections during rituximab, abatacept and anakinra treatments for rheumatoid arthritis: meta-analyses of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis 68:25–32
Schneeweiss S, Setoguchi S, Weinblatt ME, Katz JN, Avorn J, Sax PE, Levin R, Solomon DH (2007) Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy and the risk of serious bacterial infections in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:1754–1764
Shakibaei M, Csaki C, Nebrich S, Mobasheri A (2008) Resveratrol suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced inflammatory signaling and apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes: potential for use as a novel nutraceutical for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1426–1439
Shakibaei M, Harikumar KB, Aggarwal BB (2009) Resveratrol addiction: to die or not to die. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:115–128
Shakibaei M, Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A (2011) Resveratrol-mediated SIRT-1 interactions with p300 modulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) activation of NF-kappaB signaling and inhibit osteoclastogenesis in bone-derived cells. J Biol Chem 286:11492–11505
Shakibaei M, Shayan P, Busch F, Aldinger C, Buhrmann C, Lueders C, Mobasheri A (2012) Resveratrol mediated modulation of Sirt-1/Runx2 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: potential role of Runx2 deacetylation. PLoS One 7:e35712
Shui C, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL, Khosla S (2003) Changes in Runx2/Cbfa1 expression and activity during osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Mineral Res 18:213–221
Siebers MC, ter Brugge PJ, Walboomers XF, Jansen JA (2005) Integrins as linker proteins between osteoblasts and bone replacing materials. A critical review. Biomaterials 26:137–146
Thompson AE, Rieder SW, Pope JE (2011) Tumor necrosis factor therapy and the risk of serious infection and malignancy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 63:1479–1485
Tseng PC, Hou SM, Chen RJ, Peng HW, Hsieh CF, Kuo ML, Yen ML (2011) Resveratrol promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating RUNX2 gene expression via the SIRT1/FOXO3A axis. J Bone Mineral Res 26:2552–2563
Weitzmann MN (2017) Bone and the immune system. Toxicol Pathol 45:911–924
Weitzmann MN, Pacifici R (2006) Estrogen deficiency and bone loss: an inflammatory tale. J Clin Invest 116:1186–1194
Wellman AS, Metukuri MR, Kazgan N, Xu X, Xu Q, Ren NSX, Czopik A, Shanahan MT, Kang A, Chen W et al (2017) Intestinal epithelial sirtuin 1 regulates intestinal inflammation during aging in mice by altering the intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology 153:772–786
Westlake SL, Colebatch AN, Baird J, Curzen N, Kiely P, Quinn M, Choy E, Ostor AJ, Edwards CJ (2011) Tumour necrosis factor antagonists and the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Rheumatology 50:518–531
Wolfe F, Caplan L, Michaud K (2006) Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of hospitalization for pneumonia: associations with prednisone, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Rheum 54:628–634
Zainabadi K, Liu CJ, Caldwell ALM, Guarente L (2017a) SIRT1 is a positive regulator of in vivo bone mass and a therapeutic target for osteoporosis. PLoS One 12:e0185236
Zainabadi K, Liu CJ, Guarente L (2017b) SIRT1 is a positive regulator of the master osteoblast transcription factor, RUNX2. PLoS One 12:e0178520
Zhao B, Grimes SN, Li S, Hu X, Ivashkiv LB (2012) TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory bone resorption are inhibited by transcription factor RBP-J. J Exp Med 209:319–334
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH (2001) Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 7:211–228
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P, Hedrick MH (2002) Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4279–4295
Acknowledgments
We thank Sabine Miech and Dr. Andreas Eimannsberger for their excellent technical assistance and Prof. Dr. Dr. U. Matis for providing the canine adipose and bone tissue.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All specimens (adipose tissue and canine primary osteoblasts) were waste products that occur during surgery from implantation of artificial hip joints in dogs.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Constanze, B., Popper, B., Aggarwal, B.B. et al. Evidence that TNF-β suppresses osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and resveratrol reverses it through modulation of NF-κB, Sirt1 and Runx2. Cell Tissue Res 381, 83–98 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03188-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03188-8