Abstract
Heart disease is a deadly syndrome affecting millions worldwide. It reflects an unmet clinical need, and the disease mechanisms are poorly understood. Cardiac fibrosis is central to heart disease. The four-membered family of transmembrane proteoglycans, syndecan-1 to -4, is believed to regulate fibrosis. We review the current literature concerning syndecans in cardiac fibrosis. Syndecan expression is up-regulated in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli in various forms of heart disease with fibrosis. Mice lacking syndecan-1 and −4 show reduced activation of pro-fibrotic signaling and increased cardiac rupture upon infarction indicating an important role for these molecules. Whereas the short cytoplasmic tail of syndecans regulates signaling, their extracellular part, substituted with heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan chains, binds a plethora of extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules involved in fibrosis, e.g., collagens, growth factors, cytokines, and immune cell adhesion proteins. Full-length syndecans induce pro-fibrotic signaling, increasing the expression of collagens, myofibroblast differentiation factors, ECM enzymes, growth factors, and immune cell adhesion molecules, thereby also increasing cardiac stiffness and preventing cardiac rupture. Upon pro-inflammatory stimuli, syndecan ectodomains are enzymatically released from heart cells (syndecan shedding). Shed ectodomains affect the expression of ECM molecules, promoting ECM degradation and cardiac rupture upon myocardial infarction. Blood levels of shed syndecan-1 and −4 ectodomains are associated with hospitalization, mortality, and heart remodeling in patients with heart failure. Improved understanding of syndecans and their modifying enzymes in cardiac fibrosis might contribute to the development of compounds with therapeutic potential, and enzymatically shed syndecan ectodomains might constitute a future prognostic tool for heart diseases with fibrosis.

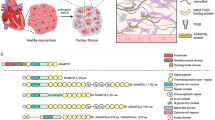
Graphical abstract summarizing the contents of the current review on syndecans in cardiac fibrosis. The heart is subjected to various forms of pathological stimuli, e.g., myocardial infarction, hypertension, valvular stenosis, infection, or an inherited genetic mutation, triggering responses in cells resident in the heart. Here, we focus on the responses of cardiac fibroblasts directing changes in the extracellular matrix resulting in cardiac fibrosis. A family of four transmembrane proteoglycans, syndecan-1 to -4, is expressed in the cell membrane of cardiac fibroblasts and is generally up-regulated in response to the above-mentioned pathological stimuli. Syndecans carry glycosaminoglycan chains on their extracellular domain, binding a plethora of molecules involved in fibrosis, e.g., growth factors, cytokines, immune cell adhesion proteins, and pathogens. Syndecans have a short cytoplasmic tail involved in pro-fibrotic signaling. The signaling and cellular processes governed by syndecans in the heart in response to pathological stimuli regulate important aspects of extracellular matrix remodeling and fibrosis and have mainly been studied in cardiac remodeling in response to cardiac infarction and pressure overload. In general, adequate timing and the quantity and quality of fibrosis are absolutely crucial for heart function and survival, determining cardiac stiffness, contractility, compliance, probability of rupture, dilation, and diastolic and systolic function. Syndecan-1 and −4 have mainly been studied in the heart and are discussed in this review (LV left ventricle).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaas VM, Haugaa KH, Strøm EH, Scott H, Dahl CP, Leren TP, Geiran OR, Endresen K, Edvardsen T, Aakhus S, Amlie JP (2013) Increased amount of interstitial fibrosis predicts ventricular arrhythmias, and is associated with reduced myocardial septal function in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Europace 15:1319–1327
Aramburu J, Garcia-Cózar F, Raghavan A, Okamura H, Rao A, Hogan PG (1998) Selective inhibition of NFAT activation by a peptide spanning the calcineurin targeting site of NFAT. Mol Cell 1:627–637
Barry SP, Townsend PA (2010) What causes a broken heart-molecular insights into heart failure. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 284:113–179
Bellin RM, Kubicek JD, Frigault MJ, Kamien AJ, Steward RLJ, Barnes HM, Digiacomo MB, Duncan LJ, Edgerly CK, Morse EM, Park CY, Fredberg JJ, Cheng CM, LeDuc PR (2009) Defining the role of syndecan-4 in mechanotransduction using surface-modification approaches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22102–22107
Bernfield M, Kokenyesi R, Kato M, Hinkes MT, Spring J, Gallo RL, Lose EJ (1992) Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulphate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:365–393
Bernfield M, Götte M, Park PW, Reizes O, Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J, Zako M (1999) Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem 68:729–777
Berry JM, Le V, Rotter D, Battiprolu PK, Grinsfelder B, Tannous P, Burchfield JS, Czubryt M, Backs J, Olson EN, Rothermel BA, Hill JA (2011) Reversibility of adverse, calcineurin-dependent cardiac remodeling. Circ Res 109:407–417
Bielecka-Dabrowa A, Haehling S von, Aronow WS, Ahmed MI, Rysz J, Banach M (2013) Heart failure biomarkers in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol 168:2404–2410
Bielecka-Dabrowa A, Gluba-Brzózka A, Michalska-Kasiczak M, Misztal M, Rysz J, Banach M (2015a) The multi-biomarker approach for heart failure in patients with hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 16:10715–10733
Bielecka-Dabrowa A, Michalska-Kasiczak M, Gluba A, Ahmed A, Gerdts E, Haehling S von, Rysz J, Banach M (2015b) Biomarkers and echocardiographic predictors of myocardial dysfunction in patients with hypertension. Sci Rep 5:8916
Bishop JR, Schuksz M, Esko JD (2007) Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 446:1030–1037
Braunwald E, Bristow MR (2000) Congestive heart failure: fifty years of progress. Circulation 102:IV14–IV23
Bui AL, Horwich TB, Fonarow GC (2011) Epidemiology and risk profile of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 8:30–41
Bujak M, Frangogiannis NG (2007) The role of TGF-beta signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc Res 74:184–195
Charalambous BM, Stephens RC, Feavers IM, Montgomery HE (2007) Role of bacterial endotoxin in chronic heart failure: the gut of the matter. Shock 28:15–23
Chen QQ, Zhang W, Chen XF, Bao YJ, Wang J, Zhu WZ (2012) Electrical field stimulation induces cardiac fibroblast proliferation through the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90:1611–1622
Clarke MS, Caldwell RW, Chiao H, Miyake K, McNeil PL (1995) Contraction-induced cell wounding and release of fibroblast growth factor in heart. Circ Res 76:927–934
Couchman JR (2010) Transmembrane signaling proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 26:89–114
Darby I, Skalli O, Gabbiani G (1990) Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab Invest 63:21–29
Davis J, Burr AR, Davis GF, Birnbaumer L, Molkentin JD (2012) A TRPC6-dependent pathway for myofibroblast transdifferentiation and wound healing in vivo. Dev Cell 23:705–715
Dobaczewski M, Chen W, Frangogiannis NG (2011) Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 51:600–606
Dovas A, Yoneda A, Couchman JR (2006) PKCbeta-dependent activation of RhoA by syndecan-4 during focal adhesion formation. J Cell Sci 119:2837–2846
Echtermeyer F, Harendza T, Hubrich S, Lorenz A, Herzog C, Mueller M, Schmitz M, Grund A, Larmann J, Stypmann J, Schieffer B, Lichtinghagen R, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Wollert KC, Heineke J, Theilmeier G (2011) Syndecan-4 signalling inhibits apoptosis and controls NFAT activity during myocardial damage and remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 92:123–131
Edwards IJ (2012) Proteoglycans in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 9:196–206
Engebretsen KV, Lunde IG, Strand ME, Waehre A, Sjaastad I, Marstein H, Skrbic B, Dahl CP, Askevold ET, Christensen G, Bjørnstad JL, Tønnessen T (2013) Lumican is increased in experimental and clinical heart failure, and its production by cardiac fibroblasts is induced by mechanical and pro-inflammatory stimuli. FEBS J 280:2382–2398
Filmus J, Capurro M, Rast J (2008) Glypicans. Genome Biol 9:224
Finsen AV, Woldbaek PR, Li J, Wu J, Lyberg T, Tønnessen T, Christensen G (2004) Increased syndecan expression following myocardial infarction indicates a role in cardiac remodeling. Physiol Genomics 16:301–308
Finsen AV, Lunde IG, Sjaastad I, Østli EK, Lyngra M, Jarstadmarken HO, Hasic A, Nygård S, Wilcox-Adelman SA, Goetinck PF, Lyberg T, Skrbic B, Florholmen G, Tønnessen T, Louch WE, Djurovic S, Carlson CR, Christensen G (2011) Syndecan-4 is essential for development of concentric myocardial hypertrophy via stretch-induced activation of the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. PLoS One 6:e28302
Frangogiannis NG (2010) Syndecan-1: a critical mediator in cardiac fibrosis. Hypertension 55:233–235
Goffin JM, Pittet P, Csucs G, Lussi JW, Meister JJ, Hinz B (2006) Focal adhesion size controls tension-dependent recruitment of alpha-smooth muscle actin to stress fibers. J Cell Biol 172:259–268
Gopal S, Søgaard P, Multhaupt HA, Pataki C, Okina E, Xian X, Pedersen ME, Stevens T, Griesbeck O, Park PW, Pocock R, Couchman JR (2015) Transmembrane proteoglycans control stretch-activated channels to set cytosolic calcium levels. J Cell Biol 210:1199–1211
Götte M (2003) Syndecans in inflammation. FASEB J 17:575–591
Gullestad L, Kjekshus J, Damås JK, Ueland T, Yndestad A, Aukrust P (2006) Agents targeting inflammation in heart failure. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:557–566
Hartmann S, Ridley AJ, Lutz S (2015) The function of Rho-associated kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol 6:276
Hartupee J, Mann DL (2016) Role of inflammatory cells in fibroblast activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 93:143–148. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.016
Herum KM, Lunde IG, Skrbic B, Florholmen G, Behmen D, Sjaastad I, Carlson CR, Gomez MF, Christensen G (2013) Syndecan-4 signaling via NFAT regulates extracellular matrix production and cardiac myofibroblast differentiation in response to mechanical stress. J Mol Cell Cardiol 54:73–81
Herum KM, Lunde IG, Skrbic B, Louch WE, Hasic A, Boye S, Unger A, Brorson SH, Sjaastad I, Tønnessen T, Linke WA, Gomez MF, Christensen G (2015) Syndecan-4 is a key determinant of collagen cross-linking and passive myocardial stiffness in the pressure-overloaded heart. Cardiovasc Res 106:217–226
Heymans S, Hirsch E, Anker SD, Aukrust P, Balligand JL, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Drexler H, Filippatos G, Felix SB, Gullestad L, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Janssens S, Latini R, Neubauer G, Paulus WJ, Pieske B, Ponikowski P, Schroen B, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C, Van Bilsen M, Zannad F, McMurray J, Shah AM (2009) Inflammation as a therapeutic target in heart failure? A scientific statement from the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 11:119–129
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007) The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 170:1807–1816
Ho CY, López B, Coelho-Filho OR, Lakdawala NK, Cirino AL, Jarolim P, Kwong R, González A, Colan SD, Seidman JG, Díez J, Seidman CE (2010) Myocardial fibrosis as an early manifestation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 363:552–563
Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D (1993) The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:6A–13A
Horowitz A, Simons M (1998) Phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tail of syndecan-4 regulates activation of protein kinase Calpha. J Biol Chem 273:25548–25551
Iozzo RV, Schaefer L (2010) Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel regulatory signaling mechanisms evoked by the small leucine-rich proteoglycans. FEBS J 277:3864–3875
Itoh N, Ohta H (2013) Pathophysiological roles of FGF signaling in the heart. Front Physiol 4:247
Kasner M, Westermann D, Lopez B, Gaub R, Escher F, Kühl U, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C (2011) Diastolic tissue Doppler indexes correlate with the degree of collagen expression and cross-linking in heart failure and normal ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:977–985
Kaye DM, Krum H (2007) Drug discovery for heart failure: a new era or the end of the pipeline? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:127–139
Kehat I, Molkentin JD (2010) Molecular pathways underlying cardiac remodeling during pathophysiological stimulation. Circulation 122:2727–2735
Keum E, Kim Y, Kim J, Kwon S, Lim Y, Han I, Oh ES (2004) Syndecan-4 regulates localization, activity and stability of protein kinase C-alpha. Biochem J 378:1007–1014
Kjellén L, Pettersson I, Höök M (1981) Cell-surface heparan sulfate: an intercalated membrane proteoglycan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:5371–5375
Kliment CR, Englert JM, Gochuico BR, Yu G, Kaminski N, Rosas I, Oury TD (2009) Oxidative stress alters syndecan-1 distribution in lungs with pulmonary fibrosis. J Biol Chem 284:3537–3545
Kojima T, Takagi A, Maeda M, Segawa T, Shimizu A, Yamamoto K, Matsushita T, Saito H (2001) Plasma levels of syndecan-4 (ryudocan) are elevated in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost 85:793–799
Koo BK, Jung YS, Shin J, Han I, Mortier E, Zimmermann P, Whiteford JR, Couchman JR, Oh ES, Lee W (2006) Structural basis of syndecan-4 phosphorylation as a molecular switch to regulate signaling. J Mol Biol 355:651–663
Lambaerts K, Wilcox-Adelman SA, Zimmermann P (2009) The signaling mechanisms of syndecan heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:662–669
Lei J, Xue SN, Wu W, Zhou SX, Zhang YL, Yuan GY, Wang JF (2012) Increased level of soluble syndecan-1 in serum correlates with myocardial expression in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem 359:177–182
Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Kupka MJ, Ho KK, Murabito JM, Vasan RS (2002) Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med 347:1397–1402
Li J, Brown LF, Laham RJ, Volk R, Simons M (1997) Macrophage-dependent regulation of syndecan gene expression. Circ Res 81:785–796
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, Gillespie C, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho PM, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott MM, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Roger VL, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Roger VL, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J, Subcommittee AHASCaSS (2010) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:e46–e215
López B, Querejeta R, González A, Larman M, Díez J (2012) Collagen cross-linking but not collagen amount associates with elevated filling pressures in hypertensive patients with stage C heart failure: potential role of lysyl oxidase. Hypertension 60:677–683
Lund O, Emmertsen K, Dørup I, Jensen FT, Flø C (2003) Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy during 10 years after valve replacement for aortic stenosis is related to the preoperative risk profile. Eur Heart J 24:1437–1446
Mack CP, Somlyo AV, Hautmann M, Somlyo AP, Owens GK (2001) Smooth muscle differentiation marker gene expression is regulated by RhoA-mediated actin polymerization. J Biol Chem 276:341–347
Mann DL, Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO (2014) Braunwald’s heart disease: a textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 10th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia
Manon-Jensen T, Itoh Y, Couchman JR (2010) Proteoglycans in health and disease: the multiple roles of syndecan shedding. FEBS J 277:3876–3889
Matsui Y, Ikesue M, Danzaki K, Morimoto J, Sato M, Tanaka S, Kojima T, Tsutsui H, Uede T (2011) Syndecan-4 prevents cardiac rupture and dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circ Res 108:1328–1339
McCullough PA, Philbin EF, Spertus JA, Kaatz S, Sandberg KR, Weaver WD, Study RUACHFR (2002) Confirmation of a heart failure epidemic: findings from the Resource Utilization Among Congestive Heart Failure (REACH) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:60–69
Molkentin JD (2004) Calcineurin-NFAT signaling regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response in coordination with the MAPKs. Cardiovasc Res 63:467–475
Molkentin JD (2013) Parsing good versus bad signaling pathways in the heart: role of calcineurin-nuclear factor of activated T-cells. Circ Res 113:16–19
Mudd JO, Kass DA (2008) Tackling heart failure in the twenty-first century. Nature 451:919–928
O’Connell JB, Bristow MR (1994) Economic impact of heart failure in the United States; time for a different approach. J Heart Lung Transpl 13:S107–S112
Oh ES, Woods A, Couchman JR (1997) Syndecan-4 proteoglycan regulates the distribution and activity of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 272:8133–8136
Parish CR (2006) The role of heparan sulphate in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 6:633–643
Petrov VV, Fagard RH, Lijnen PJ (2002) Stimulation of collagen production by transforming growth factor-beta1 during differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. Hypertension 39:258–263
Porter KE, Turner NA (2009) Cardiac fibroblasts: at the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacol Ther 123:255–278
Ramos G, Hofmann U, Frantz S (2016) Myocardial fibrosis seen through the lenses of T-cell biology. J Mol Cell Cardiol 92:41–45
Rapraeger AC, Krufka A, Olwin BB (1991) Requirement of heparan sulfate for bFGF-mediated fibroblast growth and myoblast differentiation. Science 252:1705–1708
Rienks M, Papageorgiou AP, Frangogiannis NG, Heymans S (2014) Myocardial extracellular matrix: an ever-changing and diverse entity. Circ Res 114:872–888
Samarel AM (2013) Syndecan-4: a component of the mechanosensory apparatus of cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 56:19–21
Schellings MW, Vanhoutte D, Almen GC van, Swinnen M, Leenders JJ, Kubben N, Leeuwen RE van, Hofstra L, Heymans S, Pinto YM (2010) Syndecan-1 amplifies angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis. Hypertension 55:249–256
Seidman CE, Seidman JG (2011) Identifying sarcomere gene mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a personal history. Circ Res 108:743–750
Small EM, Thatcher JE, Sutherland LB, Kinoshita H, Gerard RD, Richardson JA, Dimaio JM, Sadek H, Kuwahara K, Olson EN (2010) Myocardin-related transcription factor-a controls myofibroblast activation and fibrosis in response to myocardial infarction. Circ Res 107:294–304
Strand ME, Herum KM, Rana ZA, Skrbic B, Askevold ET, Dahl CP, Vistnes M, Hasic A, Kvaløy H, Sjaastad I, Carlson CR, Tønnessen T, Gullestad L, Christensen G, Lunde IG (2013) Innate immune signaling induces expression and shedding of the heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan-4 in cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes, affecting inflammation in the pressure-overloaded heart. FEBS J 280:2228–2247
Strand ME, Aronsen JM, Braathen B, Sjaastad I, Kvaløy H, Tønnessen T, Christensen G, Lunde IG (2015) Shedding of syndecan-4 promotes immune cell recruitment and mitigates cardiac dysfunction after lipopolysaccharide challenge in mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol 88:133–144
Strunz CM, Matsuda M, Salemi VM, Nogueira A, Mansur AP, Cestari IN, Marquezini MV (2011) Changes in cardiac heparan sulfate proteoglycan expression and streptozotocin-induced diastolic dysfunction in rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol 10:35
Takahashi R, Negishi K, Watanabe A, Arai M, Naganuma F, Ohyama Y, Kurabayash M (2011) Serum syndecan-4 is a novel biomarker for patients with chronic heart failure. J Cardiol 57:325–332
Tromp J, Pol A van der, Klip IT, Boer RA de, Jaarsma T, Gilst WH van, Voors AA, Veldhuisen DJ van, Meer P van der (2014) The fibrosis marker syndecan-1 and outcome in heart failure patients with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail 7:457–462
Vanhoutte D, Schellings MW, Götte M, Swinnen M, Herias V, Wild MK, Vestweber D, Chorianopoulos E, Cortés V, Rigotti A, Stepp MA, Van de Werf F, Carmeliet P, Pinto YM, Heymans S (2007) Increased expression of syndecan-1 protects against cardiac dilatation and dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circulation 115:475–482
Velasquez LS, Sutherland LB, Liu Z, Grinnell F, Kamm KE, Schneider JW, Olson EN, Small EM (2013) Activation of MRTF-A-dependent gene expression with a small molecule promotes myofibroblast differentiation and wound healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:16850–16855
Vistnes M, Aronsen JM, Lunde IG, Sjaastad I, Carlson CR, Christensen G (2014) Pentosan polysulfate decreases myocardial expression of the extracellular matrix enzyme ADAMTS4 and improves cardiac function in vivo in rats subjected to pressure overload by aortic banding. PLoS One 9:e89621
Vizzardi E, Regazzoni V, Caretta G, Gavazzoni M, Sciatti E, Bonadei I, Trichaki E, Raddino R, Metra M (2014) Mineralcorticoid receptor antagonist in heart failure. Past, present and future perspectives. IJC Heart Vessels 3:6–14
Wang L, Fuster M, Sriramarao P, Esko JD (2005) Endothelial heparan sulfate deficiency impairs L-selectin- and chemokine-mediated neutrophil trafficking during inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol 6:902–910
Wang J, Wang Y, Zhang W, Zhao X, Chen X, Xiao W, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhu WZ (2016) Phenylephrine promotes cardiac fibroblast proliferation through calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Front Biosci 21:502–513
Wei L (2011) Immunological aspect of cardiac remodeling: T lymphocyte subsets in inflammation-mediated cardiac fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol 90:74–78
Whiteford JR, Ko S, Lee W, Couchman JR (2008) Structural and cell adhesion properties of zebrafish syndecan-4 are shared with higher vertebrates. J Biol Chem 283:29322–29330
Woods A, Longley RL, Tumova S, Couchman JR (2000) Syndecan-4 binding to the high affinity heparin-binding domain of fibronectin drives focal adhesion formation in fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 374:66–72
Xie J, Wang J, Li R, Dai Q, Yong Y, Zong B, Xu Y, Li E, Ferro A, Xu B (2012) Syndecan-4 over-expression preserves cardiac function in a rat model of myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 53:250–258
Yayon A, Klagsbrun M, Esko JD, Leder P, Ornitz DM (1991) Cell surface, heparin-like molecules are required for binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its high affinity receptor. Cell 64:841–848
Yndestad A, Damås JK, Øie E, Ueland T, Gullestad L, Aukrust P (2007) Role of inflammation in the progression of heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep 9:236–241
Yu Q, Vazquez R, Zabadi S, Watson RR, Larson DF (2010) T-lymphocytes mediate left ventricular fibrillar collagen cross-linking and diastolic dysfunction in mice. Matrix Biol 29:511–518
Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S (2001) Global burden of cardiovascular diseases. Part I: general considerations, the epidemiologic transition, risk factors, and impact of urbanization. Circulation 104:2746–2753
Zhang Y, Li J, Partovian C, Sellke FW, Simons M (2003) Syndecan-4 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor 2 signaling in vivo. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H2078–H2082
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Mari E. Strand for technical assistance with the graphical abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This work was funded by the Research Council of Norway, Stiftelsen Kristian Gerhard Jebsen, Anders Jahre’s Fund for the Promotion of Science, the South-Eastern Regional Health Authority, Olav Raagholt and Gerd Meidel Raagholt’s Fund for Science, Norway, and the Simon Fougner Hartmanns Family Fund, Denmark.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lunde, I.G., Herum, K.M., Carlson, C.C. et al. Syndecans in heart fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res 365, 539–552 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2454-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2454-2