Abstract
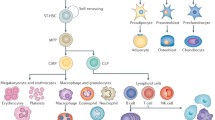
The bone marrow (BM) niche is a specific physiological environment for hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Several signaling pathways (including Wnt/β-catenin) regulate various aspects of stem cell growth, function and death in the BM niche. In addition, the canonical Wnt pathway is crucial for directing self-renewal and differentiation as important mechanisms in many types of stem cells. We review the role of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in the BM niche and its importance in stem cells. Relevant literature was identified by a PubMed search (1997–2014) of English-language literature by using the following keywords: BM niche, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, osteoblast, osteoclast and bone disease. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates the stability of the β-catenin proto-oncogene. The stabilized β-catenin then translocates to the nucleus, forming a β-catenin-TCF/LEF complex regulating the transcription of specific target genes. Stem cells require β-catenin to mediate their response to Wnt signaling for maintenance and transition from the pluripotent state during embryogenesis. In adult stem cells, Wnt signaling functions at various hierarchical levels to contribute to the specification of the diverse tissues. Aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling and its downstream transcriptional regulators are observed in several malignant stem cells and human cancers. Because Wnt signaling can maintain stem cells and cancer cells, the ability to modulate the Wnt pathway either positively or negatively may be of therapeutic relevance. The controlled activation of Wnt signaling might allow us to enhance stem and progenitor cell activity when regeneration is needed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai M, Holmen SL, Van Hul W, Williams BO, Warman ML (2005) Reduced affinity to and inhibition by DKK1 form a common mechanism by which high bone mass-associated missense mutations in LRP5 affect canonical Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol 25:4946–4955
Albers J, Keller J, Baranowsky A, Beil FT, Catala-Lehnen P, Schulze J, Amling M, Schinke T (2013) Canonical Wnt signaling inhibits osteoclastogenesis independent of osteoprotegerin. J Cell Biol 200:537–549
Anastas JN, Moon RT (2013) WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 13:11–26
Arioka M, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Sasaki M, Yoshihara T, Morimoto S, Hirata M, Mori Y, Sasaguri T (2014) Acceleration of bone regeneration by local application of lithium: Wnt signal-mediated osteoblastogenesis and Wnt signal-independent suppression of osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol 90:397–405
Ashihara E, Kawata E, Nakagawa Y, Shimazaski C, Kuroda J, Taniguchi K, Uchiyama H, Tanaka R, Yokota A, Takeuchi M, Kamitsuji Y, Inaba T, Taniwaki M, Kimura S, Maekawa T (2009) Beta-catenin small interfering RNA successfully suppressed progression of multiple myeloma in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 15:2731–2738
Austin TW, Solar GP, Ziegler FC, Liem L, Matthews W (1997) A role for the Wnt gene family in hematopoiesis: expansion of multilineage progenitor cells. Blood 89:3624–3635
Baek SH, Kioussi C, Briata P, Wang D, Nguyen HD, Ohgi KA, Glass CK, Wynshaw-Boris A, Rose DW, Rosenfeld MG (2003) Regulated subset of G1 growth-control genes in response to derepression by the Wnt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:3245–3250
Baksh D, Tuan RS (2007) Canonical and non-canonical Wnts differentially affect the development potential of primary isolate of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol 212:817–826
Barker N, Clevers H (2006) Mining the Wnt pathway for cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:997–1014
Baron R, Kneissel M (2013) WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med 19:179–192
Baron R, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S (2006) Wnt signaling: a key regulator of bone mass. Curr Top Dev Biol 76:103–127
Bellon M, Ko NL, Lee MJ, Yao Y, Waldmann TA, Trepel JB, Nicot C (2013) Adult T-cell leukemia cells overexpress Wnt5a and promote osteoclast differentiation. Blood 121:5045–5054
Benhaj K, Akcali KC, Ozturk M (2006) Redundant expression of canonical Wnt ligands in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 15:701–707
Bitler BG, Nicodemus JP, Li H, Cai Q, Wu H, Hua X, Li T, Birrer MJ, Godwin AK, Cairns P, Zhang R (2011) Wnt5a suppresses epithelial ovarian cancer by promoting cellular senescence. Cancer Res 71:6184–6194
Blank U, Karlsson G, Karlsson S (2008) Signaling pathways governing stem-cell fate. Blood 111:492–503
Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ, Tuan RS (2004) Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem 93:1210–1230
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423:337–342
Calvi L, Adams G, Weibrecht K, Weber J, Olson D, Knight M, Martin R, Schipani E, Divieti P, Bringhurst F (2003) Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature 425:841–846
Camilli TC, Weeraratna AT (2010) Striking the target in Wnt-y conditions: intervening in Wnt signaling during cancer progression. Biochem Pharmacol 80:702–711
Campisi J (2005a) Aging, tumor suppression and cancer: high wire-act! Mech Ageing Dev 126:51–58
Campisi J (2005b) Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120:513–522
Campisi J, Fagagna FDA di (2007) Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:729–740
Campisi J, Andersen JK, Kapahi P, Melov S (2011) Cellular senescence: a link between cancer and age-related degenerative disease? Semin Cancer Biol 21:354–359
Canepa ET, Scassa ME, Ceruti JM, Marazita MC, Carcagno AL, Sirkin PF, Ogara MF (2007) INK4 proteins, a family of mammalian CDK inhibitors with novel biological functions. IUBMB Life 59:419–426
Chim CS, Pang R, Fung TK, Choi CL, Liang R (2007) Epigenetic dysregulation of Wnt signaling pathway in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 21:2527–2536
Cho HH, Kim YJ, Kim SJ, Kim JH, Bae YC, Ba B, Jung JS (2006) Endogenous Wnt signaling promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation in human adipose derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng 12:111–121
Chotinantakul K, Leeanansaksiri W (2012) Hematopoietic stem cell development, niches, and signaling pathways. Bone Marrow Res 2012:270425
Christodoulides C, Scarda A, Granzotto M, Milan G, Dalla Nora E, Keogh J, De Pergola G, Stirling H, Pannacciulli N, Sethi JK, Federspil G, Vidal-Puig A, Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S, Vettor R (2006) WNT10B mutations in human obesity. Diabetologia 49:678–684
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127:469–480
Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149:1192–1205
Clines GA, Guise TA (2008) Molecular mechanisms and treatment of bone metastasis. Expert Rev Mol Med 10:e7
Clines GA, Mohammad KS, Bao Y, Stephens OW, Suva LJ, Shaughnessy JD Jr, Fox JW, Chirgwin JM, Guise TA (2007) Dickkopf homolog 1 mediates endothelin-1-stimulated new bone formation. Mol Endocrinol 21:486–498
Conidi A, Berghe V van den, Huylebroeck D (2013) Aptamers and their potential to selectively target aspects of EGF, Wnt/beta-Catenin and TGFbeta-Smad family signaling. Int J Mol Sci 14:6690–6719
Davidson KC, Adams AM, Goodson JM, McDonald CE, Potter JC, Berndt JD, Biechele TL, Taylor RJ, Moon RT (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes differentiation, not self-renewal, of human embryonic stem cells and is repressed by Oct4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:4485–4490
Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y (2005) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell 8:739–750
De Boer J, Wang HJ, Van Blitterswijk C (2004) Effects of Wnt signaling on proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng 10:393–401
DeCarolis NA, Wharton KA Jr, Eisch AJ (2008) Which way does the Wnt blow? Exploring the duality of canonical Wnt signaling on cellular aging. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol 30:102–106
Dreesen O, Brivanlou AH (2007) Signaling pathways in cancer and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev 3:7–17
Dufourcq P, Descamps B, Tojais NF, Leroux L, Oses P, Daret D, Moreau C, Lamaziere JM, Couffinhal T, Duplaa C (2008) Secreted frizzled-related protein-1 enhances mesenchymal stem cell function in angiogenesis and contributes to neovessel maturation. Stem Cells 26:2991–3001
Edwards CM, Zhuang J, Mundy GR (2008) The pathogenesis of the bone disease of multiple myeloma. Bone 42:1007–1013
Ellies DL, Viviano B, McCarthy J, Rey JP, Itasaki N, Saunders S, Krumlauf R (2006) Bone density ligand, Sclerostin, directly interacts with LRP5 but not LRP5G171V to modulate Wnt activity. J Bone Miner Res 21:1738–1749
Endo-Munoz L, Evdokiou A, Saunders NA (2012) The role of osteoclasts and tumour-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1826:434–442
Fehrer C, Lepperdinger G (2005) Mesenchymal stem cell aging. Exp Gerontol 40:926–930
Feng J, Iwama A, Satake M, Kohu K (2009) MicroRNA-27 enhances differentiation of myeloblasts into granulocytes by post-transcriptionally downregulating Runx1. Br J Haematol 145:412–423
Fodde R, Brabletz T (2007) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:150–158
Frattini A, Vezzoni P, Villa A (2006) The genetics of dominant osteopetrosis. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech 2:503–509
Frisch BJ, Porter RL, Calvi LM (2008) Hematopoietic niche and bone meet. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 2:211–217
Galli C, Piemontese M, Lumetti S, Manfredi E, Macaluso GM, Passeri G (2013) GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:921–927
Gerdes JM, Davis EE, Katsanis N (2009) The vertebrate primary cilium in development, homeostasis, and disease. Cell 137:32–45
Glass DA 2nd, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G (2005) Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell 8:751–764
Goessling W, North TE, Loewer S, Lord AM, Lee S, Stoick-Cooper CL, Weidinger G, Puder M, Daley GQ, Moon RT, Zon LI (2009) Genetic interaction of PGE2 and Wnt signaling regulates developmental specification of stem cells and regeneration. Cell 136:1136–1147
Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, Zacharin M, Oexle K, Marcelino J, Suwairi W, Heeger S, Sabatakos G, Apte S, Adkins WN, Allgrove J, Arslan-Kirchner M, Batch JA, Beighton P, Black GC, Boles RG, Boon LM, Borrone C, Brunner HG, Carle GF, Dallapiccola B, De Paepe A, Floege B, Halfhide ML, Hall B, Hennekam RC, Hirose T, Jans A, Juppner H, Kim CA, Keppler-Noreuil K, Kohlschuetter A, LaCombe D, Lambert M, Lemyre E, Letteboer T, Peltonen L, Ramesar RS, Romanengo M, Somer H, Steichen-Gersdorf E, Steinmann B, Sullivan B, Superti-Furga A, Swoboda W, Boogaard MJ van den, Van Hul W, Vikkula M, Votruba M, Zabel B, Garcia T, Baron R, Olsen BR, Warman ML (2001) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107:513–523
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H, Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Magnusson KP, Walters GB, Palsdottir E, Jonsdottir T, Gudmundsdottir T, Gylfason A, Saemundsdottir J, Wilensky RL, Reilly MP, Rader DJ, Bagger Y, Christiansen C, Gudnason V, Sigurdsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Gulcher JR, Kong A, Stefansson K (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 38:320–323
Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Reyes E, Smolarz AJ, Munoz J, Spees JL, Prockop DJ (2005) How Wnt signaling affects bone repair by mesenchymal stem cells from the bone marrow. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1049:97–106
Gu Z, Tan W, Feng G, Meng Y, Shen B, Liu H, Cheng C (2014) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates the senescence of bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients through the p53/p21 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 387:27–37
Hall CL, Keller ET (2006) The role of Wnts in bone metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:551–558
Henriksen K, Gram J, Hoegh-Andersen P, Jemtland R, Ueland T, Dziegiel MH, Schaller S, Bollerslev J, Karsdal MA (2005) Osteoclasts from patients with autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type I caused by a T253I mutation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 are normal in vitro, but have decreased resorption capacity in vivo. Am J Pathol 167:1341–1348
Herbst A, Kolligs FT (2007) Wnt signaling as a therapeutic target for cancer. Methods Mol Biol 361:63–91
Hiyama A, Sakai D, Risbud MV, Tanaka M, Arai F, Abe K, Mochida J (2010) Enhancement of intervertebral disc cell senescence by WNT/beta-catenin signaling-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum 62:3036–3047
Hoffman MD, Benoit DS (2013) Agonism of Wnt-beta-catenin signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) expansion. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, doi 10.1002/term.1736
Hu H, Hilton MJ, Tu X, Yu K, Ornitz DM, Long F (2005) Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development. Development 132:49–60
Iwasaki H, Suda T (2009) Cancer stem cells and their niche. Cancer Sci 100:1166–1172
Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, Muijtjens M, Jones C, Zehnder JL, Gotlib J, Li K, Manz MG, Keating A, Sawyers CL, Weissman IL (2004) Granulocyte-macrophage progenitors as candidate leukemic stem cells in blast-crisis CML. N Engl J Med 351:657–667
Jang HD, Shin JH, Park DR, Hong JH, Yoon K, Ko R, Ko CY, Kim HS, Jeong D, Kim N, Lee SY (2011) Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is required for osteoclast differentiation. J Biol Chem 286:39043–39050
Jin L, Hope KJ, Zhai Q, Smadja-Joffe F, Dick JE (2006) Targeting of CD44 eradicates human acute myeloid leukemic stem cells. Nat Med 12:1167–1174
Johnson ML, Harnish K, Nusse R, Van Hul W (2004) LRP5 and Wnt signaling: a union made for bone. J Bone Miner Res 19:1749–1757
Jost E, Schmid J, Wilop S, Schubert C, Suzuki H, Herman JG, Osieka R, Galm O (2008) Epigenetic inactivation of secreted Frizzled-related proteins in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 142:745–753
Ju Z, Choudhury AR, Rudolph KL (2007) A dual role of p21 in stem cell aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1100:333–344
Kaarbo M, Klokk TI, Saatcioglu F (2007) Androgen signaling and its interactions with other signaling pathways in prostate cancer. Bioessays 29:1227–1238
Kanazawa A, Tsukada S, Sekine A, Tsunoda T, Takahashi A, Kashiwagi A, Tanaka Y, Babazono T, Matsuda M, Kaku K, Iwamoto Y, Kawamori R, Kikkawa R, Nakamura Y, Maeda S (2004) Association of the gene encoding wingless-type mammary tumor virus integration-site family member 5B (WNT5B) with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hum Genet 75:832–843
Kapinas K, Kessler C, Ricks T, Gronowicz G, Delany AM (2010) miR-29 modulates Wnt signaling in human osteoblasts through a positive feedback loop. J Biol Chem 285:25221–25231
Katagiri T, Takahashi N (2002) Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Oral Dis 8:147–159
Kim JA, Kang YJ, Park G, Kim M, Park YO, Kim H, Leem SH, Chu IS, Lee JS, Jho EH, Oh IH (2009) Identification of a stroma-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signal promoting self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells in the stem cell niche. Stem Cells 27:1318–1329
Kim JH, Liu X, Wang J, Chen X, Zhang H, Kim SH, Cui J, Li R, Zhang W, Kong Y, Zhang J, Shui W, Lamplot J, Rogers MR, Zhao C, Wang N, Rajan P, Tomal J, Statz J, Wu N, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC (2013) Wnt signaling in bone formation and its therapeutic potential for bone diseases. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 5:13–31
Kobayashi Y, Maeda K, Uehara S, Yamashita T, Takahashi N (2011) Regulatory mechanism of osteoclastogenesis by Wnt signaling. Inflamm Regen 31:413–419
Konopleva MY, Jordan CT (2011) Leukemia stem cells and microenvironment: biology and therapeutic targeting. J Clin Oncol 29:591–599
Kosar M, Bartkova J, Hubackova S, Hodny Z, Lukas J, Bartek J (2011) Senescence-associated heterochromatin foci are dispensable for cellular senescence, occur in a cell type- and insult-dependent manner and follow expression of p16(ink4a). Cell Cycle 10:457–468
Kramer I, Halleux C, Keller H, Pegurri M, Gooi JH, Weber PB, Feng JQ, Bonewald LF, Kneissel M (2010) Osteocyte Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for normal bone homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol 30:3071–3085
Larue L, Luciani F, Kumasaka M, Champeval D, Demirkan N, Bonaventure J, Delmas V (2009) Bypassing melanocyte senescence by beta-catenin: a novel way to promote melanoma. Pathol Biol 57:543–547
Lee E, Salic A, Kruger R, Heinrich R, Kirschner MW (2003) The roles of APC and Axin derived from experimental and theoretical analysis of the Wnt pathway. PLoS Biol 1:E10
Li G, Xu J, Li Z (2012) Receptor for advanced glycation end products inhibits proliferation in osteoblast through suppression of Wnt, PI3K and ERK signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423:684–689
Li X, Liu P, Liu W, Maye P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Hurley M, Guo C, Boskey A, Sun L, Harris SE, Rowe DW, Ke HZ, Wu D (2005) Dkk2 has a role in terminal osteoblast differentiation and mineralized matrix formation. Nat Genet 37:945–952
Lien WH, Fuchs E (2014) Wnt some lose some: transcriptional governance of stem cells by Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Genes Dev 28:1517–1532
Ling L, Nurcombe V, Cool SM (2009) Wnt signaling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene 433:1–7
Liu N, Shi S, Deng M, Tang L, Zhang G, Liu N, Ding B, Liu W, Liu Y, Shi H, Liu L, Jin Y (2011) High levels of beta-catenin signaling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in inflammatory microenvironments through inhibition of the noncanonical Wnt pathway. J Bone Miner Res 26:2082–2095
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Luis TC, Ichii M, Brugman MH, Kincade P, Staal FJ (2012) Wnt signaling strength regulates normal hematopoiesis and its deregulation is involved in leukemia development. Leukemia 26:414–421
Luu HH, Zhang R, Haydon RC, Rayburn E, Kang Q, Si W, Park JK, Wang H, Peng Y, Jiang W (2004) Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway as novel cancer drug targets. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4:653–671
Ma L, Wang HY (2007) Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 regulates the Wnt/cyclic GMP/Ca2+ non-canonical pathway. J Biol Chem 282:28980–28990
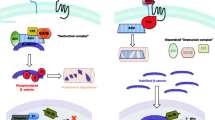
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17:9–26
Manolagas SC, Almeida M (2007) Gone with the Wnts: beta-catenin, T-cell factor, forkhead box O, and oxidative stress in age-dependent diseases of bone, lipid, and glucose metabolism. Mol Endocrinol 21:2605–2614
Mikami I, You L, He B, Xu Z, Batra S, Lee AY, Mazieres J, Reguart N, Uematsu K, Koizumi K, Jablons DM (2005) Efficacy of Wnt-1 monoclonal antibody in sarcoma cells. BMC Cancer 5:53
Mikesch JH, Steffen B, Berdel WE, Serve H, Muller-Tidow C (2007) The emerging role of Wnt signaling in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 21:1638–1647
Milat F, Ng KW (2009) Is Wnt signalling the final common pathway leading to bone formation? Mol Cell Endocrinol 310:52–62
Miller JR, Hocking AM, Brown JD, Moon RT (1999) Mechanism and function of signal transduction by the Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt/Ca2+ pathways. Oncogene 18:7860–7872
Monroe DG, McGee-Lawrence ME, Oursler MJ, Westendorf JJ (2012) Update on Wnt signaling in bone cell biology and bone disease. Gene 492:1–18
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A (2004) WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 5:691–701
Moore KA, Lemischka IR (2006) Stem cells and their niches. Science 311:1880–1885
Nagasawa T (2006) Microenvironmental niches in the bone marrow required for B-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol 6:107–116
Neth P, Ries C, Karow M, Egea V, Ilmer M, Jochum M (2007) The Wnt signal transduction pathway in stem cells and cancer cells: influence on cellular invasion. Stem Cell Rev 3:18–29
Oh IH (2010) Microenvironmental targeting of Wnt/beta-catenin signals for hematopoietic stem cell regulation. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:1315–1329
Pardal R, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ (2003) Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:895–902
Park I-K, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2004) Bmi1, stem cells, and senescence regulation. J Clin Invest 113:175
Pederson L, Ruan M, Westendorf JJ, Khosla S, Oursler MJ (2008) Regulation of bone formation by osteoclasts involves Wnt/BMP signaling and the chemokine sphingosine-1-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:20764–20769
Qiang YW, Shaughnessy JD Jr, Yaccoby S (2008) Wnt3a signaling within bone inhibits multiple myeloma bone disease and tumor growth. Blood 112:374–382
Qiang YW, Chen Y, Brown N, Hu B, Epstein J, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD Jr (2010) Characterization of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in osteoclasts in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 148:726–738
Rahim F, Hajizamani S, Mortaz E, Ahmadzadeh A, Shahjahani M, Shahrabi S, Saki N (2014) Molecular regulation of bone marrow metastasis in prostate and breast cancer. Bone Marrow Res 2014:405920
Rattis FM, Voermans C, Reya T (2004) Wnt signaling in the stem cell niche. Curr Opin Hematol 11:88–94
Rawadi G, Vayssiere B, Dunn F, Baron R, Roman-Roman S (2003) BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner Res 18:1842–1853
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434:843–850
Rich JN (2007) Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res 67:8980–8984
Rizo A, Vellenga E, de Haan G, Schuringa JJ (2006) Signaling pathways in self-renewing hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells: do all stem cells need a niche? Hum Mol Genet 15:R210–R219
Rodier F, Campisi J (2011) Four faces of cellular senescence. J Cell Biol 192:547–556
Roodman GD (2004) Mechanisms of bone metastasis. N Engl J Med 350:1655–1664
Rosenbluh J, Wang X, Hahn WC (2014) Genomic insights into WNT/beta-catenin signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:103–109
Rybchyn MS, Slater M, Conigrave AD, Mason RS (2011) An Akt-dependent increase in canonical Wnt signaling and a decrease in sclerostin protein levels are involved in strontium ranelate-induced osteogenic effects in human osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 286:23771–23779
Saki N, Abroun S, Hagh MF, Asgharei F (2011) Neoplastic bone marrow niche: hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells. Cell J 13:131
Salazar VS, Zarkadis N, Huang L, Watkins M, Kading J, Bonar S, Norris J, Mbalaviele G, Civitelli R (2013) Postnatal ablation of osteoblast Smad4 enhances proliferative responses to canonical Wnt signaling through interactions with beta-catenin. J Cell Sci 126:5598–5609
Sanaa E, Jérôme L, Annelise B, Ali T (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells: pivotal players in hematopoietic stem cell microenvironment. J Stem Cell Res Ther 4:2
Schaniel C, Sirabella D, Qiu J, Niu X, Lemischka IR, Moore KA (2011) Wnt-inhibitory factor 1 dysregulation of the bone marrow niche exhausts hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 118:2420–2429
Schuettpelz LG, Link DC (2011) Niche competition and cancer metastasis to bone. J Clin Invest 121:1253–1255
Sharma M, Jamieson C, Johnson M, Molloy MP, Henderson BR (2012) Specific armadillo repeat sequences facilitate beta-catenin nuclear transport in live cells via direct binding to nucleoporins Nup62, Nup153, and RanBP2/Nup358. J Biol Chem 287:819–831
Shim JH, Greenblatt MB, Zou W, Huang Z, Wein MN, Brady N, Hu D, Charron J, Brodkin HR, Petsko GA, Zaller D, Zhai B, Gygi S, Glimcher LH, Jones DC (2013) Schnurri-3 regulates ERK downstream of WNT signaling in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest 123:4010–4022
Sims NA, Vrahnas C (2014) Regulation of cortical and trabecular bone mass by communication between osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 561:22–28
Singh M, Piekorz RP (2013) Senescence-associated lysosomal alpha-L-fucosidase (SA-alpha-Fuc): a sensitive and more robust biomarker for cellular senescence beyond SA-beta-Gal. Cell Cycle 12:1996
Suda T, Arai F (2008) Wnt signaling in the niche. Cell 132:729–730
Tian E, Zhan F, Walker R, Rasmussen E, Ma Y, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD Jr (2003) The role of the Wnt-signaling antagonist DKK1 in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 349:2483–2494
Toledo EM, Colombres M, Inestrosa NC (2008) Wnt signaling in neuroprotection and stem cell differentiation. Prog Neurobiol 86:281–296
Tothova Z, Kollipara R, Huntly BJ, Lee BH, Castrillon DH, Cullen DE, McDowell EP, Lazo-Kallanian S, Williams IR, Sears C, Armstrong SA, Passegue E, DePinho RA, Gilliland DG (2007) FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell 128:325–339
Valencia A, Roman-Gomez J, Cervera J, Such E, Barragan E, Bolufer P, Moscardo F, Sanz GF, Sanz MA (2009) Wnt signaling pathway is epigenetically regulated by methylation of Wnt antagonists in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 23:1658–1666
Verkaar F, Zaman GJ (2011) New avenues to target Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Drug Discov Today 16:35–41
Vermeulen L, De Sousa EMF, Heijden M van der, Cameron K, Jong JH de, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M, Merz C, Rodermond H, Sprick MR, Kemper K, Richel DJ, Stassi G, Medema JP (2010) Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol 12:468–476
Vormer TL, Wojciechowicz K, Dekker M, Vries S de, Wal A van der, Delzenne-Goette E, Naik SH, Song JY, Dannenberg JH, Hansen JB, Te Riele H (2014) RB family tumor suppressor activity may not relate to active silencing of E2F target genes. Cancer Res 74:5266–5276
Wagner W, Horn P, Castoldi M, Diehlmann A, Bork S, Saffrich R, Benes V, Blake J, Pfister S, Eckstein V, Ho AD (2008) Replicative senescence of mesenchymal stem cells: a continuous and organized process. PLoS One 3:e2213
Wan Y, Zhao W, Jiang Y, Liu D, Meng G, Cai Y (2014) Beta-catenin is a valuable marker for differential diagnosis of osteoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Hum Pathol 45:1459–1465
Wang T, Xu Z (2010) miR-27 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402:186–189
Wang Y, Li YP, Paulson C, Shao JZ, Zhang X, Wu M, Chen W (2014) Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark edition) 19:379–407
Watt FM, Hogan B (2000) Out of Eden: stem cells and their niches. Science 287:1427–1430
Wend P, Holland JD, Ziebold U, Birchmeier W (2010) Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:855–863
Westendorf JJ, Kahler RA, Schroeder TM (2004) Wnt signaling in osteoblasts and bone diseases. Gene 341:19–39
Wu JY, Scadden DT, Kronenberg HM (2009) Role of the osteoblast lineage in the bone marrow hematopoietic niches. J Bone Miner Res 24:759–764
Xu M, Yu Q, Subrahmanyam R, Difilippantonio MJ, Ried T, Sen JM (2008) Beta-catenin expression results in p53-independent DNA damage and oncogene-induced senescence in prelymphomagenic thymocytes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 28:1713–1723
Yaccoby S, Ling W, Zhan F, Walker R, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD Jr (2007) Antibody-based inhibition of DKK1 suppresses tumor-induced bone resorption and multiple myeloma growth in vivo. Blood 109:2106–2111
Yao H, Ashihara E, Maekawa T (2011) Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15:873–887
Yavropoulou MP, Yovos JG (2007) The role of the Wnt signaling pathway in osteoblast commitment and differentiation. Hormones (Athens) 6:279–294
Yeung J, Esposito MT, Gandillet A, Zeisig BB, Griessinger E, Bonnet D, So CW (2010) Beta-catenin mediates the establishment and drug resistance of MLL leukemic stem cells. Cancer Cell 18:606–618
Yin T, Li L (2006) The stem cell niches in bone. J Clin Invest 116:1195–1201
Yin JJ, Mohammad KS, Kakonen SM, Harris S, Wu-Wong JR, Wessale JL, Padley RJ, Garrett IR, Chirgwin JM, Guise TA (2003) A causal role for endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of osteoblastic bone metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:10954–10959
Yoon JC, Ng A, Kim BH, Bianco A, Xavier RJ, Elledge SJ (2010) Wnt signaling regulates mitochondrial physiology and insulin sensitivity. Genes Dev 24:1507–1518
Zhang DY, Wang HJ, Tan YZ (2011) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling induces the aging of mesenchymal stem cells through the DNA damage response and the p53/p21 pathway. PLoS One 6:e21397
Zhang DY, Pan Y, Zhang C, Yan BX, Yu SS, Wu DL, Shi MM, Shi K, Cai XX, Zhou SS, Wang JB, Pan JP, Zhang LH (2013a) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling induces the aging of mesenchymal stem cells through promoting the ROS production. Mol Cell Biochem 374:13–20
Zhang R, Oyajobi BO, Harris SE, Chen D, Tsao C, Deng HW, Zhao M (2013b) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activates bone morphogenetic protein 2 expression in osteoblasts. Bone 52:145–156
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all our colleagues in Shafa Hospital and Allied Health Sciences School, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Authors’ contributions
N.S. and F.N. conceived the manuscript and revised it. N.S. and M.Sh. wrote the manuscript. A.A. prepared the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadzadeh, A., Norozi, F., Shahrabi, S. et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in bone marrow niche. Cell Tissue Res 363, 321–335 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2300-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2300-y