Abstract
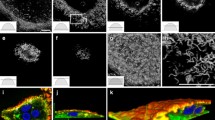
Osteoclasts are highly polarized cells from both morphological and functional points of view. Using quick-freeze, rotary-replication methods combined with cell-shearing, we clarified the variability of cytoplasmic surface of the polarized membranes of osteoclasts seeded on apatite. As to the organization of actin filaments and clathrin sheets, we confirmed almost the same ventral membrane specializations of osteoclasts on apatite as seen on glass plates. The organized actin filaments and membrane-associated particles supported the ruffled border membranes. Inside the actin sealing zone, membrane specializations were not always occupied with the ruffled border but also with other types of membranes. Some osteoclasts formed an actin ring but lacked the ruffled border projections. We report a unique and distinctive membrane modification of apatite-attached osteoclasts, i.e., the presence of dense aggregates of membrane-associated particles and related structures not found in the osteoclasts seeded on glass plates. Actin filament polarity in the podosomes was determined by decoration with myosin S1. The actin filament polarity within podosome appears to be oriented predominantly with its barbed ends toward the core, whereas the interconnecting F-actin appears to be mixed oriented. Two different types of clathrin plaques displayed different distributions: clathrin-dependent endocytosis was observed in the ruffled border regions, whereas flat clathrin sheets were found in the leading edge of lamellipodia and near podosomes. The clathrin sheets adhered to the apatite surface tightly on the ventral membranes overlaying the resorption lacunae. All these membrane specializations as mentioned above may indicate the functional variability of osteoclasts seeded on apatite.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggele J, Werb Z (1982) Initial events during phagocytosis by macrophages view from outside and inside the cell membrane-particle interactions and clathrin. J Cell Biol 94:613–623
Aggeler J, Takemura R, Werb Z (1983) High-resolution three-dimensional views of membrane-associated clathrin and cytoskeleton in critical-point-dried macrophages. J Cell Biol 97:1452–1458
Akisaka T, Miyaji T, Yoshida H, Inoue M (1997) Ultrastructure of quick-frozen and freeze-substituted chick osteoclasts. J Anat 190:433–445
Akisaka T, Yoshida H, Inoue S, Shimizu K (2001) Organization of cytoskeletal F-actin, G-actin, and gelsolin in the adhesion structures in cultured osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 16:1248–1255
Akisaka T, Yoshida H, Suzuki R, Shimizu K, Takama K (2003) Clathrin sheets on the protoplasmic surface of ventral membrane of osteoclasts in culture. J Electron Microsc 52:535–543
Akisaka T, Yoshida H, Suzuki R (2006) The ruffled border and attachment region of the apposing membrane of resorbing osteoclasts as visualized from the cytoplasmic face of the membrane. J Electron Microsc 55:53–61
Akisaka T, Yoshida H, Suzuki R, Takama K (2008) Adhesion structures and their cytoskeleton-membrane interactions at podosomes of osteoclasts in culture. Cell Tissue Res 331:625–641
Akisaka T, Yoshida H, Takigawa T (2011) Differential distribution of posttranslationally modified microtubules in osteoclasts. J Histochem Cytochem 59:630–638
Babb SG, Matsudaira P, Sato M, Correia I, Lim SS (1997) Fimbrin in podosomes of monocyte-derived osteoclasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 37:308–325
Badowski C, Pawlak G, Grichine A, Chabadel A, Oddou C, Jurdic P, Pfaff M, Albiges-Rizo C, Block MR (2008) Paxillin phosphorylation controls invadopodia/podosomes spatiotemporal organization. Mol Biol Cell 19:633–645
Batchelder EM, Yarar D (2010) Differential requirements for clathrin-dependent endocytosis at sites of cell-substrate adhesion. Mol Biol Cell 21:3070–3079
Block MR, Badowski C, Millon-Fremillon A, Bouvard D, Bouin A-P, Faurobert E, Gerber-Scokaert D, Planus E, Albiges-Rizo C (2008) Podosomes-type adhesions and focal adhesions, so alike yet so different. Eur J Cell Biol 87:491–506
Chabadel A, Banon-Rodriguez I, Cluet D, Rudkin BB, Wehrle-Haller B, Genot E, Jurdic P, Anton IM, Saltel F (2007) CD44 and β3 integrin organize two functionally distinct actin-based domains in osteoclasts. Mol Biol Cell 18:4899–4910
Chao W-T, Kunz J (2009) Focal adhesion disassembly requires clathrin-dependent endocytosis of integrin. FEBS Lett 583:1337–1343
Collins A, Warrington A, Taylor KA, Svitkina T (2011) Structural organization of the actin cytoskeleton at sites of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Curr Biol 21:1157–1175
De Deyne PG, O’Neill A, Resneck WG, Dmytrenko GM, Pumplin DW, Bloch RJ (1998) The vitronectin receptor associates with clathrin-coated membrane domains via the cytoplasmic domain of its β5 subunit. J Cell Sci 111:2729–2740
Destaing O, Saltel F, Ceminard JC, Jurdic P, Bard F (2003) Podosomes display actin turnover and dynamic self-organization in osteoclasts expressing actin-green fluorescent protein. Mol Biol Cell 14:407–416
Evans JG, Correia I, Krasavina O, Watson N, Matsudaira P (2003) Macrophage podosomes assemble at the leading lamella by growth and fragmentation. J Cell Biol 161:697–706
Gavazzi I, Nermut MV, Marchisio PC (1989) Ultrastructure and gold-immunolabelling of cell-substratum adhesions (podosomes) in RSV-transformed BHK cells. J Cell Sci 94:85–99
Geblinger D, Geiger B, Addadi L (2009) Surface-induced regulation of podosome organization and dynamics in cultured osteoclasts. Chembiochem 10:158–165
Heuser JE, Cooke R (1983) Actin-myosin interactions visualized by the quick-freeze, deep-etch replica technique. Mol Biol 160:97–122
Jurdic P, Saltel F, Chabadel A, Destaing O (2006) Podosome and sealing zone: specificity of the osteoclast model. Eur J Cell Biol 85:195–202
Lakkakorpi PT, Väänänen HK (1991) Kinetics of the osteoclast cytoskeleton during the resorption cycle in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 6:817–826
Lakkakorpi PT, Väänänen HK (1996) Cytoskeletal changes in osteoclasts during the resorption cycle. Microsc Res Tech 33:171–181
Larkin JM, Donzell WC, Anderson RGW (1986) Potassium-dependent assembly of coated pits: new coated pits form as planar clathrin lattices. J Cell Biol 103:2619–2627
Lewis AK, Bridgman PC (1992) Nerve growth cone lamellipodia contain two populations of actin filaments that differ in organization and polarity. J Cell Biol 119:1219–1243
Linder S, Aepfelbacher M (2003) Podosomes: adhesion hot-spots of invasive cells. Trends Cell Biol 13:376–385
Linder S, Hüfner K, Wintergerst U, Aepfelbacher M (2000) Microtubule-dependent formation of podosomal adhesion structures in primary human macrophages. J Cell Sci 113:4165–4176
Luxenburg C, Addadi L, Geiger B (2006) The molecular dynamics of osteoclast adhesion. Eur J Cell Biol 85:203–211
Luxenburg C, Geblinger D, Klein E, Anderson K, Hanein D, Geiger B, Addadi L (2007) The architecture of the adhesive apparatus of cultured osteoclasts: from podosome formation to sealing zone assembly. PLoS ONE 2:e179
Marchisio PC, Cirillo D, Naldini L, Primavera MV, Teti A, Zambonin-Zallone A (1984) Cell-substratum interaction of cultured avian osteoclasts is mediated by specific adhesion structures.J Cell Biol99:1696–705
Maupin P, Pollard TD (1983) Improved preservation and staining of HeLa cell actin filaments, clathrin-coated membranes, and other cytoplasmic structures by tannic acid-glutaraldehyde-saponin fixation. J Cell Biol 96:51–62
Mulari MT, Zhao H, Lakkakorpi PT, Väänänen HK (2003) Osteoclast ruffled border has distinct subdomains for secretion and degraded matrix uptake. Traffic 4:113–125
Nermut MV, Williams LD, Stamatoglou SC (1986) Ultrastructure of ventral membranes of rat hepatocytes spread on type IV collagen. Eur J Cell Biol 42:35–44
Nermut MV, Eason P, Hirst EMA, Kellie S (1991) Cell/substratum adhesions in RSV-transformed rat fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 193:382–397
Nicol A, Nermut MV (1987) A new type of substratum adhesion structure in NRK cells revealed by correlated interference reflection and electron microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol 43:348–357
Ono M, Murakami T, Tomita M, Ishikawa H (1993) Association of the actin cytoskeleton with glass-adherent proteins in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biol Cell 77:219–230
Palokangas H, Mulari MT, Väänänen HK (1997) Endocytic pathway from the basal plasma membranes to the ruffled border membrane in bone-resorbing osteoclast. J Cell Sci 110:1767–1780
Pierce A, Lindskog S (1988) Coated pits and vesicles in the osteoclasts. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 20:161–167
Pumplin DW (1989) Acetylcholine receptor clusters of rat myotubes have at least three domains with distinctive cytoskeletal and membranous components. J Cell Biol 109:739–753
Pumplin DW, Bloch RJ (1990) Clathrin-coated membrane: a distinct membrane domain in acetylcholine receptor clusters of rat myotubes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 15:123–134
Saffarian S, Cocucci E, Kirchhausen T (2009) Distinct dynamics of endocytic clathrin-coated pits and coated plaques. PLoS One 7:e1000191
Saltel F, Destaing O, Bard F, Eichert D, Jurdic P (2004) Apatite-mediated actin dynamics in resorbing osteoclasts. Mol Biol Cell 15:5231–5241
Saltel F, Chabadel A, Bonnelye E, Jurdic P (2008) Actin cytoskeletal organization in osteoclasts: a model to decipher transmigration and matrix degradation. Eur J Cell Biol 87:459–468
Samuelsson SJ, Luther PW, Pumplin DW, Bloch RJ (1993) Structures linking microfilament bundles to the membrane at focal contacts. J Cell Biol 122:485–496
Stenbeck G, Horton MA (2000) A new specialized cell-matrix interaction in actively resorbing osteoclasts. J Cell Sci 113:1577–1587
Stenbeck G, Horton MA (2003) Endocytic trafficking in actively resorbing osteoclasts. J Cell Sci 117:827–836
Svitkina TM, Verkhovsky AB (1995) Improved procedures for electron microscopic visualization of the cytoskeleton of cultured cells. J Struct Biol 115:290–303
Svitkina TM, Verkhovsky AB, McQuade KM, Borisy GG (1997) Analysis of the actin-myosin II system in fish epidermal keratocytes: mechanism of cell body translocation. J Cell Biol 139:397–415
Szewczyk KA, Fuller K, Chambers TJ (2013) Distinctive subdomains in the resorbing surface of osteoclasts. PLoS ONE 8:e60285
Traub LM (2009) Clathrin couture: fashioning distinctive membrane coats at the cell surface. PLoS ONE 7:e1000192
Traub LM (2011) Regarding the amazing choreography of clathrin coats. PLoS ONE 9:e1001037
Verschueren H (1985) Interference reflection microscopy in cell biology:methodology and applications. J Cell Sci 75:279–301
Verkhovsky AB, Svitkina TM, Borisy GG (1997) Polarity sorting of actin filaments in cytochalasin-treated fibroblast. J Cell Sci 110:1693–1704
Zambonin-Zallone A, Teti A, Carano A, Marchisio PC (1988) The distribution of podosomes in osteoclasts cultured bone lamina: effect of retinol. J Bone Miner Res 3:517–523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akisaka, T., Yoshida, A. Visualization of structural organization of ventral membranes of sheared-open resorbing osteoclasts attached to apatite pellets. Cell Tissue Res 360, 347–362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2085-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2085-4