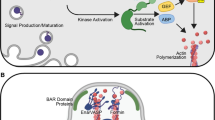
Abstract
Cell-to-cell communication is vital for animal tissues and organs to develop and function as organized units. Throughout development, intercellular communication is crucial for the generation of structural diversity, mainly by the regulation of differentiation and growth. During these processes, several signaling molecules function as messengers between cells and are transported from producing to receptor cells. Thus, a tight spatial and temporal regulation of signaling transport is likely to be critical during morphogenesis. Despite much experimental and theoretical work, the question as to how these signals move between cells remains. Cell-to-cell contact is probably the most precise spatial and temporal mechanism for the transference of signaling molecules from the producing to the receiving cells. However, most of these molecules can also function at a distance between cells that are not juxtaposed. Recent research has shown the way in which cells may achieve direct physical contact and communication through actin-based filopodia. In addition, increasing evidence is revealing the role of such filopodia in regulating spatial patterning during development; in this context, the filopodia are referred to as cytonemes. In this review, we highlight recent work concerning the roles of these filopodia in cell signaling during development. The processes that initiate and regulate the formation, orientation and dynamics of cytonemes are poorly understood but are potentially extremely important areas for our knowledge of intercellular communication.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affolter M, Basler K (2011) Cell biology. Cytonemes show their colors. Science 332:312–313
Baeg GH, Lin X, Khare N, Baumgartner S, Perrimon N (2001) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are critical for the organization of the extracellular distribution of Wingless. Development 128:87–94
Beckett K, Monier S, Palmer L, Alexandre C, Green H, Bonneil E, Raposo G, Thibault P, Borgne RL, Vincent JP (2012) Drosophila S2 cells secrete Wingless on exosome-like vesicles but the Wingless gradient forms independently of exosomes. Traffic 14:82-96
Bilioni A, Sánchez-Hernández D, Callejo A, Gradilla AC, Ibáñez C, Mollica E, Carmen Rodríguez-Navas M, Simon E, Guerrero I (2012) Balancing hedgehog, a retention and release equilibrium given by Dally, Ihog, Boi and shifted/dWif. Dev Biol. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.12.013
Block J, Stradal TE, Hänisch J, Geffers R, Köstler SA, Urban E, Small JV, Rottner K, Faix J (2008) Filopodia formation induced by active mDia2/Drf3. J Microsc 231:506–517
Callejo A, Bilioni A, Mollica E, Gorfinkiel N, Andrés G, Ibáñez C, Torroja C, Doglio L, Sierra J, Guerrero I (2011) Dispatched mediates Hedgehog basolateral release to form the long-range morphogenetic gradient in the Drosophila wing disk epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:12591–12598
Castrillon DH, Wasserman SA (1994) Diaphanous is required for cytokinesis in Drosophila and shares domains of similarity with the products of the limb deformity gene. Development 120:3367–3377
Chu T, Chiu M, Zhang E, Kunes S (2006) A C-terminal motif targets Hedgehog to axons, coordinating assembly of the Drosophila eye and brain. Dev Cell 10:635–646
Cohen M, Georgiou M, Stevenson NL, Miodownik M, Baum B (2010) Dynamic filopodia transmit intermittent Delta-Notch signaling to drive pattern refinement during lateral inhibition. Dev Cell 19:78–89
Crick F (1970) Diffusion in embryogenesis. Nature 225:420–422
Davis DM, Sowinski S (2008) Membrane nanotubes: dynamic long-distance connections between animal cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:431–436
De Joussineau C, Soulé J, Martin M, Anguille C, Montcourrier P, Alexandre D (2003) Delta-promoted filopodia mediate long-range lateral inhibition in Drosophila. Nature 426:555–559
Entchev EV, Schwabedissen A, González-Gaitán M (2000) Gradient formation of the TGF-beta homolog Dpp. Cell 103:981–991
Georgiou M, Baum B (2010) Polarity proteins and Rho GTPases cooperate to spatially organise epithelial actin-based protrusions. J Cell Sci 123:1089–1098
Gerdes HH, Carvalho RN (2008) Intercellular transfer mediated by tunneling nanotubes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:470–475
Gerdes HH, Rustom A, Wang X (2012) Tunneling nanotubes, an emerging intercellular communication route in development. Mech Dev (in press9
Gibson MC, Schubiger G (2000) Peripodial cells regulate proliferation and patterning of Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 103:343–350
Greco V, Hannus M, Eaton S (2001) Argosomes: a potential vehicle for the spread of morphogens through epithelia. Cell 106:633–645
Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M (2012) Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol 14:1036–1045
Guerrero I, Chiang C (2007) A conserved mechanism of Hedgehog gradient formation by lipid modifications. Trends Cell Biol 17:1–5
Hanna-Alava A (1958) Morphology and chaetotaxy of the legs of Drosophila melanogaster. J Morphol 103:281–310
Hsiung F, Ramirez-Weber FA, Iwaki DD, Kornberg TB (2005) Dependence of Drosophila wing imaginal disc cytonemes on Decapentaplegic. Nature 437:560–563
Huang Z, Kunes S (1996) Hedgehog, transmitted along retinal axons, triggers neurogenesis in the developing visual centers of the Drosophila brain. Cell 86:411–422
Kalinina J, Byron SA, Makarenkova HP, Olsen SK, Eliseenkova AV, Larochelle WJ, Dhanabal M, Blais S, Ornitz DM, Day LA, Neubert TA, Pollock PM, Mohammadi M (2009) Homodimerization controls the fibroblast growth factor 9 subfamily’s receptor binding and heparan sulfate-dependent diffusion in the extracellular matrix. Mol Cell Biol 29:4663–4678
Kicheva A, Pantazis P, Bollenbach T, Kalaidzidis Y, Bittig T, Jülicher F, González-Gaitán M (2007) Kinetics of morphogen gradient formation. Science 315:521–525
Kimura S, Hase K, Ohno H (2012) The molecular basis of induction and formation of tunneling nanotubes. Cell Tissue Res (in press)
Koizumi K, Takano K, Kaneyasu A, Watanabe-Takano H, Tokuda E, Abe T, Watanabe N, Takenawa T, Endo T (2012) RhoD activated by fibroblast growth factor induces cytoneme-like cellular protrusions through mDia3C. Mol Biol Cell 23:4647–4661
Koles K, Nunnari J, Korkut C, Barria R, Brewer C, Li Y, Leszyk J, Zhang B, Budnik V (2012) Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons. J Biol Chem 287:16820–16834
Korkut C, Ataman B, Ramachandran P, Ashley J, Barria R, Gherbesi N, Budnik V (2009) Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless. Cell 139:393–404
Kornberg TB (2012) The imperative of context and contour for morphogen dispersion. Biophys J 103:2252–2256
Lawrence PA (2001) Morphogens: how big is the big picture? Nat Cell Biol 3:E151–E154
Miura GI, Treisman JE (2006) Lipid modification of secreted signaling proteins. Cell Cycle 5:1184–1188
Miura GI, Buglino J, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Resh MD, Treisman JE (2006) Palmitoylation of the EGFR ligand Spitz by rasp increases Spitz activity by restricting its diffusion. Dev Cell 10:167–176
Müller P, Rogers KW, Jordan BM, Lee JS, Robson D, Ramanathan SW, Schier AF (2012) Differential diffusivity of Nodal and Lefty underlies a reaction–diffusion patterning system. Science 336:721–724
Musse AA, Meloty-Kapella L, Weinmaster G (2012) Notch ligand endocytosis: mechanistic basis of signaling activity. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:429–436
Panakova D, Sprong H, Marois E, Thiele C, Eaton S (2005) Lipoprotein particles are required for Hedgehog and Wingless signalling. Nature 435:58–65
Peng Y, Han C, Axelrod JD (2012) Planar polarized protrusions break the symmetry of EGFR signaling during Drosophila bract cell fate induction. Dev Cell 23:507–518
Pepinsky RB, Zeng C, Wen D, Rayhorn P, Baker DP, Williams KP et al (1998) Identification of a palmitic acid-modified form of human Sonic hedgehog. J Biol Chem 273:14037–14045
Pyrgaki C, Trainor P, Hadjantonakis AK, Niswander L (2010) Dynamic imaging of mammalian neural tube closure. Dev Biol 344:941–947
Ramirez-Weber FA, Kornberg TB (1999) Cytonemes: cellular processes that project to the principal signaling center in Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 97:599–607
Reed CT, Murphy C, Fristrom D (1975) The ultrastructure of the differentiating pupal leg of Drosophila melanogaster. Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 178:285–302
Rojas-Ríos P, Guerrero I, González-Reyes A (2012) Cytoneme-mediated delivery of hedgehog regulates the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins to maintain germline stem cells in Drosophila. PLoS Biol 10:e1001298
Roy S, Kornberg TB (2011) Direct delivery mechanisms of morphogen dispersion. Sci Signal 4:pt8
Roy S, Hsiung F, Kornberg TB (2011) Specificity of Drosophila cytonemes for distinct signaling pathways. Science 332:354–358
Salas-Vidal E, Lomeli H (2004) Imaging filopodia dynamics in the mouse blastocyst. Dev Biol 265:75–89
Sato M, Kornberg TB (2002) FGF is an essential mitogen and chemoattractant for the air sacs of the Drosophila tracheal system. Dev Cell 3:195–207
Schirenbeck A, Bretschneider T, Arasada R, Schleicher M, Faix J (2005) The Diaphanous-related formin dDia2 is required for the formation and maintenance of filopodia. Nat Cell Biol 7:619–625
Steinhauer J, Treisman JE (2009) Lipid-modified morphogens: functions of fats. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19:308–314
Steinhauer J, Gijón MA, Riekhof WR, Voelker DR, Murphy RC, Treisman JE (2009) Drosophila lysophospholipid acyltransferases are specifically required for germ cell development. Mol Biol Cell 20:5224–5235
Tien AC, Rajan A, Bellen HJ (2009) A Notch updated. J Cell Biol 184:621–629
Walt H, Tobler H (1978) Ultrastructural analysis of differentiating bristles organs in wild type, shaven-depilated and Mytomycin C-treated larvae of Drosophila melanogaster. Biol Cell 32:291–298
Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan AW, Weissman IL, Reya T et al (2003) Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature 423:448–452
Yan D, Wu Y, Yang Y, Belenkaya TY, Tang X, Lin X (2010) The cell-surface proteins Dally-like and Ihog differentially regulate Hedgehog signaling strength and range during development. Development 137:2033–2044
Yang C, Czech L, Gerboth S, Kojima S, Scita G, Svitkina T (2007) Novel roles of formin mDia2 in lamellipodia and filopodia formation in motile cells. PLoS Biol 5:e317
Yu SR, Burkhardt M, Nowak M, Ries J, Petrásek Z, Scholpp S, Schwille P, Brand M (2009) Fgf8 morphogen gradient forms by a source-sink mechanism with freely diffusing molecules. Nature 461:533–536
Zeng X, Goetz JA, Suber LM, Scott WJ Jr, Schreiner CM, Robbins DJ (2001) A freely diffusible form of Sonic hedgehog mediates long-range signalling. Nature 411:716–720
Zheng X, Mann RK, Sever N, Beachy PA (2010) Genetic and biochemical definition of the Hedgehog receptor. Genes Dev 24:57–71
Zhou S, Lo WC, Suhalim JL, Digman MA, Gratton E, Nie Q, Lander AD (2012) Free extracellular diffusion creates the Dpp morphogen gradient of the Drosophila wing disc. Curr Biol 22:668–675
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to T. Kornberg for helpful insights and to Marcus Bischoff and to the members of Isabel Guerrero laboratory for their results and discussions on Hh localization in cytonemes. We also thank R. Wilson, C. Delidakis and D. Gubb for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants BFU2011-25987 and Consolider Program CDS 2007–00008 from the Spanish MICINN and by an institutional grant from the Fundación Areces. A.C.G. was financed by a Marie Curie ITN-238186, FP7 contract.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gradilla, AC., Guerrero, I. Cytoneme-mediated cell-to-cell signaling during development. Cell Tissue Res 352, 59–66 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1578-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1578-x