Abstract
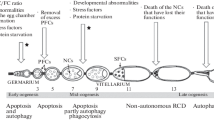
We describe the features of programmed cell death occurring in the egg chambers of Drosophila virilis during mid-oogenesis and late oogenesis. During mid-oogenesis, the spontaneously degenerating egg chambers exhibit typical characteristics of apoptotic cell death. As revealed by propidium iodide, rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin staining, and the TUNEL assay, respectively, the nurse cells contain condensed chromatin, altered actin cytoskeleton, and fragmented DNA. In vitro caspase activity assays and immunostaining procedures demonstrate that the atretic egg chambers possess high levels of caspase activity. Features of autophagic cell death are also observed during D. virilis mid-oogenesis, as shown by monodansylcadaverine staining, together with an ultrastructural examination by transmission electron microscopy. During the late stages of oogenesis in D. virilis, once again, the two mechanisms, viz., nurse cell cluster apoptosis and autophagy, operate together, manifesting features of cell death similar to those detailed above. Moreover, an altered form of cytochrome c seems to be released from the mitochondria in the nurse cells proximal to the oocyte. We propose that apoptosis and autophagy function synergistically during oogenesis in D. virilis in order to achieve a more efficient elimination of the degenerated nurse cells and abnormal egg chambers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arama E, Bader M, Srivastava M, Bergmann A, Steller H (2006) The two Drosophila cytochrome c proteins can function in both respiration and caspase activation. EMBO J 25:232–243
Baker NE, Yu SY (2001) The EGF receptor defines domains of cell cycle progression and survival to regulate cell number in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell 104:699–708
Baum JS, St George JP, McCall K (2005) Programmed cell death in the germline. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:245–259
Berg CA (2005) The Drosophila shell game: patterning and morphological change. Trends Genet 21:346–355
Biederbick A, Kern HF, Elsasser HP (1995) Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol 66:3–14
Bursch W (2001) The autophagosomal-lysosomal compartment in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 8:569–581
Bursch W (2004) Multiple cell death programs: Charon’s lifts to Hades. FEMS Yeast Res 5:101–110
Buszczak M, Freeman MR, Carlson JR, Bender M, Cooley L, Segraves WA (1999) Ecdysone response genes govern egg chamber development during mid-oogenesis in Drosophila. Development 126:4581–4589
Cavaliere V, Taddei C, Gargiulo G (1998) Apoptosis of nurse cells at the late stages of oogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genes Evol 208:106–112
Chao S, Nagoshi RN (1999) Induction of apoptosis in the germline and follicle layer of Drosophila egg chambers. Mech Dev 88:159–172
Chwieralski CE, Welte T, Buhling F (2006) Cathepsin-regulated apoptosis. Apoptosis 2:143–149
Clarke PG (1990) Developmental cell death: morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol (Berlin) 181:195–213
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116:205–219
De Lorenzo C, Strand D, Mechler BM (1999) Requirement of Drosophila I(2)gl function for survival of the germline cells and organization of the follicle cells in a columnar epithelium during oogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 43:207–217
Drummond-Barbosa D, Spradling AC (2001) Stem cells and their progeny respond to nutritional changes during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev Biol 231:265–278
Foley K, Cooley L (1998) Apoptosis in late stage Drosophila nurse cells does not require genes within the H99 deficiency. Development 125:1075–1082
Giorgi F, Deri P (1976) Cell death in ovarian chambers of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol 35:521–533
Gozuacik D, Kimchi A (2004) Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene 23:2891–2906
Juhasz G, Sass M (2005) Hid can induce, but is not required for autophagy in polyploid larval Drosophila tissues. Eur J Cell Biol 84:491–502
Kelekar A (2005) Autophagy. Ann NY Acad Sci 1066:259–271
King RC (1970) Origin and development of the egg chamber within the adult ovarioles. In: King RC (ed) Ovarian development in Drosophila melanogaster. Academic Press, New York London, pp 38–54
Kornbluth S, White K (2005) Apoptosis in Drosophila: neither fish nor fowl (nor man, nor worm). J Cell Sci 118:1779–1787
Krieser RJ, White K (2002) Engulfment mechanism of apoptotic cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:734–738
Kumar S, Doumanis J (2000) The fly caspases. Cell Death Differ 11:1039–1044
Laundrie B, Peterson JS, Baum JS, Chang JC, Fileppo D, Thompson SR, McCall K (2003) Germline cell death is inhibited by P-element insertions disrupting the dcp-1/pita nested gene pair in Drosophila. Genetics 165:1881–1888
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2004) Apoptosis, autophagy and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2405–2419
Mahajan-Miklos S, Cooley L (1994) Intercellular cytoplasm transport during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev Biol 165:336–351
Margaritis LH (1985) Structure and physiology of the eggshell. In: Gilbert LI, Kerkut GA (eds) Comprehensive insect biochemistry, physiology and pharmacology, vol 1. Pergammon, Oxford New York, pp 151–230
Margaritis LH (1986) The eggshell of Drosophila melanogaster. New staging characteristics and fine structural analysis of choriogenesis. Can J Zool 64:2152–2175
Martin DN, Baehrecke EH (2004) Caspases function in autophagic programmed cell death in Drosophila. Development 131:275–284
Mazzalupo S, Cooley L (2006) Illuminating the role of caspases during Drosophila oogenesis. Cell Death Differ, DOI 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401892
McCall K (2004) Eggs over easy: cell death in the Drosophila ovary. Dev Biol 274:3–14
McCall K, Steller H (1998) Requirement for DCP-1 caspase during Drosophila oogenesis. Science 279:230–234
Mueller CM, Jemmerson R (1996) Maturation of the antibody response to the major epitope on the self antigen mouse cytochrome c. Restricted V gene usage, selected mutations and increased affinity. J Immunol 157:5329–5338
Muller F, Adori C, Sass M (2004) Autophagic and apoptotic features during programmed cell death in the fat body of the tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta). Eur J Cell Biol 83:67–78
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri I, Robert-Nicoud M, Margaritis LH (2000) Stage-specific apoptotic patterns during Drosophila oogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol 79:610–620
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri I, Margaritis LH (2001) Actin cytoskeleton reorganization of the apoptotic nurse cells during the late developmental stages of oogenesis in Dacus oleae. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 48:224–233
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri I, Robert-Nicoud M, Margaritis LH (2002) The dynamics of apoptosis in the ovarian follicle cells during the late stages of Drosophila oogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 307:401–409
Nezis IP, Modes V, Mpakou V, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri IS, Mammali I, Margaritis LH (2003) Modes of programmed cell death during Ceratitis capitata oogenesis. Tissue Cell 35:113–119
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri IS, Stergiopoulos C, Margaritis LH (2005) Morphological irregularities and features of resistance to apoptosis in the dcp-1/pita double mutated egg chambers during Drosophila oogenesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 60:14–23
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Margaritis LH, Papassideri IS (2006a) Follicular atresia during Dacus oleae oogenesis. J Insect Physiol 52:282–290
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Margaritis LH, Papassideri IS (2006b) Programmed cell death of follicular epithelium during the late developmental stages of oogenesis in the fruit flies Bactrocera oleae and Ceratitis capitata (Diptera, Tephritidae) is mediated by autophagy. Dev Growth Differ 48:189–198
Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Margaritis LH, Papassideri IS (2006c) Chromatin condensation of ovarian nurse and follicle cells is regulated independently from DNA fragmentation during Drosophila late oogenesis. Differentiation 74:293–304
Peterson JS, Barkett M, McCall K (2003) Stage-specific regulation of caspase activity in Drosophila oogenesis. Dev Biol 260:113–123
Richardson H, Kumar S (2002) Death to flies: Drosophila as a model system to study programmed cell death. J Immunol Methods 265:21–38
Soller M, Bownes M, Kubli E (1999) Control of oocyte maturation in sexually mature Drosophila females. Dev Biol 208:337–351
Srinivasan A, Roth KA, Sayers RO, Shindler KS, Wong AM, Fritz LC, Tomaselli KJ (1998) In situ immunodetection of activated caspase-3 in apoptotic neurons in the developing nervous system. Cell Death Differ 5:1004–1016
Terashima J, Bownes M (2005) A microarray analysis of genes involved in relating egg production to nutritional intake in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Death Differ 12:429–440
Trougakos IP, Margaritis LH (2002) Novel morphological and physiological aspects of insect eggs. In: Hilker M, Meiners T (eds) Chemoecology of insect eggs and egg deposition. Blackwell, Berlin, pp 3–36
Uchida K, Ohmori D, Ueno T, Nishizuka M, Eshita Y, Fukunaga A, Kominami E (2001) Preoviposition activation of cathepsin-like proteinases in degenerating ovarian follicles of the mosquito Culex pipiens pallens. Dev Biol 237:68–78
Uchida K, Nishizuka M, Ohmori D, Ueno T, Eshita Y, Fukunaga A (2004) Follicular epithelial cell apoptosis of atretic follicles within developing ovaries of the mosquito Culex pipiens pallens. J Insect Physiol 50:903–912
Varkey J, Chen P, Jemmerson R, Abrams JM (1999) Altered cytochrome c display precedes apoptotic cell death in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 144:701–710
Velentzas AD, Nezis IP, Stravopodis DJ, Papassideri IS, Margaritis LH (2006) Stage-specific regulation of programmed cell death during oogenesis in the medfly Ceratitis capitata. Int J Dev Biol (in press)
Waldhuber M, Emoto K, Petritsch C (2005) The Drosophila caspase DRONC is required for metamorphosis and cell death in response to irradiation and developmental signals. Mech Dev 122:914–927
Witkus ER, Altman LG, Taparowsky JA (1980) An investigation of the presence of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and GERL during vitellogenesis in the ovary of Drosophila melanogaster. Exp Cell Biol 48:373–383
Yu SY, Yoo SJ, Yang L, Zapata C, Srinivasan A, Hay BA, Baker NE (2002) A pathway of signals regulating effector and initiator caspases in the developing Drosophila eye. Development 129:3269–3278
Yu X, Wang L, Acehan D, Wang X, Akey CW (2006) Three-dimensional structure of a double apoptosome formed by the Drosophila Apaf-1 related killer. J Mol Biol 355:577–589
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Professors R. Jemmerson, C. Petritsch, and K. Homma for kindly supplying us with antibodies and to Professor H.M. Moutsopoulos (Department of Pathophysiology, Medical School, University of Athens, Athens, Greece), for kindly providing confocal laser scanning microscope facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The present study was co-financed within Op. Education by the European Social Fund and by National Resources via a grant (HRAKLEITOS 70/3/7164) to Professor L.H. Margaritis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velentzas, A.D., Nezis, I.P., Stravopodis, D.J. et al. Mechanisms of programmed cell death during oogenesis in Drosophila virilis . Cell Tissue Res 327, 399–414 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0298-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0298-x