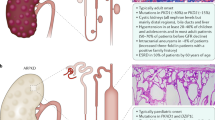
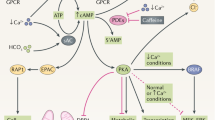
Abstract
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) belongs to a group of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes characterized by dual renal and hepatic involvement of variable severity. Despite the wide clinical spectrum of ARPKD (MIM 263200), genetic linkage studies indicate that mutations at a single locus, PKHD1 (polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1), located on human chromosome region 6p21.1–p12, are responsible for all phenotypes of ARPKD. Identification of cystic disease genes and their encoded proteins has provided investigators with critical tools to begin to unravel the molecular and cellular mechanisms of PKD. PKD cystic epithelia share common phenotypic abnormalities despite the different genetic mutations that underlie the disease. Recent studies have shown that many cyst-causing proteins are expressed in multimeric complexes at distinct subcellular locations within epithelia. This co-expression of cystoproteins suggests that cyst formation, regardless of the underlying disease gene, results from perturbations in convergent and/or integrated signal transduction pathways. To date, no specific therapies are in clinical use for ameliorating cyst growth in ARPKD. However, studies noted in this review suggest that therapeutic targeting of the cAMP and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-axis abnormalities in cystic epithelia may translate into effective therapies for ARPKD and, by analogy, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). A particularly promising approach appears to be the targeting of downstream intermediates of both the cAMP and EGFR axis. This review focuses on ARPKD and presents a concise summary of the current understanding of the molecular genetics and cellular pathophysiology of this disease. It also highlights phenotypic and mechanistic similarities between ARPKD and ADPKD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeva M, El-Youssef M, Rosetti S, Kamath PS, Kubly V, Consugar MB, Milliner DM, King BF, Torres VE, Harris PC (2006) Clinical and molecular characterizations defines a broadened spectrum of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Medicine 85:1–21
Belibi FA, Reif G, Wallace DP, Yamaguchi T, Olsen L, Li H, Helmkamp GM Jr, Grantham JJ (2004) Cyclic AMP promotes growth and secretion in human polycystic kidney epithelial cells. Kidney Int 66:964–973
Bergmann C, Senderek J, Sedlacek B, Pegiazoglou I, Puglia P, Eggermann T, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Furu L, Onuchic LF, De Baca M, Germino GG, Guay-Woodford L, Somlo S, Moser M, Buttner R, Zerres K (2003) Spectrum of mutations in the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD/PKHD1). J Am Soc Nephrol 14:76–89
Bergmann C, Senderek J, Kupper F, Schneider F, Dornia C, Windelen E, Eggermann T, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Kirfel J, Furu L, Onuchic LF, Rossetti S, Harris PC, Somlo S, Guay-Woodford L, Germino GG, Moser M, Buttner R, Zerres K (2004a) PKHD1 mutations in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Hum Mutat 23:453–463
Bergmann C, Senderek J, Schneider F, Dornia C, Kupper F, Eggermann T, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Kirfel J, Moser M, Buttner R, Zerres K (2004b) PKHD1 mutations in families requesting prenatal diagnosis for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Hum Mutat 23:487–495
Bergmann C, Kupper F, Dornia C, Schneider F, Senderek J, Zerres K (2005a) Algorithm for efficient PKHD1 mutation screening in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Hum Mutat 25:225–231
Bergmann C, Kupper F, Schmitt CP, Vester U, Neuhaus TJ, Senderek J, Zerres K (2005b) Multi-exon deletions of the PKHD1 gene cause autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). J Med Genet 42:e63
Bergmann C, Senderek J, Windelen E, Kupper F, Middeldorf I, Schneider F, Dornia C, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Konrad M, Schmitt CP, Seeman T, Neuhaus TJ, Vester U, Kirfel J, Buttner R, Zerres K (2005c) Clinical consequences of PKHD1 mutations in 164 patients with autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Kidney Int 67:829–848
Bernstein J, Slovis TL (1992) Polycystic diseases of the kidney. In: Edelmann C (ed) Pediatric kidney diseases. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 1139–1157
Blyth H, Ockenden BG (1971) Polycystic disease of kidneys and liver presenting in childhood. J Med Genet 8:257–284
Boschelli DH, Wu B, Barrios Sosa AC, Chen JJ, Golas JM, Boschelli F (2005a) Inhibition of Src kinase activity by 7-[(2,4-dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)amino]-2-heteroaryl-thieno[3,2-b]pyridine-6-carbonitriles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:4681–4684
Boschelli DH, Wu B, Barrios Sosa AC, Durutlic H, Chen JJ, Wang Y, Golas JM, Lucas J, Boschelli F (2005b) Synthesis and Src kinase inhibitory activity of 2-phenyl- and 2-thienyl-7-phenylaminothieno[3,2-b]pyridine-6-carbonitriles. J Med Chem 48:3891–3902
Clarke LL, Grubb BR, Gabriel SE, Smithies O, Koller BH, Boucher RC (1992) Defective epithelial chloride transport in a gene-targeted mouse model of cystic fibrosis. Science 257:1125–1128
Cole BR, Conley SB, Stapleton FB (1987) Polycystic kidney disease in the first year of life. J Pediatr 111:693–699
Davis ID, MacRae Dell K, Sweeney WE, Avner ED (2001) Can progression of autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease be prevented? Semin Nephrol 21:430–440
Davis ID, Ho M, Hupertz V, Avner ED (2003) Survival of childhood polycystic kidney disease following renal transplantation: the impact of advanced hepatobiliary disease. Pediatr Transplant 7:364–369
Dell K, Avner E (2003) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease gene reviews; genetic disease online reviews at gene tests-gene clinics. University of Washington, Seattle
Dell KM, Nemo R, Sweeney WE, Levin JI, Frost P, Avner ED (2001) A novel inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme ameliorates polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 60:1240–1248
Dell K, McDonald R, Watkins SL, Avner ED (2004) Polycystic kidney disease. In: Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P (eds) Pediatric nephrology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 675–699
Desmet VJ (1992) Congenital diseases of intrahepatic bile ducts: variations on the theme “ductal plate malformation”. Hepatology 16:1069–1083
Du J, Wilson PD (1995) Abnormal polarization of EGF receptors and autocrine stimulation of cyst epithelial growth in human ADPKD. Am J Physiol 269:C487–C495
Furu L, Onuchic LF, Gharavi A, Hou X, Esquivel EL, Nagasawa Y, Bergmann C, Senderek J, Avner E, Zerres K, Germino GG, Guay-Woodford LM, Somlo S (2003) Milder presentation of recessive polycystic kidney disease requires presence of amino acid substitution mutations. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2004–2014
Gabow PA (1993) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 329:332–342
Gattone VH 2nd, Kuenstler KA, Lindemann GW, Lu X, Cowley BD Jr, Rankin CA, Calvet JP (1996) Renal expression of a transforming growth factor-alpha transgene accelerates the progression of inherited, slowly progressive polycystic kidney disease in the mouse. J Lab Clin Med 127:214–222
Gattone VH 2nd, Wang X, Harris PC, Torres VE (2003) Inhibition of renal cystic disease development and progression by a vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist. Nat Med 9:1323–1326
Grantham JJ (1996) The etiology, pathogenesis, and treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: recent advances. Am J Kidney Dis 28:788–803
Grantham JJ (1997a) Mechanisms of progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 63:S93–S97
Grantham JJ (1997b) Renal cell proliferation and the two faces of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Lab Clin Med 130:460–469
Grantham JJ (2000) Time to treat polycystic kidney diseases like the neoplastic disorders that they are. Kidney Int 57:339–340
Grantham JJ, Geiser JL, Evan AP (1987) Cyst formation and growth in autosomal dominant polcystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 31:1145–1152
Grantham JJ, Ye M, Davidow C, Holub B, Sharma M (1995) Evidence for a potent lipid secretagogue in the cyst fluids of patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1242–1249
Guan KL, Figueroa C, Brtva TR, Zhu T, Taylor J, Barber TD, Vojtek AB (2000) Negative regulation of the serine/threonine kinase B-Raf by Akt. J Biol Chem 275:27354–27359
Guay-Woodford L (1996) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. In: Watson M, Torres VH (eds) Polycystic kidney disease. Oxford University Press, New York
Guay-Woodford LM (2003) Murine models of polycystic kidney disease: molecular and therapeutic insights. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F1034–F1049
Guay-Woodford LM, Desmond RA (2003) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: the clinical experience in North America. Pediatrics 111:1072–1080
Guay-Woodford LM, Muecher G, Hopkins SD, Avner ED, Germino GG, Guillot AP, Herrin J, Holleman R, Irons DA, Primack W, Thomson PD, Waldo FB, Lunt PW, Zerres K (1995) The severe perinatal form of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease maps to chromosome 6p21.1–p12: implications for genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet 56:1101–1107
Gunay-Aygun M, Avner ED, Bacallao RL, et al (2006) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease NIH symposium summary statement. J Pediatr (in press)
Harris PC, Rossetti S (2004) Molecular genetics of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Mol Genet Metab 81:75–85
Hiesberger T, Bai Y, Shao X, McNally BT, Sinclair AM, Tian X, Somlo S, Igarashi P (2004) Mutation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1{beta} inhibits Pkhd1 gene expression and produces renal cysts in mice. J Clin Invest 113:814–825
Hildebrandt F, Otto E (2005) Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet 6:928–940
Hogan MC, Griffin MD, Rossetti S, Torres VE, Ward CJ, Harris PC (2003) PKHDL1, a homolog of the autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease gene, encodes a receptor with inducible T lymphocyte expression. Hum Mol Genet 12:685–698
Igarashi P, Somlo S (2002) Genetics and pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2384–2398
Igarashi P, Shao X, McNally BT, Hiesberger T (2005) Roles of HNF-1beta in kidney development and congenital cystic diseases. Kidney Int 68:1944–1947
Jafar TH, Stark PC, Schmid CH, Strandgaard S, Kamper AL, Maschio G, Becker G, Perrone RD, Levey AS (2005) The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors on progression of advanced polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 67:265–271
Jiang ST, Chiou YY, Wang E, Lin HK, Lin YT, Chi YC, Wang CK, Tang MJ, Li H (2006) Defining a link with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease in mice with congenitally low expression of pkd1. Am J Pathol 168:205–220
Jorgensen MJ (1977) The ductal plate malformation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl 257:1–87
Kaariainen H, Koskimies O, Norio R (1988) Dominant and recessive polycystic kidney disease in children: evaluation of clinical features and laboratory data. Pediatr Nephrol 2:296–302
Kaplan BS, Fay J, Shah V, Dillon MJ, Barratt TM (1989) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 3:43–49
Klingel R, Dippold W, Storkel S, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Kohler H (1992) Expression of differentiation antigens and growth-related genes in normal kidney, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and renal cell carcinoma. Am J Kidney Dis 19:22–30
Lakshmanan J, Fisher DA (1993) An inborn error in epidermal growth factor prohormone metabolism in a mouse model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 196:892–901
Lin F, Hiesberger T, Cordes K, Sinclair AM, Goldstein LS, Somlo S, Igarashi P (2003) Kidney-specific inactivation of the KIF3A subunit of kinesin-II inhibits renal ciliogenesis and produces polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5286–5291
Losekoot M, Haarloo C, Ruivenkamp C, White SJ, Breuning MH, Peters DJ (2005) Analysis of missense variants in the PKHD1-gene in patients with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Hum Genet 118:185–206
Lowden DA, Lindemann GW, Merlino G, Barash BD, Calvet JP, Gattone VH 2nd (1994) Renal cysts in transgenic mice expressing transforming growth factor-alpha. J Lab Clin Med 124:386–394
Lu W, Fan X, Babakhanlou H, Law T, Rifal N, Harris PC, Perez-Atayde AR, Renneke HG, Zhou J (1999) Late onset of renal and hepatic cysts in Pkd1-targeted heterozygotes. Nat Gen 21:160–161
MacRae Dell K, Nemo R, Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED (2004) EGF-related growth factors in the pathogenesis of murine ARPKD. Kidney Int 65:2018–2029
Masyuk TV, Huang BQ, Ward CJ, Masyuk AI, Yuan D, Splinter PL, Punyashthiti R, Ritman EL, Torres VE, Harris PC, LaRusso NF (2003) Defects in cholangiocyte fibrocystin expression and ciliary structure in the PCK rat. Gastroenterology 125:1303–1310
Menezes LF, Cai Y, Nagasawa Y, Silva AM, Watkins ML, Da Silva AM, Somlo S, Guay-Woodford LM, Germino GG, Onuchic LF (2004) Polyductin, the PKHD1 gene product, comprises isoforms expressed in plasma membrane, primary cilium, and cytoplasm. Kidney Int 66:1345–1355
Murcia NS, Sweeney WE, Avner ED (1999) New insights into the molecular pathophysiology of polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 55:1187–1197
Nagano J, Kitamura K, Hujer KM, Ward CJ, Bram RJ, Hopfer U, Tomita K, Huang C, Miller RT (2005) Fibrocystin interacts with CAML, a protein involved in Ca(2+) signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:880–889
Nagasawa Y, Matthiesen S, Onuchic LF, Hou X, Bergmann C, Esquivel E, Senderek J, Ren Z, Zeltner R, Furu L, Avner E, Moser M, Somlo S, Guay-Woodford L, Buttner R, Zerres K, Germino GG (2002) Identification and characterization of Pkhd1, the mouse orthologue of the human ARPKD gene. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2246–2258
Nakanishi K, Sweeney WE Jr, Macrae Dell K, Cotton CU, Avner ED (2001) Role of CFTR in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:719–725
Nauli SM, Zhou J (2004) Polycystins and mechanosensation in renal and nodal cilia. Bioessays 26:844–856
Nauli SM, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, Williams E, Vassilev P, Li X, Elia AE, Lu W, Brown EM, Quinn SJ, Ingber DE, Zhou J (2003) Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nat Genet 33:129–137
Nauta J, Sweeney WE, Rutledge JC, Avner ED (1995) Biliary epithelial cells from mice with congenital polycystic kidney disease are hyperresponsive to epidermal growth factor. Pediatr Res 37:755–763
Neufield TK, Douglass D, Grant M, Ye M, Silva F, Nadasdy T, Grantham JJ (1992) In vitro formation and expansion of cysts derived from human renal cortex epithelial cells. Kidney Int 41:1222–1236
Onuchic LF, Furu L, Nagasawa Y, Hou X, Eggermann T, Ren Z, Bergmann C, Senderek J, Esquivel E, Zeltner R, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Mrug M, Sweeney W, Avner ED, Zerres K, Guay-Woodford LM, Somlo S, Germino GG (2002) PKHD1, the polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 gene, encodes a novel large protein containing multiple immunoglobulin-like plexin-transcription-factor domains and parallel beta-helix 1 repeats. Am J Hum Genet 70:1305–1317
Orellana SA, Sweeney WE, Neff CD, Avner ED (1995) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is abnormal in murine polycystic kidney. Kidney Int 47:490–499
Osathanondh V, Potter EL (1964a) Pathogenesis of polycystic kidneys. Historical survey. Arch Pathol 77:459–465
Osathanondh V, Potter EL (1964b) Pathogenesis of polycystic kidneys. Survey of results of microdissection. Arch Pathol 77:510–512
Osathanondh V, Potter EL (1964c) Pathogenesis of polycystic kidneys. Type 1 due to hyperplasia of interstitial portions of collecting tubules. Arch Pathol 77:466–473
Pazour GJ (2004) Intraflagellar transport and cilia-dependent renal disease: the ciliary hypothesis of polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:2528–2536
Pazour GJ, Rosenbaum JL (2002) Intraflagellar transport and cilia-dependent diseases. Trends Cell Biol 12:551–555
Pazour GJ, Dickert BL, Vucica Y, Seeley ES, Rosenbaum JL, Witman GB, Cole DG (2000) Chlamydomonas IFT88 and its mouse homologue, polycystic kidney disease gene tg737, are required for assembly of cilia and flagella. J Cell Biol 151:709–718
Pazour GJ, San Agustin JT, Follit JA, Rosenbaum JL, Witman GB (2002) Polycystin-2 localizes to kidney cilia and the ciliary level is elevated in orpk mice with polycystic kidney disease. Curr Biol 12:R378–R380
Phillips CL, Miller KJ, Filson AJ, Nurnberger J, Clendenon JL, Cook GW, Dunn KW, Overbeek PA, Gattone VH 2nd, Bacallao RL (2004) Renal cysts of inv/inv mice resemble early infantile nephronophthisis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1744–1755
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2001) Bending the MDCK cell primary cilium increases intracellular calcium. J Membr Biol 184:71–79
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2003a) Removal of the MDCK cell primary cilium abolishes flow sensing. J Membr Biol 191:69–76
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2003b) The renal cell primary cilium functions as a flow sensor. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:517–520
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2005) A physiological view of the primary cilium. Annu Rev Physiol 67:515–529
Praetorius HA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S, Spring KR (2003) Bending the primary cilium opens Ca2+-sensitive intermediate-conductance K+ channels in MDCK cells. J Membr Biol 191:193–200
Praetorius HA, Praetorius J, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Spring KR (2004) Beta1-integrins in the primary cilium of MDCK cells potentiate fibronectin-induced Ca2+ signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F969–F978
Pugh JL, Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED (1995) Tyrosine kinase activity of the EGF receptor in murine metanephric organ culture. Kidney Int 47:774–781
Richards WG, Sweeney WE, Yoder BK, Wilkinson JE, Woychik RP, Avner ED (1998) Epidermal growth factor receptor activity mediates renal cyst formation in polycystic kidney disease. J Clin Invest 101:935–939
Rohatgi R, Greenberg A, Burrow CR, Wilson PD, Satlin LM (2003) Na transport in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) cyst lining epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:827–836
Rohatgi R, Zavilowitz B, Vergara M, Woda C, Kim P, Satlin LM (2004) Cyst fluid composition in human autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 20:552–553
Rossetti S, Torra R, Coto E, Consugar M, Kubly V, Malaga S, Navarro M, El-Youssef M, Torres VE, Harris PC (2003) A complete mutation screen of PKHD1 in autosomal-recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) pedigrees. Kidney Int 64:391–403
Roy S, Dillon MJ, Trompeter RS, Barratt TM (1997) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: long-term outcome of neonatal survivors. Pediatr Nephrol 11:302–306
Sato Y, Harada K, Kizawa K, Sanzen T, Furubo S, Yasoshima M, Ozaki S, Ishibashi M, Nakanuma Y (2005) Activation of the MEK5/ERK5 cascade is responsible for biliary dysgenesis in a rat model of Caroli’s disease. Am J Pathol 166:49–60
Sharp AM, Messiaen LM, Page G, Antignac C, Gubler MC, Onuchic LF, Somlo S, Germino GG, Guay-Woodford LM (2005) Comprehensive genomic analysis of PKHD1 mutations in ARPKD cohorts. J Med Genet 42:336–349
Sullivan LP, Grantham JJ (1996) Mechanisms of fluid secretion by polycystic epithelia. Kidney Int 49:1586–1591
Sullivan LP, Wallace DP, Grantham JJ (1998) Chloride and fluid secretion in polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:903–916
Sun Z, Amsterdam A, Pazour GJ, Cole DG, Miller MS, Hopkins N (2004) A genetic screen in zebrafish identifies cilia genes as a principal cause of cystic kidney. Development 131:4085–4093
Sweeney WE, Avner ED (1996) BPK cyst fluid contains EGF and TGF-a like peptides which are motogenic and phosphorylate apical EGFR. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1606
Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED (1998) Functional activity of epidermal growth factor receptors in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Am J Physiol 275:F387–F394
Sweeney WE, Chen Y, Nakanishi K, Frost P, Avner ED (2000) Treatment of polycystic kidney disease with a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Kidney Int 57:33–40
Sweeney WE Jr, Hamahira K, Sweeney J, Garcia-Gatrell M, Frost P, Avner ED (2003) Combination treatment of PKD utilizing dual inhibition of EGF-receptor activity and ligand bioavailability. Kidney Int 64:1310–1319
Torres VE (2004) Therapies to slow polycystic kidney disease. Nephron Exp Nephrol 98:e1–e7
Torres VE (2005) Vasopressin antagonists in polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 68:2405–2418
Torres VE, Wang X, Qian Q, Somlo S, Harris PC, Gattone VH (2004) Effective treatment of an orthologous model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Med 10:363–364
Veizis IE, Cotton CU (2005) Abnormal EGF-dependent regulation of sodium absorption in ARPKD collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F474–F482
Veizis EI, Carlin CR, Cotton CU (2004) Decreased amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption in collecting duct principal cells isolated from BPK ARPKD mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F244–F254
Wallace DP, Christensen M, Reif G, Belibi F, Thrasher B, Herrell D, Grantham JJ (2002) Electrolyte and fluid secretion by cultured human inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F1337–F1350
Wang S, Luo Y, Wilson PD, Witman GB, Zhou J (2004) The autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease protein is localized to primary cilia, with concentration in the basal body area. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:592–602
Ward CJ, Hogan MC, Rossetti S, Walker D, Sneddon T, Wang X, Kubly V, Cunningham JM, Bacallao R, Ishibashi M, Milliner DS, Torres VE, Harris PC (2002) The gene mutated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease encodes a large, receptor-like protein. Nat Genet 30:259–269
Ward CJ, Yuan D, Masyuk TV, Wang X, Punyashthiti R, Whelan S, Bacallao R, Torra R, LaRusso NF, Torres VE, Harris PC (2003) Cellular and subcellular localization of the ARPKD protein; fibrocystin is expressed on primary cilia. Hum Mol Genet 12:2703–2710
Welling LW, Grantham JJ (1991) Cystic and developmental diseases of the kidney. In: Brenner BMR, Rector FC (eds) The kidney. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1657–1694
Wilson PD (2004a) Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 350:151–164
Wilson PD (2004b) Polycystic kidney disease: new understanding in the pathogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1868–1873
Witzgall R (2005) New developments in the field of cystic kidney diseases. Curr Mol Med 5:455–465
Xiong H, Chen Y, Yi Y, Tsuchiya K, Moeckel G, Cheung J, Liang D, Tham K, Xu X, Chen XZ, Pei Y, Zhao ZJ, Wu G (2002) A novel gene encoding a TIG multiple domain protein is a positional candidate for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Genomics 80:96–104
Yamaguchi T, Pelling JC, Ramaswamy NT, Eppler JW, Wallace DP, Nagao S, Rome LA, Sullivan LP, Grantham JJ (2000) cAMP stimulates the in vitro proliferation of renal cyst epithelial cells by activating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Kidney Int 57:1460–1471
Yamaguchi T, Nagao S, Wallace DP, Belibi FA, Cowley BD, Pelling JC, Grantham JJ (2003) Cyclic AMP activates B-Raf and ERK in cyst epithelial cells from autosomal-dominant polycystic kidneys. Kidney Int 63:1983–1994
Yamaguchi T, Wallace DP, Magenheimer BS, Hempson SJ, Grantham JJ, Calvet JP (2004) Calcium restriction allows cAMP activation of the B-Raf/ERK pathway, switching cells to a cAMP-dependent growth-stimulated phenotype. J Biol Chem 279:40419–40430
Yamaguchi T, Hempson SJ, Reif GA, Hedge AM, Wallace DP (2006) Calcium restores a normal proliferation phenotype in human polycystic kidney disease epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:178–187
Ye M, Grant M, Sharma M, Elzinga L, Swan S, Torres VE, Grantham JJ (1992) Cyst fluid from human autosomal dominant polycystic kidneys promotes cyst formation and expansion by renal epithelial cells in vitro. J Am Soc Nephrol 3:984–994
Yoder BK, Hou X, Guay-Woodford LM (2002) The polycystic kidney disease proteins, polycystin-1, polycystin-2, polaris, and cystin, are co-localized in renal cilia. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2508–2516
Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Steinkamm C, Mucher G (1996) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11 (Suppl 6):29–33
Zerres K, Mücher G, Becker J, Steinkamm C, Rudnik-Schöneborn S, Heikkilä P, Rapola J, Salonen R, Germino GG, Onuchic L, Somlo S, Avner ED, Harman LA, Stockwin JM, Guay-Woodford LM (1998) Prenatal diagnosis of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD): molecular genetics, clinical experience, and fetal morphology. Am J Med Genet 76:137–144
Zerres K, Senderek J, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Eggermann T, Kunze J, Mononen T, Kaariainen H, Kirfel J, Moser M, Buettner R, Bergmann C (2004) New options for prenatal diagnosis in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease by mutation analysis of the PKHD1 gene. Clin Genet 66:53–57
Zhang BH, Guan KL (2000) Activation of B-Raf kinase requires phosphorylation of the conserved residues Thr598 and Ser601. EMBO J 19:5429–5439
Zhang MZ, Mai W, Li C, Cho SY, Hao C, Moeckel G, Zhao R, Kim I, Wang J, Xiong H, Wang H, Sato Y, Wu Y, Nakanuma Y, Lilova M, Pei Y, Harris RC, Li S, Coffey RJ, Sun L, Wu D, Chen XZ, Breyer MD, Zhao ZJ, McKanna JA, Wu G (2004) PKHD1 protein encoded by the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease associates with basal bodies and primary cilia in renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2311–2316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors are supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant no. 1-P50-DK57306), the PKD Foundation (grant no. 76a2r), and the Children’s Research Institute, Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sweeney, W.E., Avner, E.D. Molecular and cellular pathophysiology of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Cell Tissue Res 326, 671–685 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0226-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-006-0226-0