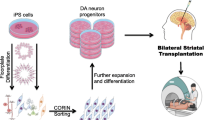
Abstract
A major neuropathological feature of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron. Patients exhibit motor symptoms, including bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor. Neural grafting has been reported to restore striatial dopaminergic neurotransmission and induce symptomatic relief. The major limitation of cell replacement therapy for PD is the shortage of suitable donor tissue. The present review describes the possible sources of cells, including embryonic stem cells and somatic adult stem cells, both of which potentially could be used in cell therapy for PD, and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each cell type.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Dolado M, Pardal R, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Fike JR, Lee HO, Pfeffer K, Lois C, Morrison SJ, Alvarez-Buylla A (2003) Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature 425:968–973
Ashkan K, Wallace B, Bell BA, Benabid AL (2004) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease 1993–2003: where are we 10 years on? Br J Neurosurg 18:19–34
Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ, DiGirolamo C, Prockop DJ (1998) Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brains of albino rats—similarities to astrocyte grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3908–3913
Barberi T, Klivenyi P, Calingasan NY, Lee H, Kawamata H, Loonam K, Perrier AL, Bruses J, Rubio ME, Topf N, Tabar V, Harrison NL, Beal MF, Moore MA, Studer L (2003) Neural subtype specification of fertilization and nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells and application in parkinsonian mice. Nat Biotechnol 21:1200–1207
Björklund LM, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Chung S, Andersson T, Chen IY, McNaught KS, Brownell AL, Jenkins BG, Wahlestedt C, Kim KS, Isacson O (2002) Embryonic stem cells develop into functional dopaminergic neurons after transplantation in a Parkinson rat model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2344–2349
Björklund A, Dunnett SB, Brundin P, Stoessl AJ, Freed CR, Breeze RE, Levivier M, Peschanski M, Studer L, Barker R (2003) Neural transplantation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2:437–445
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE (1998) Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 279:349–352
Bohm N, Noltemeyer N (1981) Development of binuclearity and DNA-polyploidization in the growing mouse liver. Histochemistry 72:55–61
Brazelton TR, Rossi FM, Keshet GI, Blau HM (2000) From marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science 290:1775–1779
Brundin P, Björklund A (1998) Survival of expanded dopaminergic precursors is critical for clinical trials. Nat Neurosci 1:537
Brundin P, Karlsson J, Emgard M, Schierle GS, Hansson O, Petersen A, Castilho RF (2000) Improving the survival of grafted dopaminergic neurons: a review over current approaches. Cell Transplant 9:179–195
Bryan TM, Englezou A, Gupta J, Bacchetti S, Reddel RR (1995) Telomere elongation in immortal human cells without detectable telomerase activity. EMBO J 14:4240–4248
Burdon T, Smith A, Savatier P (2002) Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Trends Cell Biol 12:432–438
Buzanska L, Machaj EK, Zablocka B, Pojda Z, Domanska-Janik K (2002) Human cord blood-derived cells attain neuronal and glial features in vitro. J Cell Sci 115:2131–2138
Caldwell MA, He X, Wilkie N, Pollack S, Marshall G, Wafford KA, Svendsen CN (2001) Growth factors regulate the survival and fate of cells derived from human neurospheres. Nat Biotechnol 19:475–479
Cazorla P, Smidt MP, O’Malley KL, Burbach JP (2000) A response element for the homeodomain transcription factor Ptx3 in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene promoter. J Neurochem 74:1829–1837
Cepko CL (1989) Immortalization of neural cells via retrovirus-mediated oncogene transduction. Annu Rev Neurosci 12:47–65
Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, Nichols J, Lee S, Tweedie S, Smith A (2003) Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 113:643–655
Chung S, Sonntag KC, Andersson T, Björklund LM, Park JJ, Kim DW, Kang UJ, Isacson O, Kim KS (2002) Genetic engineering of mouse embryonic stem cells by Nurr1 enhances differentiation and maturation into dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 16:1829–1838
Ciechanover A, Brundin P (2003) The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron 40:427–446
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
Deng W, Obrocka M, Fischer I, Prockop DJ (2001) In vitro differentiation of human marrow stromal cells into early progenitors of neural cells by conditions that increase intracellular cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 282:148–152
Draper JS, Smith K, Gokhale P, Moore HD, Maltby E, Johnson J, Meisner L, Zwaka TP, Thomson JA, Andrews PW (2004) Recurrent gain of chromosomes 17q and 12 in cultured human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 22:53–54
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH (1981) Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292:154–156
Flax JD, Aurora S, Yang C, Simonin C, Wills AM, Billinghurst LL, Jendoubi M, Sidman RL, Wolfe JH, Kim SU, Snyder EY (1998) Engraftable human neural stem cells respond to developmental cues, replace neurons, and express foreign genes. Nat Biotechnol 16:1033–1039
Frederiksen K, Jat PS, Valtz N, Levy D, McKay R (1988) Immortalization of precursor cells from the mammalian CNS. Neuron 1:439–448
Freed CR, Greene PE, Breeze RE, Tsai WY, DuMouchel W, Kao R, Dillon S, Winfield H, Culver S, Trojanowski JQ, Eidelberg D, Fahn S (2001) Transplantation of embryonic dopamine neurons for severe Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 344:710–719
Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287:1433–1438
Galli R, Borello U, Gritti A, Minasi MG, Bjornson C, Coletta M, Mora M, De Angelis MG, Fiocco R, Cossu G, Vescovi AL (2000) Skeletal myogenic potential of human and mouse neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 3:986–991
Giasson BI, Lee VM (2003) Are ubiquitination pathways central to Parkinson’s disease? Cell 114:1–8
Gross RE, Lombardi WJ, Hutchison WD, Narula S, Saint-Cyr JA, Dostrovsky JO, Tasker RR, Lang AE, Lozano AM (1999) Variability in lesion location after microelectrode-guided pallidotomy for Parkinson’s disease: anatomical, physiological, and technical factors that determine lesion distribution. J Neurosurg 90:468–477
Hagell P, Piccini P, Björklund A, Brundin P, Rehncrona S, Widner H, Crabb L, Pavese N, Oertel WH, Quinn N, Brooks DJ, Lindvall O (2002) Dyskinesias following neural transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 5:627–628
Hardy J, Cookson MR, Singleton A (2003) Genes and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol 2:221–228
Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW (1990) Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 345:458–460
Horrocks GM, Lauder L, Stewart R, Przyborski S (2003) Formation of neurospheres from human embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:411–416
Hoshimaru M, Ray J, Sah DW, Gage FH (1996) Differentiation of the immortalized adult neuronal progenitor cell line HC2S2 into neurons by regulatable suppression of the v-myc oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1518–1523
Jiang Y, Vaessen B, Lenvik T, Blackstad M, Reyes M, Verfaillie CM (2002) Multipotent progenitor cells can be isolated from postnatal murine bone marrow, muscle, and brain. Exp Hematol 30:896–904
Jiang Y, Henderson D, Blackstad M, Chen A, Miller RF, Verfaillie CM (2003) Neuroectodermal differentiation from mouse multipotent adult progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 (Suppl 1):11854–11860
Kawasaki H, Mizuseki K, Nishikawa S, Kaneko S, Kuwana Y, Nakanishi S, Nishikawa SI, Sasai Y (2000) Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity. Neuron 28:31–40
Kawasaki H, Suemori H, Mizuseki K, Watanabe K, Urano F, Ichinose H, Haruta M, Takahashi M, Yoshikawa K, Nishikawa S, Nakatsuji N, Sasai Y (2002) Generation of dopaminergic neurons and pigmented epithelia from primate ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1580–1585
Kerr DA, Llado J, Shamblott MJ, Maragakis NJ, Irani DN, Crawford TO, Krishnan C, Dike S, Gearhart JD, Rothstein JD (2003) Human embryonic germ cell derivatives facilitate motor recovery of rats with diffuse motor neuron injury. J Neurosci 23:5131–5140
Kim JH, Auerbach JM, Rodriguez-Gomez JA, Velasco I, Gavin D, Lumelsky N, Lee SH, Nguyen J, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Bankiewicz K, McKay R (2002) Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 418:50–56
Kim JY, Koh HC, Lee JY, Chang MY, Kim YC, Chung HY, Son H, Lee YS, Studer L, McKay R, Lee SH (2003a) Dopaminergic neuronal differentiation from rat embryonic neural precursors by Nurr1 overexpression. J Neurochem 85:1443–1454
Kim TE, Lee HS, Lee YB, Hong SH, Lee YS, Ichinose H, Kim SU, Lee MA (2003b) Sonic hedgehog and FGF8 collaborate to induce dopaminergic phenotypes in the Nurr1-overexpressing neural stem cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:1040–1048
Kitchens DL, Snyder EY, Gottlieb DI (1994) FGF and EGF are mitogens for immortalized neural progenitors. J Neurobiol 25:797–807
Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Koyama H, Kasai S (1982) A new preadipose cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria can promote the proliferation of pluripotent hemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol 112:89–95
Kodama H, Sudo H, Koyama H, Kasai S, Yamamoto S (1984) In vitro hemopoiesis within a microenvironment created by MC3T3-G2/PA6 preadipocytes. J Cell Physiol 118:233–240
Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG (1999) Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10711–10716
Lee SH, Lumelsky N, Studer L, Auerbach JM, McKay RD (2000) Efficient generation of midbrain and hindbrain neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 18:675–679
Limousin P, Pollak P, Benazzouz A, Hoffmann D, Le Bas JF, Broussolle E, Perret JE, Benabid AL (1995) Effect of parkinsonian signs and symptoms of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation. Lancet 345:91–95
Lotharius J, Barg S, Wiekop P, Lundberg C, Raymon HK, Brundin P (2002) Effect of mutant alpha-synuclein on dopamine homeostasis in a new human mesencephalic cell line. J Biol Chem 277:38884–38894
Lundblad V, Wright WE (1996) Telomeres and telomerase: a simple picture becomes complex. Cell 87:369–375
Martin GR (1981) Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7634–7638
Matsuura N, Lie DC, Hoshimaru M, Asahi M, Hojo M, Ishizaki R, Hashimoto N, Noji S, Ohuchi H, Yoshioka H, Gage FH (2001) Sonic hedgehog facilitates dopamine differentiation in the presence of a mesencephalic glial cell line. J Neurosci 21:4326–4335
Mezey E, Chandross KJ, Harta G, Maki RA, McKercher SR (2000) Turning blood into brain: cells bearing neuronal antigens generated in vivo from bone marrow. Science 290:1779–1782
Mintz B, Baker WW (1967) Normal mammalian muscle differentiation and gene control of isocitrate dehydrogenase synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 58:592–598
Morizane A, Takahashi J, Takagi Y, Sasai Y, Hashimoto N (2002) Optimal conditions for in vivo induction of dopaminergic neurons from embryonic stem cells through stromal cell-derived inducing activity. J Neurosci Res 69:934–939
Nakao N, Yokote H, Nakai K, Itakura T (2000) Promotion of survival and regeneration of nigral dopamine neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease after implantation of embryonal carcinoma-derived neurons genetically engineered to produce glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosurg 92:659–670
Nishimura F, Yoshikawa M, Kanda S, Nonaka M, Yokota H, Shiroi A, Nakase H, Hirabayashi H, Ouji Y, Birumachi J, Ishizaka S, Sakaki T (2003) Potential use of embryonic stem cells for the treatment of mouse parkinsonian models: improved behavior by transplantation of in vitro differentiated dopaminergic neurons from embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 21:171–180
Olanow CW, Tatton WG (1999) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:123–144
Olanow CW, Goetz CG, Kordower JH, Stoessl AJ, Sossi V, Brin MF, Shannon KM, Nauert GM, Perl DP, Godbold J, Freeman TB (2003) A double-blind controlled trial of bilateral fetal nigral transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 54:403–414
Ostenfeld T, Caldwell MA, Prowse KR, Linskens MH, Jauniaux E, Svendsen CN (2000) Human neural precursor cells express low levels of telomerase in vitro and show diminishing cell proliferation with extensive axonal outgrowth following transplantation. Exp Neurol 164:215–226
Ostenfeld T, Joly E, Tai YT, Peters A, Caldwell M, Jauniaux E, Svendsen CN (2002) Regional specification of rodent and human neurospheres. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134:43–55
Piccini P, Brooks DJ, Björklund A, Gunn RN, Grasby PM, Rimoldi O, Brundin P, Hagell P, Rehncrona S, Widner H, Lindvall O (1999) Dopamine release from nigral transplants visualized in vivo in a Parkinson’s patient. Nat Neurosci 2:1137–1140
Ramalho-Santos M, Yoon S, Matsuzaki Y, Mulligan RC, Melton DA (2002) “Stemness”: transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells. Science 298:597–600
Ratajczak MZ, Kucia M, Reca R, Majka M, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak J (2004) Stem cell plasticity revisited: CXCR4-positive cells expressing mRNA for early muscle, liver and neural cells “hide out” in the bone marrow. Leukemia 18:29–40
Renfranz PJ, Cunningham MG, McKay RD (1991) Region-specific differentiation of the hippocampal stem cell line HiB5 upon implantation into the developing mammalian brain. Cell 66:713–729
Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A, Bongso A (2000) Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol 18:399–404
Reubinoff BE, Itsykson P, Turetsky T, Pera MF, Reinhartz E, Itzik A, Ben-Hur T (2001) Neural progenitors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 19:1134–1140
Rietze RL, Valcanis H, Brooker GF, Thomas T, Voss AK, Bartlett PF (2001) Purification of a pluripotent neural stem cell from the adult mouse brain. Nature 412:736–739
Rolletschek A, Chang H, Guan K, Czyz J, Meyer M, Wobus AM (2001) Differentiation of embryonic stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons is enhanced by survival-promoting factors. Mech Dev 105:93–104
Rosler ES, Fisk GJ, Ares X, Irving J, Miura T, Rao MS, Carpenter MK (2004) Long-term culture of human embryonic stem cells in feeder-free conditions. Dev Dyn 229:259–274
Roy NS, Nakano T, Keyoung HM, Windrem M, Rashbaum WK, Alonso ML, Kang J, Peng W, Carpenter MK, Lin J, Nedergaard M, Goldman SA (2004) Telomerase immortalization of neuronally restricted progenitor cells derived from the human fetal spinal cord. Nat Biotechnol 22:297–305
Rubio FJ, Bueno C, Villa A, Navarro B, Martinez-Serrano A (2000) Genetically perpetuated human neural stem cells engraft and differentiate into the adult mammalian brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 16:1–13
Ryder EF, Snyder EY, Cepko CL (1990) Establishment and characterization of multipotent neural cell lines using retrovirus vector-mediated oncogene transfer. J Neurobiol 21:356–375
Sah DW, Ray J, Gage FH (1997) Bipotent progenitor cell lines from the human CNS. Nat Biotechnol 15:574–580
Sakurada K, Ohshima-Sakurada M, Palmer TD, Gage FH (1999) Nurr1, an orphan nuclear receptor, is a transcriptional activator of endogenous tyrosine hydroxylase in neural progenitor cells derived from the adult brain. Development 126:4017–4026
Saucedo-Cardenas O, Quintana-Hau JD, Le WD, Smidt MP, Cox JJ, De Mayo F, Burbach JP, Conneely OM (1998) Nurr1 is essential for the induction of the dopaminergic phenotype and the survival of ventral mesencephalic late dopaminergic precursor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4013–4018
Sauer H, Oertel WH (1994) Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: a combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 59:401–415
Schulz TC, Palmarini GM, Noggle SA, Weiler DA, Mitalipova MM, Condie BG (2003) Directed neuronal differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. BMC Neurosci 4:27
Shamblott MJ, Axelman J, Wang S, Bugg EM, Littlefield JW, Donovan PJ, Blumenthal PD, Huggins GR, Gearhart JD (1998) Derivation of pluripotent stem cells from cultured human primordial germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13726–13731
Shamblott MJ, Axelman J, Littlefield JW, Blumenthal PD, Huggins GR, Cui Y, Cheng L, Gearhart JD (2001) Human embryonic germ cell derivatives express a broad range of developmentally distinct markers and proliferate extensively in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:113–118
Sharma HW, Sokoloski JA, Perez JR, Maltese JY, Sartorelli AC, Stein CA, Nichols G, Khaled Z, Telang NT, Narayanan R (1995) Differentiation of immortal cells inhibits telomerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:12343–12346
Shim JW, Koh HC, Chang MY, Roh E, Choi CY, Oh YJ, Son H, Lee YS, Studer L, Lee SH (2004) Enhanced in vitro midbrain dopamine neuron differentiation, dopaminergic function, neurite outgrowth, and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridium resistance in mouse embryonic stem cells overexpressing Bcl-XL. J Neurosci 24:843–852
Smidt MP, Schaick HS van, Lanctot C, Tremblay JJ, Cox JJ, Kleij AA van der, Wolterink G, Drouin J, Burbach JP (1997) A homeodomain gene Ptx3 has highly restricted brain expression in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13305–13310
Smidt MP, Asbreuk CH, Cox JJ, Chen H, Johnson RL, Burbach JP (2000) A second independent pathway for development of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons requires Lmx1b. Nat Neurosci 3:337–341
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Bouwmeester H, Hamers FP, Linden AJ van der, Hellemons AJ, Graw J, Burbach JP (2004) Early developmental failure of substantia nigra dopamine neurons in mice lacking the homeodomain gene Pitx3. Development 131:1145–1155
Snyder EY, Deitcher DL, Walsh C, Arnold-Aldea S, Hartwieg EA, Cepko CL (1992) Multipotent neural cell lines can engraft and participate in development of mouse cerebellum. Cell 68:33–51
Snyder EY, Yoon C, Flax JD, Macklis JD (1997) Multipotent neural precursors can differentiate toward replacement of neurons undergoing targeted apoptotic degeneration in adult mouse neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:11663–11668
Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Kim KS, Isacson O (2004) Temporally induced Nurr1 can induce a non-neuronal dopaminergic cell type in embryonic stem cell differentiation. Eur J Neurosci 19:1141–1152
Studer L, Tabar V, McKay RD (1998) Transplantation of expanded mesencephalic precursors leads to recovery in parkinsonian rats. Nat Neurosci 1:290–295
Svendsen CN, Caldwell MA, Shen J, Borg MG ter, Rosser AE, Tyers P, Karmiol S, Dunnett SB (1997) Long-term survival of human central nervous system progenitor cells transplanted into a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 148:135–146
Tang K, Yang J, Gao X, Wang C, Liu L, Kitani H, Atsumi T, Jing N (2002) Wnt-1 promotes neuronal differentiation and inhibits gliogenesis in P19 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:167–173
Thomson JA, Kalishman J, Golos TG, Durning M, Harris CP, Becker RA, Hearn JP (1995) Isolation of a primate embryonic stem cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7844–7848
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282:1145–1147
Tropepe V, Hitoshi S, Sirard C, Mak TW, Rossant J, Kooy D van der (2001) Direct neural fate specification from embryonic stem cells: a primitive mammalian neural stem cell stage acquired through a default mechanism. Neuron 30:65–78
Vassilopoulos G, Wang PR, Russell DW (2003) Transplanted bone marrow regenerates liver by cell fusion. Nature 422:901–904
Villa A, Snyder EY, Vescovi A, Martinez-Serrano A (2000) Establishment and properties of a growth factor-dependent, perpetual neural stem cell line from the human CNS. Exp Neurol 161:67–84
Villa A, Navarro B, Martinez-Serrano A (2002) Genetic perpetuation of in vitro expanded human neural stem cells: cellular properties and therapeutic potential. Brain Res Bull 57:789–794
Vitry S, Bertrand JY, Cumano A, Dubois-Dalcq M (2003) Primordial hematopoietic stem cells generate microglia but not myelin-forming cells in a neural environment. J Neurosci 23:10724–10731
Wagner J, Akerud P, Castro DS, Holm PC, Canals JM, Snyder EY, Perlmann T, Arenas E (1999) Induction of a midbrain dopaminergic phenotype in Nurr1-overexpressing neural stem cells by type 1 astrocytes. Nat Biotechnol 17:653–659
Wakayama T, Tabar V, Rodriguez I, Perry AC, Studer L, Mombaerts P (2001) Differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines generated from adult somatic cells by nuclear transfer. Science 292:740–743
Wakitani S, Takaoka K, Hattori T, Miyazawa N, Iwanaga T, Takeda S, Watanabe TK, Tanigami A (2003) Embryonic stem cells injected into the mouse knee joint form teratomas and subsequently destroy the joint. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42:162–165
Wallen-Mackenzie A, de Urquiza AM, Petersson S, Rodriguez FJ, Friling S, Wagner J, Ordentlich P, Lengqvist J, Heyman RA, Arenas E, Perlmann T (2003) Nurr1-RXR heterodimers mediate RXR ligand-induced signaling in neuronal cells. Genes Dev 17:3036–3047
Wang X, Willenbring H, Akkari Y, Torimaru Y, Foster M, Al-Dhalimy M, Lagasse E, Finegold M, Olson S, Grompe M (2003) Cell fusion is the principal source of bone-marrow-derived hepatocytes. Nature 422:897–901
Weimann JM, Johansson CB, Trejo A, Blau HM (2003) Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant. Nat Cell Biol 5:959–966
Westerman KA, Leboulch P (1996) Reversible immortalization of mamalian cells mediated by retroviral transfer and site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8971–8976
Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, Black IB (2000) Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res 61:364–370
Wu KJ, Grandori C, Amacker M, Simon-Vermot N, Polack A, Lingner J, Dalla-Favera R (1999) Direct activation of TERT transcription by c-MYC. Nat Genet 21:220–224
Xu C, Inokuma MS, Denham J, Golds K, Kundu P, Gold JD, Carpenter MK (2001) Feeder-free growth of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 19:971–974
Yan J, Studer L, McKay RD (2001) Ascorbic acid increases the yield of dopaminergic neurons derived from basic fibroblast growth factor expanded mesencephalic precursors. J Neurochem 76:307–311
Zetterstrom RH, Solomin L, Jansson L, Hoffer BJ, Olson L, Perlmann T (1997) Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science 276:248–250
Zhao S, Maxwell S, Jimenez-Beristain A, Vives J, Kuehner E, Zhao J, O’Brien C, de Felipe C, Semina E, Li M (2004) Generation of embryonic stem cells and transgenic mice expressing green fluorescence protein in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 19:1133–1140
Acknowledgment
We thank Emma Lane for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Our work described in this article was supported by the National Institute of Health, USA, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Parkinson’s Disease Foundation, the Syskonen Svenssons Foundation, an USAMRMC grant, and an ATV grant
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roybon, L., Christophersen, N.S., Brundin, P. et al. Stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease: where do we stand?. Cell Tissue Res 318, 261–273 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0946-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0946-y