Abstract
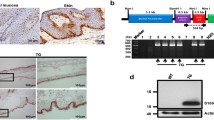
We have generated transgenic mice harboring the murine matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) promoter cloned in front of human TIMP-1 cDNA. The transgenic mice were viable and fertile and exhibited normal growth and general development. During wound healing the mice were shown to express human TIMP-1 in keratinocytes that normally express MMP-9. However, the healing of skin wounds was significantly retarded with slow migration of keratinocytes over the wound in transgenic mice. In situ zymography carried out on wound tissues revealed total blockage of gelatinolytic activity (i.e., MMP-9 and MMP-2). The results confirm studies with MMP-9 knockout mice showing that MMP-9 is not essential for general development, but they also demonstrate an important role of keratinocyte MMP-9, as well that of other keratinocyte MMPs that are inhibited by TIMP-1, in wound healing. The transgenic mice generated in this study provide a model for the role of MMPs in MMP-9-producing cells in other challenging situations such as bone fracture recovery and cancer invasion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott RE, Corral CJ, MacIvor DM, Lin X, Ley TJ, Mustoe TA (1998) Augmented inflammatory responses and altered wound healing in cathepsin G-deficient mice. Arch Surg 133:1002–1006
Agren MS (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are required for re-epithelialization of cutaneous wounds. Arch Dermatol Res 291:583–590
Agren MS, Mirastschijski U, Karlsmark T, Saarialho-Kere UK (2001) Topical synthetic inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases delays epidermal regeneration of human wounds. Exp Dermatol 10:337–348
Apte SS, Mattei MG, Olsen BR (1994) Cloning of the cDNA encoding human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) and mapping of the TIMP3 gene to chromosome 22. Genomics 19:86–90
Balbin M, Fueyo A, Knauper V, Lopez JM, Alvarez J, Sanchez LM, Quesada V, Bordallo J, Murphy G, Lopez-Otin C (2001) Identification and enzymatic characterization of two diverging murine counterparts of human interstitial collagenase (MMP-1) expressed at sites of embryo implantation. J Biol Chem 276:10253–10262
Bancroft JD, Stevens A (eds) (1990) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK
Behringer RR, Crotty DA, Tennyson VM, Brinster RL, Palmiter RD, Wolgemuth DJ (1993) Sequences 5’ of the homeobox of the Hox-1.4 gene direct tissue-specific expression of lacZ during mouse development. Development 117:823–833
Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WG, Bodden MK, Windsor LJ, Birkedal-Hansen B, DeCarlo A, Engler JA (1993) Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 4:197–250
Carmichael DF, Sommer A, Thompson RC, Anderson DC, Smith CG, Welgus HG, Stricklin GP (1986) Primary structure and cDNA cloning of human fibroblast collagenase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:2407–2411
Clark RAF (ed) (1996) The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair. Plenum Press, New York
Daci E, Udagawa N, Martin TJ, Bouillon R, Carmeliet G (1999) The role of the plasminogen system in bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 14:946–952
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Libby P (1995) Microscopic localization of active proteases by in situ zymography: detection of matrix metalloproteinase activity in vascular tissue. FASEB J 9:974–980
Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Yoshiji H, Thorgeirsson UP (1997) Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur J Cell Biol 74:111–122
Hanley T, Merlie JP (1991) Transgene detection in unpurified mouse tail DNA by polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques 10:56
Hernandez-Barrantes S, Bernardo M, Toth M, Fridman R (2002) Regulation of membrane type-matrix metalloproteinases. Semin Cancer Biol 12:131–138
Hogan B, Beddington R, Constantini F, Lacy E (1986) Manipulating the mouse embryo: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Hurskainen T, Soini Y, Tuuttila A, Höyhtyä M, Oikarinen A, Autio-Harmainen H (1996) Expression of the tissue metalloproteinase inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in malignant fibrous histiocytomas and dermatofibromas as studied by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Hum Pathol 27:42–49
Inaoka T, Bilbe G, Ishibashi O, Tezuka K, Kumegawa M, Kokubo T (1995) Molecular cloning of human cDNA for cathepsin K: novel cysteine proteinase predominantly expressed in bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 206:89–96
Koivunen E, Arap W, Valtanen H, Rainisalo A, Medina OP, Heikkila P, Kantor C, Gahmberg CG, Salo T, Konttinen YT, Sorsa T, Ruoslahti E, Pasqualini R (1999) Tumor targeting with a selective gelatinase inhibitor. Nat Biotechnol 17:768–774
Leco KJ, Khokha R, Pavloff N, Hawkes SP, Edwards DR (1994) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) is an extracellular matrix-associated protein with a distinctive pattern of expression in mouse cells and tissues. J Biol Chem 269:9352–9360
Leco KJ, Apte SS, Taniguchi GT, Hawkes SP, Khokha R, Schultz GA, Edwards DR (1997) Murine tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4 (Timp-4): cDNA isolation and expression in adult mouse tissues. FEBS Lett 401:213–217
Lund LR, Romer J, Bugge TH, Nielsen BS, Frandsen TL, Degen JL, Stephens RW, Dano K (1999) Functional overlap between two classes of matrix-degrading proteases in wound healing. EMBO J 18:4645–4656
Madlener M (1998) Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their physiological inhibitors in acute murine skin wounds. Arch Dermatol Res 290 Suppl: S24–29
Madlener M, Parks WC, Werner S (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their physiological inhibitors (TIMPs) are differentially expressed during excisional skin wound repair. Exp Cell Res 242:201–210
Mainardi CL, Hibbs MS, Hasty KA, Seyer JM (1984) Purification of a type V collagen degrading metalloproteinase from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Coll Relat Res 4:479–492
Mäkelä M, Larjava H, Pirilä E, Maisi P, Salo T, Sorsa T, Uitto VJ (1999) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (gelatinase A) is related to migration of keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res 251:67–78
Mignatti P, Rifkin D, Welgus H, Parks W (1996) In: Clark RAF (ed) The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York, pp 427–442
Munaut C, Salonurmi T, Kontusaari S, Reponen P, Morita T, Foidart JM, Tryggvason K (1999) Murine matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene. 5’-upstream region contains cis-acting elements for expression in osteoclasts and migrating keratinocytes in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 274:5588–5596
Nelson AR, Fingleton B, Rothenberg ML, Matrisian LM (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol 18:1135–1149
Ohsawa Y, Nitatori T, Higuchi S, Kominami E, Uchiyama Y (1993) Lysosomal cysteine and aspartic proteinases, acid phosphatase, and an endogenous cysteine proteinase inhibitor, cystatin-beta, in rat osteoclasts. J Histochem Cytochem 41:1075–1083
Okada A, Tomasetto C, Lutz Y, Bellocq JP, Rio MC, Basset P (1997) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases during rat skin wound healing: evidence that membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase is a stromal activator of pro-gelatinase A. J Cell Biol 137:67–77
Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Van Damme J (2001) Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol 22:571–579
Parikka M, Kainulainen T, Tasanen K, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Salo T (2001) Altered expression of collagen XVII in ameloblastomas and basal cell carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med 30:589–595
Pirilä E, Maisi P, Salo T, Koivunen E, Sorsa T (2001) In vivo localization of gelatinases (MMP-2 and -9) by in situ zymography with a selective gelatinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287:766–774
Quantin B, Murphy G, Breathnach R (1989) Pump-1 cDNA codes for a protein with characteristics similar to those of classical collagenase family members. Biochemistry 28:5327–5334
Rantakokko J, Aro HT, Savontaus M, Vuorio E (1996) Mouse cathepsin K: cDNA cloning and predominant expression of the gene in osteoclasts, and in some hypertrophying chondrocytes during mouse development. FEBS Lett 393:307–313
Reponen P, Sahlberg C, Munaut C, Thesleff I, Tryggvason K (1994) High expression of 92-kD type IV collagenase (gelatinase B) in the osteoclast lineage during mouse development. J Cell Biol 124:1091–1102
Reponen P, Leivo I, Sahlberg C, Apte SS, Olsen BR, Thesleff I, Tryggvason K (1995) 92-kDa type IV collagenase and TIMP-3, but not 72-kDa type IV collagenase or TIMP-1 or TIMP-2, are highly expressed during mouse embryo implantation. Dev Dyn 202:388–396
Saarialho-Kere UK, Chang ES, Welgus HG, Parks WC (1992) Distinct localization of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases expression in wound healing associated with ulcerative pyogenic granuloma. J Clin Invest 90:1952–1957
Salo T, Makela M, Kylmaniemi M, Autio-Harmainen H, Larjava H (1994) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 during early human wound healing. Lab Invest 70:176–182
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y, Cao J, Shinagawa A, Yamamoto E, Seiki M (1994) A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature 370:61–65
Sato T, del Carmen Ovejero M, Hou P, Heegaard AM, Kumegawa M, Foged NT, Delaisse JM (1997) Identification of the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP in osteoclasts. J Cell Sci 110:589–596
Shapiro SD, Kobayashi DK, Ley TJ (1993) Cloning and characterization of a unique elastolytic metalloproteinase produced by human alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem 268:23824–23829
Soo C, Shaw WW, Zhang X, Longaker MT, Howard EW, Ting K (2000) Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue-derived inhibitors in cutaneous wound repair. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:638–647
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Krutzsch HC, Liotta LA (1989) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). A new member of the metalloproteinase inhibitor family. J Biol Chem 264:17374–17378
Sudbeck BD, Pilcher BK, Welgus HG, Parks WC (1997) Induction and repression of collagenase-1 by keratinocytes is controlled by distinct components of different extracellular matrix compartments. J Biol Chem 272:22103–22110
Vaalamo M, Leivo T, Saarialho-Kere U (1999) Differential expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1, -2, -3, and -4) in normal and aberrant wound healing. Hum Pathol 30:795–802
Will H, Hinzmann B (1995) cDNA sequence and mRNA tissue distribution of a novel human matrix metalloproteinase with a potential transmembrane segment. Eur J Biochem 231:602–608
Woessner JF Jr, Taplin CJ (1988) Purification and properties of a small latent matrix metalloproteinase of the rat uterus. J Biol Chem 263:16918–16925
Vu TH, Shipley JM, Bergers G, Berger JE, Helms JA, Hanahan D, Shapiro SD, Senior RM, Werb Z (1998) MMP-9/gelatinase B is a key regulator of growth plate angiogenesis and apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Cell 93:411–422
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The expert technical assistance of M. Jarva, L. Ollitervo, S. Kangas, and R. Jokisalo is gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported in part by grants from the Finnish Academy of Science, the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Novo Nordisk Foundation and EC contract QLG1-CT-2000-01131 (K.T.), the Finnish Dental Society Apollonia and the Northern Finland Cancer Foundation (M.P.), as well as the K. Albin Johansson Foundation and the Einar and Karin Stroems Foundation (E.P.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salonurmi, T., Parikka, M., Kontusaari, S. et al. Overexpression of TIMP-1 under the MMP-9 promoter interferes with wound healing in transgenic mice. Cell Tissue Res 315, 27–37 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0814-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0814-1