Abstract
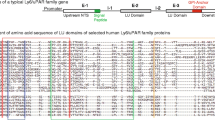
In both Aspergillus nidulans and the mouse, studies of the nuclear distribution gene C (NudC) have strongly suggested that the NudC protein interacts with NudF, which is the product of NudF, a homologue of human LIS1 (also know as PAFAH1B1), one of the causative genes for classical lissencephaly. We have isolated the human NUDC gene and its two processed pseudogenes. The human NUDC gene is highly conserved and its predicted amino acid sequence shows 94% identity to mouse NudC and 95% identity to rat NudC. The genomic structure of NUDC, its chromosomal localization, and expression pattern in human tissues were characterized. NUDC consists of at least 9 exons ranging from 66 bp to 266 bp in size and 8 introns from 92 bp to 2.0 kb in length, and the total genomic region spans about 8 kb. NUDC was mapped to 1p34-p35 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Northern analysis showed a major 1.6 kb transcript in all fetal and adult tissues examined. Primers which amplify individual exons of NUDC were developed for mutation analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 February 1999 / Accepted: 5 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, N., Ledbetter, D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human NUDC gene. Hum Genet 104, 498–504 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050994
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050994