Abstract
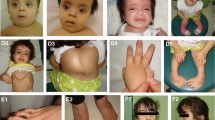
Autosomal recessive cutis laxa (ARCL) syndromes are phenotypically overlapping, but genetically heterogeneous disorders. Mutations in the ATP6V0A2 gene were found to underlie both, autosomal recessive cutis laxa type 2 (ARCL2), Debré type, and wrinkly skin syndrome (WSS). The ATP6V0A2 gene encodes the a2 subunit of the V-type H+-ATPase, playing a role in proton translocation, and possibly also in membrane fusion. Here, we describe a highly variable phenotype in 13 patients with ARCL2, including the oldest affected individual described so far, who showed strikingly progressive dysmorphic features and heterotopic calcifications. In these individuals we identified 17 ATP6V0A2 mutations, 14 of which are novel. Furthermore, we demonstrate a localization of ATP6V0A2 at the Golgi-apparatus and a loss of the mutated ATP6V0A2 protein in patients’ dermal fibroblasts. Investigation of brefeldin A-induced Golgi collapse in dermal fibroblasts as well as in HeLa cells deficient for ATP6V0A2 revealed a delay, which was absent in cells deficient for the ARCL-associated proteins GORAB or PYCR1. Furthermore, fibroblasts from patients with ATP6V0A2 mutations displayed elevated TGF-β signalling and increased TGF-β1 levels in the supernatant. Our current findings expand the genetic and phenotypic spectrum and suggest that, besides the known glycosylation defect, alterations in trafficking and signalling processes are potential key events in the pathogenesis of ATP6V0A2-related ARCL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht B, de Brouwer AP, Lefeber DJ, Cremer K, Hausser I, Rossen N, Wortmann SB, Wevers RA, Kornak U, Morava E (2011) MACS syndrome: a combined collagen and elastin disorder due to abnormal Golgi trafficking. Am J Med Genet A 152A:2916–2918
Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB (2003) Making sense of latent TGFβ activation. J Cell Sci 116:217–224
Barzilay E, Ben-Califa N, Hirschberg K, Neumann D (2005) Uncoupling of brefeldin a-mediated coatomer protein complex-I dissociation from Golgi redistribution. Traffic 6:794–802. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00317.x
Bascom CC, Wolfshohl JR, Coffey RJ Jr, Madisen L, Webb NR, Purchio AR, Derynck R, Moses HL (1989) Complex regulation of transforming growth factor beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3 mRNA expression in mouse fibroblasts and keratinocytes by transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2. Mol Cell Biol 9:5508–5515
Basel-Vanagaite L, Sarig O, Hershkovitz D, Fuchs-Telem D, Rapaport D, Gat A, Isman G, Shirazi I, Shohat M, Enk CD, Birk E, Kohlhase J, Matysiak-Scholze U, Maya I, Knopf C, Peffekoven A, Hennies HC, Bergman R, Horowitz M, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Sprecher E (2009) RIN2 deficiency results in macrocephaly, alopecia, cutis laxa, and scoliosis: MACS syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 85:254–263
Beyenbach KW, Wieczorek H (2006) The V-type H+ ATPase: molecular structure and function, physiological roles and regulation. J Exp Biol 209:577–589
Bicknell LS, Pitt J, Aftimos S, Ramadas R, Maw MA, Robertson SP (2008) A missense mutation in ALDH18A1, encoding Delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS), causes an autosomal recessive neurocutaneous syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 16:1176–1186
Callewaert B, Renard M, Hucthagowder V, Albrecht B, Hausser I, Blair E, Dias C, Albino A, Wachi H, Sato F, Mecham RP, Loeys B, Coucke PJ, De Paepe A, Urban Z (2011) New insights into the pathogenesis of autosomal-dominant cutis laxa with report of five ELN mutations. Hum Mutat 32:445–455
Chen YG (2009) Endocytic regulation of TGF-β signaling. Cell Res 19:58–70. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.315
de Barsy AM, Moens E, Dierckx L (1968) Dwarfism, oligophrenia and degeneration of the elastic tissue in skin and cornea. A new syndrome? Helv Paediatr Acta 23:305–313
Detorakis ET, Spandidos DA (2009) Pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment options for ophthalmic pterygium: trends and perspectives (review). Int J Mol Med 23:439–447
Dietz HC (2010) TGF-β in the pathogenesis and prevention of disease: a matter of aneurysmic proportions. J Clin Invest 120:403–407. doi:10.1172/JCI42014
Flanagan-Steet H, Johnson S, Smith RD, Bangiyeva J, Lupashin V, Steet R (2011) Mislocalization of large ARF-GEFs as a potential mechanism for BFA resistance in COG-deficient cells. Exp Cell Res 317:2342–2352. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.06.005
Guillard M, Dimopoulou A, Fischer B, Morava E, Lefeber DJ, Kornak U, Wevers RA (2009) Vacuolar H+-ATPase meets glycosylation in patients with cutis laxa. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:903–914
Hendricks LC, McClanahan SL, McCaffery M, Palade GE, Farquhar MG (1992) Golgi proteins persist in the tubulovesicular remnants found in brefeldin A-treated pancreatic acinar cells. Eur J Cell Biol 58:202–213
Hennies HC, Kornak U, Zhang H, Egerer J, Zhang X, Seifert W, Kuhnisch J, Budde B, Natebus M, Brancati F, Wilcox WR, Muller D, Kaplan PB, Rajab A, Zampino G, Fodale V, Dallapiccola B, Newman W, Metcalfe K, Clayton-Smith J, Tassabehji M, Steinmann B, Barr FA, Nurnberg P, Wieacker P, Mundlos S (2008) Gerodermia osteodysplastica is caused by mutations in SCYL1BP1, a Rab-6 interacting golgin. Nat Genet 40:1410–1412
Hoyer J, Kraus C, Hammersen G, Geppert JP, Rauch A (2009) Lethal cutis laxa with contractural arachnodactyly, overgrowth and soft tissue bleeding due to a novel homozygous fibulin-4 gene mutation. Clin Genet 76:276–281
Hucthagowder V, Sausgruber N, Kim KH, Angle B, Marmorstein LY, Urban Z (2006) Fibulin-4: a novel gene for an autosomal recessive cutis laxa syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 78:1075–1080
Hucthagowder V, Morava E, Kornak U, Lefeber DJ, Fischer B, Dimopoulou A, Aldinger A, Choi J, Davis EC, Abuelo DN, Adamowicz M, Al-Aama J, Basel-Vanagaite L, Fernandez B, Greally MT, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Kayserili H, Lemyre E, Tekin M, Turkmen S, Tuysuz B, Yuksel-Konuk B, Mundlos S, Van Maldergem L, Wevers RA, Urban Z (2009) Loss-of-function mutations in ATP6V0A2 impair vesicular trafficking, tropoelastin secretion and cell survival. Hum Mol Genet 18:2149–2165
Hurtado-Lorenzo A, Skinner M, El Annan J, Futai M, Sun-Wada GH, Bourgoin S, Casanova J, Wildeman A, Bechoua S, Ausiello DA, Brown D, Marshansky V (2006) V-ATPase interacts with ARNO and Arf6 in early endosomes and regulates the protein degradative pathway. Nat Cell Biol 8:124–136
Jefferies KC, Cipriano DJ, Forgac M (2008) Function, structure and regulation of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPases. Arch Biochem Biophys 476:33–42
Kawasaki-Nishi S, Nishi T, Forgac M (2003) Proton translocation driven by ATP hydrolysis in V-ATPases. FEBS Lett 545:76–85
Kornak U (2011) Animal models with pathological mineralization phenotypes. Jt Bone Spine 78:561–567. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.03.020
Kornak U, Reynders E, Dimopoulou A, van Reeuwijk J, Fischer B, Rajab A, Budde B, Nurnberg P, Foulquier F, Lefeber D, Urban Z, Gruenewald S, Annaert W, Brunner HG, van Bokhoven H, Wevers R, Morava E, Matthijs G, Van Maldergem L, Mundlos S (2008) Impaired glycosylation and cutis laxa caused by mutations in the vesicular H+-ATPase subunit ATP6V0A2. Nat Genet 40:32–34
Kunze J, Majewski F, Montgomery P, Hockey A, Karkut I, Riebel T (1985) De Barsy syndrome—an autosomal recessive, progeroid syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 144:348–354
Loeys B, Van Maldergem L, Mortier G, Coucke P, Gerniers S, Naeyaert JM, De Paepe A (2002) Homozygosity for a missense mutation in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) results in a severe form of cutis laxa. Hum Mol Genet 11:2113–2118
McHenry P, Wang WL, Devitt E, Kluesner N, Davisson VJ, McKee E, Schweitzer D, Helquist P, Tenniswood M (2010) Iejimalides A and B inhibit lysosomal vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) activity and induce S-phase arrest and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. J Cell Biochem 109:634–642
Mohamed M, Guillard M, Wortmann SB, Cirak S, Marklova E, Michelakakis H, Korsch E, Adamowicz M, Koletzko B, van Spronsen FJ, Niezen-Koning KE, Matthijs G, Gardeitchik T, Kouwenberg D, Lim BC, Zeevaert R, Wevers RA, Lefeber DJ, Morava E (2011a) Clinical and diagnostic approach in unsolved CDG patients with a type 2 transferrin pattern. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:691–698. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.02.011
Mohamed M, Kouwenberg D, Gardeitchik T, Kornak U, Wevers RA, Morava E (2011b) Metabolic cutis laxa syndromes. J Inherit Metab Dis 34:907–916. doi:10.1007/s10545-011-9305-9
Morava E, Wopereis S, Coucke P, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Voit T, Smeitink J, Wevers R, Grunewald S (2005) Defective protein glycosylation in patients with cutis laxa syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 13:414–421
Morava E, Zeevaert R, Korsch E, Huijben K, Wopereis S, Matthijs G, Keymolen K, Lefeber DJ, De Meirleir L, Wevers RA (2007) A common mutation in the COG7 gene with a consistent phenotype including microcephaly, adducted thumbs, growth retardation, VSD and episodes of hyperthermia. Eur J Hum Genet 15:638–645
Morava E, Guillard M, Lefeber DJ, Wevers RA (2009a) Autosomal recessive cutis laxa syndrome revisited. Eur J Hum Genet 17:1099–1110
Morava E, Wevers RA, Willemsen MA, Lefeber D (2009b) Cobblestone-like brain dysgenesis and altered glycosylation in congenital cutis laxa, Debre type. Neurology 73:1164 (author reply 1164–1165)
Nishi T, Forgac M (2002) The vacuolar (H+)-ATPases—nature’s most versatile proton pumps. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:94–103
Noordam C, Funke S, Knoers NV, Jira P, Wevers RA, Urban Z, Morava E (2009) Decreased bone density and treatment in patients with autosomal recessive cutis laxa. Acta Paediatr 98:490–494
Ntrivalas E, Gilman-Sachs A, Kwak-Kim J, Beaman K (2007) The N-terminus domain of the a2 isoform of vacuolar ATPase can regulate interleukin-1β production from mononuclear cells in co-culture with JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells. Am J Reprod Immunol 57:201–209
Rajab A, Kornak U, Budde BS, Hoffmann K, Jaeken J, Nurnberg P, Mundlos S (2008) Geroderma osteodysplasticum hereditaria and wrinkly skin syndrome in 22 patients from Oman. Am J Med Genet A 146A:965–976
Reversade B, Escande-Beillard N, Dimopoulou A, Fischer B, Chng SC, Li Y, Shboul M, Tham PY, Kayserili H, Al-Gazali L, Shahwan M, Brancati F, Lee H, O’Connor BD, Schmidt-von Kegler M, Merriman B, Nelson SF, Masri A, Alkazaleh F, Guerra D, Ferrari P, Nanda A, Rajab A, Markie D, Gray M, Nelson J, Grix A, Sommer A, Savarirayan R, Janecke AR, Steichen E, Sillence D, Hausser I, Budde B, Nurnberg G, Nurnberg P, Seemann P, Kunkel D, Zambruno G, Dallapiccola B, Schuelke M, Robertson S, Hamamy H, Wollnik B, Van Maldergem L, Mundlos S, Kornak U (2009) Mutations in PYCR1 cause cutis laxa with progeroid features. Nat Genet 41:1016–1021
Saito T, Kinoshita A, Yoshiura K, Makita Y, Wakui K, Honke K, Niikawa N, Taniguchi N (2001) Domain-specific mutations of a transforming growth factor (TGF)-β 1 latency-associated peptide cause Camurati–Engelmann disease because of the formation of a constitutively active form of TGF-β 1. J Biol Chem 276:11469–11472. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000859200
Schwarz JM, Rodelsperger C, Schuelke M, Seelow D (2010) MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat Methods 7:575–576
Shestakova A, Zolov S, Lupashin V (2006) COG complex-mediated recycling of Golgi glycosyltransferases is essential for normal protein glycosylation. Traffic 7:191–204
Steet R, Kornfeld S (2006) COG-7-deficient human fibroblasts exhibit altered recycling of Golgi proteins. Mol Biol Cell 17:2312–2321
Sun-Wada GH, Tabata H, Kuhara M, Kitahara I, Takashima Y, Wada Y (2011) Generation of chicken monoclonal antibodies against the a1, a2, and a3 subunit isoforms of vacuolar-type proton ATPase. Hybridoma (Larchmt) 30:199–203
ten Dijke P, Arthur HM (2007) Extracellular control of TGFβ signalling in vascular development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:857–869
Urban Z, Hucthagowder V, Schurmann N, Todorovic V, Zilberberg L, Choi J, Sens C, Brown CW, Clark RD, Holland KE, Marble M, Sakai LY, Dabovic B, Rifkin DB, Davis EC (2009) Mutations in LTBP4 cause a syndrome of impaired pulmonary, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, musculoskeletal, and dermal development. Am J Hum Genet 85:593–605
Van Maldergem L, Yuksel-Apak M, Kayserili H, Seemanova E, Giurgea S, Basel-Vanagaite L, Leao-Teles E, Vigneron J, Foulon M, Greally M, Jaeken J, Mundlos S, Dobyns WB (2008) Cobblestone-like brain dysgenesis and altered glycosylation in congenital cutis laxa, Debre type. Neurology 71:1602–1608
Vanakker OM, Leroy BP, Schurgers LJ, Vermeer C, Coucke PJ, De Paepe A (2011) Atypical presentation of pseudoxanthoma elasticum with abdominal cutis laxa: evidence for a spectrum of ectopic calcification disorders? Am J Med Genet A 155A:2855–2859. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.34264
Wu X, Steet RA, Bohorov O, Bakker J, Newell J, Krieger M, Spaapen L, Kornfeld S, Freeze HH (2004) Mutation of the COG complex subunit gene COG7 causes a lethal congenital disorder. Nat Med 10:518–523
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the patients and their family members whose cooperation made this study possible. We would like to thank the family of patient 2 especially for their great contribution and interest in our work. We thank Traute Burmester for her excellent help with fibroblast cultivation from skin biopsies. We additionally thank E. Ntrivalas for providing the ATP6V0A2 antibody. This study was funded by the Fritz Thyssen Stiftung to Uwe Kornak.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Egerer and T. Gardeitchik contributed equally. B. Fischer and A. Dimopoulou contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1 Control experiments: Target mRNA expression in patient fibroblasts and HeLa cells after RNAi. a ATP6V0A2 mRNA level was determined by quantitative PCR in patient and control dermal fibroblasts. In patient 5 and 2 a significant reduction of ATP6V0A2 mRNA was detectable whereas in patient 10 transcript levels were almost unchanged. b Verification of target gene knockdown efficiency upon 72 h RNAi by quantitative PCR.
Supplementary Fig. 2 Control experiments: Specificity of delayed retrograde trafficking defect after brefeldin A treatment in HeLa cells upon RNAi. The experiment was performed in HeLa cells after 72 h RNA interference. After 10 min of 5 μg/ml brefeldin A treatment, 20 % of control cells and 60 % of ATP6V0A2-depleted cells had incompletely collapsed Golgi structures, respectively. GORAB- as well as PYCR1-depleted cells behaved similar like control cells. All experiments were done at least three times and errors are given as SEM.
Supplementary Fig. 3 ATP6V0A2 and TGFB1 expression level in three day confluent fibroblasts. To investigate whether elevated TGF-β1 levels are due to transcriptional upregulation we determined TGFB1 mRNA levels. As control we measured ATP6V0A2 mRNA and found on average a ~50 % reduction whereas TGFB1 remained unchanged. P-values were determined by t test.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, B., Dimopoulou, A., Egerer, J. et al. Further characterization of ATP6V0A2-related autosomal recessive cutis laxa. Hum Genet 131, 1761–1773 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-012-1197-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-012-1197-8