Abstract
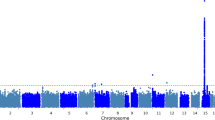
African Americans have increased susceptibility to non-diabetic (non-DM) forms of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and extensive evidence supports a genetic contribution. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) using pooled DNA was performed in 1,000 African Americans to detect associated genes. DNA from 500 non-DM ESRD cases and 500 non-nephropathy controls was quantified using gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometric analysis and pools of 50 case and 50 control DNA samples were created. DNA pools were genotyped in duplicate on the Illumina HumanHap550-Duo BeadChip. Normalization methods were developed and applied to array intensity values to reduce inter-array variance. Allele frequencies were calculated from normalized channel intensities and compared between case and control pools. Three SNPs had p values of <1.0E−6: rs4462445 (ch 13), rs4821469 (ch 22) and rs8077346 (ch 17). After normalization, top scoring SNPs (n = 65) were genotyped individually in 464 of the original cases and 478 of the controls, with replication in 336 non-DM ESRD cases and 363 non-nephropathy controls. Sixteen SNPs were associated with non-DM ESRD (p < 7.7E−4, Bonferroni corrected). Twelve of these SNPs are in or near the MYH9 gene. The four non-MYH9 SNPs that were associated with non-DM ESRD in the pooled samples were not associated in the replication set. Five SNPs that were modestly associated in the pooled samples were more strongly associated in the replication and/or combined samples. This is the first GWAS for non-DM ESRD in African Americans using pooled DNA. We demonstrate strong association between non-DM ESRD in African Americans with MYH9, and have identified additional candidate loci.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel LJ, Wright JT Jr, Greene T, Kusek JW, Lewis JB, Wang X, Lipkowitz MS, Norris KC, Bakris GL, Rahman M, Contreras G, Rostand SG, Kopple JD, Gabbai FB, Schulman GI, Gassman JJ, Charleston J, Agodoa LY (2008) Long-term effects of renin-angiotensin system-blocking therapy and a low blood pressure goal on progression of hypertensive chronic kidney disease in African Americans. Arch Intern Med 168:832–839
Chou JW, Paules RS, Bushel PR (2005) Systematic variation normalization in microarray data to get gene expression comparison unbiased. J Bioinform Comput Biol 3:225–241
Dusel JA, Burdon KP, Hicks PJ, Hawkins GA, Bowden DW, Freedman BI (2005) Identification of podocin (NPHS2) gene mutations in African Americans with nondiabetic end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 68:256–262
Freedman BI, Langefeld CD, Rich SS, Valis CJ, Sale MM, Williams AH, Brown WM, Beck SR, Hicks PJ, Bowden DW (2004) A genome scan for ESRD in black families enriched for nondiabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:2719–2727
Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Rich SS, Valis CJ, Sale MM, Hicks PJ, Langefeld CD (2005) A genome scan for all-cause end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:712–718
Freedman BI, Hicks PJ, Bostrom MA, Comeau ME, Divers J, Bleyer AJ, Kopp JB, Winkler CA, Nelson GW, Langefeld CD, Bowden DW (2009a) Non-muscle myosin heavy chain 9 gene MYH9 associations in African Americans with clinically diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated ESRD. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3366–3371
Freedman BI, Hicks PJ, Bostrom MA, Cunningham ME, Liu Y, Divers J, Kopp JB, Winkler CA, Nelson GW, Langefeld CD, Bowden DW (2009b) Polymorphisms in the non-muscle myosin heavy chain 9 gene (MYH9) are strongly associated with end-stage renal disease historically attributed to hypertension in African Americans. Kidney Int 75:736–745
Freedman BI, Kopp JB, Winkler CA, Nelson GW, Rao DC, Eckfeldt JH, Leppert MF, Hicks PJ, Divers J, Langefeld CD, Hunt SC (2009c) Polymorphisms in the nonmuscle myosin heavy chain 9 gene (MYH9) are associated with albuminuria in hypertensive African Americans: the HyperGEN study. Am J Nephrol 29:626–632
Freedman BI, Nagaraj SK, Lin JJ, Gautreaux MD, Bowden DW, Iskandar SS, Stratta RJ, Rogers J, Hartmann EL, Farney AC, Reeves-Daniel AM (2009d) Potential donor-recipient MYH9 genotype interactions in posttransplant nephrotic syndrome after pediatric kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 9:2435–2440
Hanson RL, Craig DW, Millis MP, Yeatts KA, Kobes S, Pearson JV, Lee AM, Knowler WC, Nelson RG, Wolford JK (2007) Identification of PVT1 as a candidate gene for end-stage renal disease in type 2 diabetes using a pooling-based genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism association study. Diabetes 56:975–983
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL, Tsao BP et al (2008) Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 40:204–210
Hicks PJ, Staten JL, Palmer ND, Langefeld CD, Ziegler JT, Keene KL, Sale MM, Bowden DW, Freedman BI (2008) Association analysis of the ephrin-B2 gene in African-Americans with end-stage renal disease. Am J Nephrol 28:914–920
Kao WH, Klag MJ, Meoni LA, Reich D, Berthier-Schaad Y, Li M, Coresh J et al (2008) MYH9 is associated with nondiabetic end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Nat Genet 40:1185–1192
Keene KL, Mychaleckyj JC, Leak TS, Smith SG, Perlegas PS, Divers J, Langefeld CD, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Sale MM (2008) Exploration of the utility of ancestry informative markers for genetic association studies of African Americans with type 2 diabetes and end stage renal disease. Hum Genet 124:147–154
Kirov G, Zaharieva I, Georgieva L, Moskvina V, Nikolov I, Cichon S, Hillmer A, Toncheva D, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC (2009) A genome-wide association study in 574 schizophrenia trios using DNA pooling. Mol Psychiatry 14:796–803
Kopp JB, Smith MW, Nelson GW, Johnson RC, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Oleksyk T, McKenzie LM, Kajiyama H, Ahuja TS, Berns JS, Briggs W, Cho ME, Dart RA, Kimmel PL, Korbet SM, Michel DM, Mokrzycki MH, Schelling JR, Simon E, Trachtman H, Vlahov D, Winkler CA (2008) MYH9 is a major-effect risk gene for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 40:1175–1184
Macgregor S, Zhao ZZ, Henders A, Nicholas MG, Montgomery GW, Visscher PM (2008) Highly cost-efficient genome-wide association studies using DNA pools and dense SNP arrays. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e35
Steer S, Abkevich V, Gutin A, Cordell HJ, Gendall KL, Merriman ME, Rodger RA, Rowley KA, Chapman P, Gow P, Harrison AA, Highton J, Jones PB, O’Donnell J, Stamp L, Fitzgerald L, Iliev D, Kouzmine A, Tran T, Skolnick MH, Timms KM, Lanchbury JS, Merriman TR (2007) Genomic DNA pooling for whole-genome association scans in complex disease: empirical demonstration of efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun 8:57–68
Steigert ML, Grab JD, Guy RT, Langefeld CD (2009) SNPGWA Version 4.0 (computer program). Public Health Sciences, Wake Forest University
U.S. Renal Data System (2008) Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Wang HT, Chang JW, Guo Z, Li BG (2007) In silico-initiated cloning and molecular characterization of cortexin 3, a novel human gene specifically expressed in the kidney and brain, and well conserved in vertebrates. Int J Mol Med 20:501–510
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by NIH Grants R01 DK 070941 (BIF) and R01 DK53591 (DWB), and by the NIDDK and NCI Intramural Research Programs. MAB was supported by F32 DK080617 from the NIDDK. We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of the participants as well as the physicians who were part of the study and the work of our study coordinators Joyce Byers, Carrie Smith, Mitzie Spainhour, Cassandra Bethea, and Sharon Warren.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bostrom, M.A., Lu, L., Chou, J. et al. Candidate genes for non-diabetic ESRD in African Americans: a genome-wide association study using pooled DNA. Hum Genet 128, 195–204 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0842-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0842-3