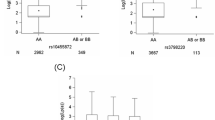
Abstract
The objective of this study was to determine whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the Interleukin-1 (IL-1) gene family are associated with central obesity and metabolic syndrome in a coronary heart disease population. The IL-1α C-889T (rs1800587) and IL-1β +3954 (rs1143634) SNPs were studied in a Western Australian coronary heart disease (CHD) population (N = 556). Subjects who were TT homozygous at either SNP had larger waist circumference (IL-1α: 1.8 cm greater, P = 0.04; IL-1β: 4 cm greater, P = 0.0004) compared with major allele homozygotes. Individuals with two copies of the IL-1α:IL-1β T:T haplotype had greater waist circumference (4.7 cm greater, P = 0.0001) compared to other haplotypes. There was a significant interaction between the IL-1β SNP and BMI level on waist circumference (P = 0.01). When the cohort was stratified by median BMI, TT carriers for IL-1β with above median BMI had greater waist circumference (6.1 cm greater, P = 0.007) compared to baseline carriers, whilst no significant association was seen in the below median group. Similarly, when the cohort was stratified by median fibrinogen level (IL-1α interaction P = 0.01; IL-1β interaction P = 0.04), TT carriers for both SNPs in the above median fibrinogen group had greater waist circumference (IL-1α 2.7 cm greater, P = 0.007; IL-1β 3.3 cm greater, P = 0.003) compared with major allele homozygotes. This association was not seen in the below median group. Also, we found a trend of increased metabolic syndrome for IL-1β TT homozygotes (P = 0.07). In conclusion, our findings suggest that in a CHD population IL-1 gene polymorphisms may be involved in increased central obesity, and the genetic influences are more evident among patients who have a higher level of obesity or inflammatory markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandraki K, Piperi C, Kalofoutis C, Singh J, Alaveras A, Kalofoutis A (2006) Inflammatory process in type 2 diabetes: the role of cytokines. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1084:89–117
Bruun JM, Pedersen SB, Kristensen K, Richelsen B (2002) Effects of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines on leptin production in human adipose tissue in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 190:91–99
Carter KW, McCaskie PA, Palmer LJ (2006) JLIN: a java based linkage disequilibrium plotter. BMC Bioinformatics 7:60
Chida D, Osaka T, Hashimoto O, Iwakura Y (2006) Combined interleukin-6 and interleukin-1 deficiency causes obesity in young mice. Diabetes 55:971–977
Di Renzo L, Bigioni M, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Barbini U, Di Lorenzo N, De Lorenzo A (2007) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist gene polymorphism in normal weight obese syndrome: relationship to body composition and IL-1 alpha and beta plasma levels. Pharmacol Res 55:131–138
Dinarello CA (1996) Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87:2095–2147
Dominici R, Cattaneo M, Malferrari G, Archi D, Mariani C, Grimaldi LM, Biunno I (2002) Cloning and functional analysis of the allelic polymorphism in the transcription regulatory region of interleukin-1 alpha. Immunogenetics 54:82–86
Engels EA, Wu X, Gu J, Dong Q, Liu J, Spitz MR (2007) Systematic evaluation of genetic variants in the inflammation pathway and risk of lung cancer. Cancer Res 67:6520–6527
Garcia MC, Wernstedt I, Berndtsson A, Enge M, Bell M, Hultgren O, Horn M, Ahren B, Enerback S, Ohlsson C, Wallenius V, Jansson JO (2006) Mature-onset obesity in interleukin-1 receptor I knockout mice. Diabetes 55:1205–1213
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F (2005) Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 112:2735–2752
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314
Jager J, Gremeaux T, Cormont M, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF (2007) Interleukin-1beta-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes through down-regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression. Endocrinology 148:241–251
de Jongh CM, Khrenova L, Kezic S, Rustemeyer T, Verberk MM, John SM (2008) Polymorphisms in the interleukin-1 gene influence the stratum corneum interleukin-1 alpha concentration in uninvolved skin of patients with chronic irritant contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis 58:263–268
Juge-Aubry CE, Somm E, Chicheportiche R, Burger D, Pernin A, Cuenod-Pittet B, Quinodoz P, Giusti V, Dayer JM, Meier CA (2004) Regulatory effects of interleukin (IL)-1, interferon-beta, and IL-4 on the production of IL-1 receptor antagonist by human adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2652–2658
Lorenzo C, Serrano-Rios M, Martinez-Larrad MT, Gonzalez-Sanchez JL, Seclen S, Villena A, Gonzalez-Villalpando C, Williams K, Haffner SM (2006) Geographic variations of the International Diabetes Federation and the National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III definitions of the metabolic syndrome in nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 29:685–691
McCaskie PA, Cadby G, Hung J, McQuillan BM, Chapman CM, Carter KW, Thompson PL, Palmer LJ, Beilby JP (2006) The C-480T hepatic lipase polymorphism is associated with HDL-C but not with risk of coronary heart disease. Clin Genet 70:114–121
McCaskie PA, Carter KW, Palmer LJ (2007) SimHap: a comprehensive modelling framework and a simulation-based approach to haplotypic analysis of population-based data. http://www.genepi.org.au/simhap
McQuillan BM, Beilby JP, Nidorf M, Thompson PL, Hung J (1999) Hyperhomocysteinemia but not the C677T mutation of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase is an independent risk determinant of carotid wall thickening. The Perth Carotid Ultrasound Disease Assessment Study (CUDAS). Circulation 99:2383–2388
Miller M, Rhyne J, Chen H, Beach V, Ericson R, Luthra K, Dwivedi M, Misra A (2007) APOC3 promoter polymorphisms C-482T and T-455C are associated with the metabolic syndrome. Arch Med Res 38:444–451
Pociot F, Molvig J, Wogensen L, Worsaae H, Nerup J (1992) A TaqI polymorphism in the human interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) gene correlates with IL-1 beta secretion in vitro. Eur J Clin Invest 22:396–402
Qatanani M, Lazar MA (2007) Mechanisms of obesity-associated insulin resistance: many choices on the menu. Genes Dev 21:1443–1455
Salmenniemi U, Ruotsalainen E, Pihlajamaki J, Vauhkonen I, Kainulainen S, Punnonen K, Vanninen E, Laakso M (2004) Multiple abnormalities in glucose and energy metabolism and coordinated changes in levels of adiponectin, cytokines, and adhesion molecules in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Circulation 110:3842–3848
Shen J, Arnett DK, Peacock JM, Parnell LD, Kraja A, Hixson JE, Tsai MY, Lai CQ, Kabagambe EK, Straka RJ, Ordovas JM (2007) Interleukin1beta genetic polymorphisms interact with polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate risk of the metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 137:1846–1851
Somm E, Cettour-Rose P, Asensio C, Charollais A, Klein M, Theander-Carrillo C, Juge-Aubry CE, Dayer JM, Nicklin MJ, Meda P, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Meier CA (2006) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist is upregulated during diet-induced obesity and regulates insulin sensitivity in rodents. Diabetologia 49:387–393
Strandberg L, Lorentzon M, Hellqvist A, Nilsson S, Wallenius V, Ohlsson C, Jansson JO (2006) Interleukin-1 system gene polymorphisms are associated with fat mass in young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2749–2754
Thalmann S, Meier CA (2007) Local adipose tissue depots as cardiovascular risk factors. Cardiovasc Res 75:690–701
Um JY, Lee KM, Kim HM (2004) Polymorphism of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene and obesity. Clin Chim Acta 340:173–177
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of the Western Australian Genetic Epidemiology Resource and the Western Australian DNA Bank (both National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia National Enabling Facilities). The work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) Project Grant 211980. KWC was supported by the Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP0663247. BLP was supported by a Howard Florey Postdoctoral Fellowship from the NHMRC. The authors thank the participants of the CUPID study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, K.W., Hung, J., Powell, B.L. et al. Association of Interleukin-1 gene polymorphisms with central obesity and metabolic syndrome in a coronary heart disease population. Hum Genet 124, 199–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-008-0540-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-008-0540-6