Abstract
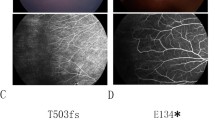
Mutations in Norrin signaling genes (NDP, FZD4 and LRP5) have been found in patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) and the altered signaling is suspected to play a critical role in its pathogenesis. To better understand this relationship, we systematically performed functional analyses on previously identified single nucleotide variants of LRP5, FZD4 and NDP, utilizing the Norrin dependent Topflash reporter assay. Cell surface binding assays and protein electrophoresis analysis of Norrin were also performed. Seven causative mutations and five possibly causative but indecisive variants were examined. We found: (1) a nonsense mutation in FZD4 completely abolished its signaling activity, while single missense mutations in LRP5 and FZD4 caused a moderate level of reduction (ranging from 26 to 48, 36% on average) and a double missense mutation in both genes caused a severe reduction in activity (71%). These observations correlated roughly with clinical phenotypes. (2) A mutational effect is suggested in four of five indecisive variants by signaling reductions comparable to those of missense mutations. (3) Norrin mutants demonstrated variable effects on signal transduction, and no apparent correlation with clinical phenotypes was observed. (4) The Norrin mutants examined demonstrated impaired cell surface binding, and some may have partially lost their ability to form a complex with unknown high molecular weight material(s). Our results illustrate the nature of FEVR in relation to Norrin signaling and further suggest the complexity of its disease causing mechanism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai M, Heeger S, Bartels C, Schelling D, Osteoporosis-Pseudoglioma Collaborative Group (2005) Clinical and molecular findings in osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 77:741–753
Baird P, Islam F, Richardson A, Cain M, Hunt N, Guymer R (2006) Analysis of the Y402H variant of the complement factor H gene in age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:4194–4198
Berger W, Ropers H (2001) Norrie disease. In: Scriver R, Beaudet L, Sly S, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw hill, New York, pp 5977–5985
Borroni B, Rao R, Liberini P, Venturelli E, Cossandi M, Archetti S, Caimi L, Padovani A (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (Glu298Asp) polymorphism is an independent risk factor for Migraine with Aura. Headache 46:1575–1579
Criswick V, Schepens C (1969) Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 68:578–594
Downey L, Bottomley H, Sheridan E, Ahmed M, Gilmour D, Inglehearn C, Reddy A, Agrawal A, Bradbury J, Toomes C (2006) Reduced bone mineral density and hyaloid vasculature remnants in a consanguineous recessive FEVR family with a mutation in LRP5. Br J Ophthalmol 90:1163–1167
Ferrari S, Deutsch S, Baudoin C, Cohen-Solal M, Ostertag A, Antonarakis S, Rizzoli R, Vernejoul Md (2005) LRP5 gene polymorphisms and idiopathic osteoporosis in men. Bone 37:770–775
Gong Y, Slee R, Fukai N, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S, Reginato A, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, Zacharin M, Oexle K, Marcelino J, Suwairi W, Heeger S, Sabatakos G, Apte S, Adkins WN, Allgrove J, Arslan-Kirchner M, Batch JA, Beighton P, Black GC, Boles RG, Boon LM, Borrone C, Brunner HG, Carle GF, Dallapiccola B, De Paepe A, Floege B, Halfhide ML, Hall B, Hennekam RC, Hirose T, Jans A, Juppner H, Kim CA, Keppler-Norevil K, Kohlschuetter A, LaCombe D, Lambert M, Lemyre E, Letteboer T, Peltonen L, Ramesar RS, Romanengo M, Somer H, Steichen-Gersdorf E, Steinmann B, Sullivan B, Superti-Furga A, Swoboda W, Van den Boogaard MJ, Van Hul W, Vikkula M, Votruba M, Zabel B, Garcia T, Baron R, Olsen BR, Warman ML (2001) LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell 107:513–523
Gordon M, Nusse R (2006) Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem 281:22429–22433
Guo J, Cooper L (2007) Influence of an LRP5 cytoplasmic SNP on Wnt signaling and osteoblastic differentiation. Bone 40:57–67
Hsieh J, Rattner A, Smallwood P, Nathans J (1999) Biochemical characterization of Wnt-frizzled interactions using a soluble, biologically active vertebrate Wnt protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3546–3551
Kiel D, Ferrari S, Cupples L, Karasik D, Manen D, Imamovic A, Herbert A, Dupuis J (2007) Genetic variation at the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) locus modulates Wnt signaling and the relationship of physical activity with bone mineral density in men. Bone 40:587–596
Jiao X, Ventruto V, Trese M, Shastry B, Hejtmancik J (2004) Autosomal recessive familial exudative vitreoretinopathy is associated with mutations in LRP5. Am J Hum Genet 75:878–884
Koh J, Jung M, Hong J, Park H, Chang J, Shin H, Kim S, Kim G (2004) Association between bone mineral density and LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene polymorphisms in young Korean men. J Korean Med Sci 19:407–412
Kondo H, Hayashi H, Oshima K, Tahira T, Hayashi K (2003) Frizzled 4 gene (FZD4) mutations in patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy with variable expressivity. Br J Ophthalmol 87:1291–1295
Kondo H, Qin M, Kusaka S, Tahira T, Hasebe H, Hayashi H, Uchio E, Hayashi K (2007) Novel mutations in Norrie disease gene in Japanese patients with Norrie disease and familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:1276–1282
Krishnan V, Bryant H, Macdougald O (2006) Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest 116:1202–1209
Laqua H (1980) Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 213:121–133
Li Y, Sun C, Yin H, Chen Y (2006) Association of polymorphism of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 Q89R, A1330V with bone mineral density in premenopausal northern Chinese women. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 35:576–579
Luhmann U, Lin J, Acar N, Lammel S, Feil S, Grimm C, Seeliger M, Hammes H, Berger W (2005) Role of the Norrie disease pseudoglioma gene in sprouting angiogenesis during development of the retinal vasculature. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:3372–3382
Moon R, Kohn A, Ferrari GD, Kaykas A (2004) WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 5:691–701
Ohlmann A, Scholz M, Goldwich A, Chauhan BK, Hudl K, Ohlmann AV, Zrenner E, Berger W, Cvekl A, Seeliger MW, Tamm ER (2005) Ectopic Norrin induces growth of ocular capillaries and restores normal retinal angiogenesis in norrie disease mutant mice. The J Neurosci 25:1701–1710
Okubo M, Horinishi A, Kim DH, Yamamoto TT, Murase T (2002) Seven novel sequence variants in the human low density lipoprotein receptor related protein 5 (LRP5) gene. Hum Mutat 19:186
Perez-Vila J, Hill RL (1997) Norrie disease protein (Norrin) forms disulfide-linked oligomers associated with the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem 272:33410–33415
Plager D, Orgel I, Ellis F, Hartzer M, Trese M, Shastry B (1992) X-linked recessive familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 114:145–148
Qin M, Hayashi H, Oshima K, Tahira T, Hayashi K, Kondo H (2005) Complexity of the genotype–phenotype correlation in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy with mutations in the LRP5 and/or FZD4 genes. Hum Mutat 26:104–112
Robitaille J, MacDonald M, Kaykas A, Sheldahl L, Zeisler J, Dube M, Zhang L, Singaraja R, Guernsey D, Zhang B, Siebert L, Hoskin-Mott A, Trese M, Pimstone S, Shastry B, Moon R, Hayden M, Goldberg Y, Samuels M (2002) Mutant frizzled-4 disrupts retinal angiogenesis in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Nat Genet 32:326–330
Saarinen A, Valimaki V, Valimaki M, Loyttyniemi E, Auro K, Uusen P, Kuris M, Lehesjoki A, Makitie O (2007) The A1330V polymorphism of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene (LRP5) associates with low peak bone mass in young healthy men. Bone 40:1006–1012
Shastry B, Trese M (1997) Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy: further evidence for genetic heterogeneity (Letter). Am J Med Genet 69:217–218
Shastry B, Hejtmancik J, Trese M (1997) Identification of novel missense mutations in the Norrie disease gene associated with one X-linked and four sporadic cases of familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Hum Mutat 9:396–401
Smallwood P, Williams J, Xu Q, Leahy D, Nathans J (2007) Mutational analysis of Norrin-frizzled4 recognition. J Biol Chem 282:4057–4068
Suwazono Y, Kobayashi E, Uetani M, Miura K, Morikawa Y, Ishizaki M, Kido T, Nakagawa H, Nogawa K (2006) G-protein beta 3 subunit polymorphism C1429T and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 polymorphism A1330V are risk factors for hypercholesterolemia in Japanese males—a prospective study over 5 years. Metabolism 55:751–757
Toomes C, Bottomley H, Jackson R, Towns K, Scott S, Mackey D, Craig J, Jiang L, Yang Z, Trembath R, Woodruff G, Gregory-Evans C, Gregory-Evans K, Parker M, Black GCM, Downey L, Zhang K, Inglehearn C (2004) Mutations in LRP5 or FZD4 underlie the common familial exudative vitreoretinopathy locus on chromosome 11q. Am J Hum Genet 74:721–730
Wright M, Aikawa M, Szeto W, Papkoff J (1999) Identification of a Wnt-responsive signal transduction pathway in primary endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:384–388
Xu Q, Wang Y, Dabdoub A, Smallwood PM, Williams J, Woods C, Kelley MW, Jiang L, Tasman W, Zhang K, Nathans J (2004) Vascular development in the retina and inner ear: control by Norrin and Frizzled-4, a high-affinity ligand-receptor pair. Cell 116:883–895
Zhang Z, Qin Y, He J, Huang Q, Li M, Hu Y, Liu Y (2005) Association of polymorphisms in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene with bone mineral density in postmenopausal Chinese women. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:1111–1116
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Randal Moon for kindly providing the reporter plasmid. Special thanks go to Dr. Jeremy Nathans for his generosity of sharing plasmids and cell line. This project was supported by a Grant-in-aid 15591883 for Scientific Research, Japan to H.K. and a Grant-in-Aid for Research Revolution 2002 from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan to K.H. in the Division of Genome Analysis, Research Center for Genetic Information, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2007_438_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Additional Norrin mutants. a Cells transfected with FZD4 were probed with indicated Norrin or its mutants. b Alkaline phosphatase stained native polyacrylamide gel was loaded as indicated. The arrowhead indicates the band specific to the Norrin mutant. c Western blot of conditioned medium, containing either wildtype or mutant Norrin as indicated, under either reducing (left) or non-reducing conditions (right) was performed using mAb anti-c-myc (clone 9E). ESM1 (TIF 283 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, M., Kondo, H., Tahira, T. et al. Moderate reduction of Norrin signaling activity associated with the causative missense mutations identified in patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Hum Genet 122, 615–623 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0438-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0438-8