Abstract
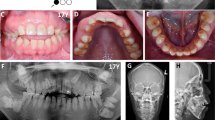
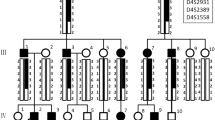
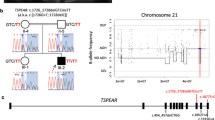
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a collective term used to describe phenotypically diverse forms of defective tooth enamel development. AI has been reported to exhibit a variety of inheritance patterns, and several loci have been identified that are associated with AI. We have performed a genome-wide scan in a large Brazilian family segregating an autosomal dominant form of AI and mapped a novel locus to 8q24.3. A maximum multipoint LOD score of 7.5 was obtained at marker D8S2334 (146,101,309 bp). The disease locus lies in a 1.9 cM (2.1 Mb) region according to the Rutgers Combined Linkage-Physical map, between a VNTR marker (at 143,988,705 bp) and the telomere (146,274,826 bp). Ten candidate genes were identified based on gene ontology and microarray-facilitated gene selection using the expression of murine orthologues in dental tissue, and examined for the presence of a mutation. However, no causative mutation was identified.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldred MJ, Savarirayan R, Crawford PJM (2003) Amelogenesis imperfecta: a classification and catalogue for the 21st century. Oral Dis 9:19–23
Aubin I, Adams CP, Opsahl S, Septier D, Bishop CE, Auge N, Salvayre R, Negre-Salvayre A, Goldberg M, Guenet J-L, Poirier C (2005) A deletion in the gene encoding sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 (Smpd3) results in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis imperfecta in the mouse. Nat Genet 37:803–805
Backman B, Holm AK (1986) Amelogenesis imperfecta: prevalence and incidence in a northern Swedish county. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 14:43–47
Bartlett JD, Simmer JP, Xue J, Margolis HC, Moreno EC (1996) Molecular cloning and mRNA tissue distribution of a novel matrix metalloproteinase isolated from porcine enamel organ. Gene 183:123–128
Bartlett JD, Skobe Z, Lee DH, Wright JT, Li Y, Kulkarni AB, Gibson CW (2006) A developmental comparison of matrix metalloproteinase-20 and amelogenin null mouse enamel. Eur J Oral Sci 114:18–23
Beniash E, Skobe Z, Bartlett JD (2006) Formation of the dentino-enamel interface in enamelysin (MMP-20)-deficient mouse incisors. Eur J Oral Sci 114:24–29
Burstein E, Hoberg JE, Wilkinson AS, Rumble JM, Csomos RA, Komarck CM, Maine GN, Wilkinson JC, Mayo MW, Duckett CS (2005) COMMD proteins, a novel family of structural and functional homologs of MURR1. J Biol Chem 280:22222–22232
Caterina J, Shi J, Krakora S, Bartlett JD, Engler JA, Kozak CA, Birkedal-Hansen H (1999) Isolation, characterization, and chromosomal location of the mouse enamelysin gene. Genomics 62:308–311
Chosack A, Eidelman E, Wisotski I, Cohen T (1979) Amelogenesis imperfecta among Israeli Jews and the description of a new type of local hypoplastic autosomal recessive amelogenesis imperfecta. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 47:148–156
Coffield KD, Phillips C, Brady M, Roberts MW, Strauss RP, Wright JT (2005) The psychosocial impact of developmental dental defects in people with hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. J Am Dent Assoc 136:620–630
Cottingham RWJ, Idury RM, Schaffer AA (1993) Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet 53:252–263
Dantonel J-C, Murthy KGK, Manley JL, Tora L (1997) Transcription factor TFIID recruits factor CPSF for formation of 3′ end of mRNA. Nature 389:399–402
Dong J, Gu TT, Simmons D, MacDougall M (2000) Enamelin maps to human chromosome 4q21 within the autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta locus. Eur J Oral Sci 108:353–358
Dong J, Amor D, Aldred MJ, Gu T, Escamilla M, MacDougall M (2005) DLX3 mutation associated with autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta with taurodontism. Am J Med Genet Part A 133A:138–141
Dufner-Beattie J, Wang F, Kuo Y-M, Gitschier J, Eide D, Andrews GK (2003) The acrodermatitis enteropathica gene ZIP4 encodes a tissue-specific, zinc-regulated zinc transporter in mice. J Biol Chem 278:33474–33481
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nuc Acids Res 30:207–210
Espiritu-Santo AR, Line SRP (2005) The enamel organic matrix: structure and function. Braz. J Oral Sci 4:716–724
Fong CD, Hammarstrom L (2000) Expression of amelin and amelogenin in epithelial root sheath remnants of fully formed rat molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90:218–223
Fujiwara S, Takeo N, Otani Y, Parry DAD, Kunimatsu M, Lu R, Sasaki M, Matsuo N, Khaleduzzaman M, Yoshioka H (2001) Epiplakin, a novel member of the Plakin family originally identified as a 450-kDa human epidermal autoantigen. Structure and tissue localization. J Biol Chem 276:13340–13347
Gentleman R, Carey V, Bates D, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini A, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang J, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80
Ghoul-Mazgar S, Hotton D, Lezot F, Blin-Wakkach C, Asselin A, Sautier JM, Berdal A (2005) Expression pattern of Dlx3 during cell differentiation in mineralized tissues. Bone 37:799–809
Hart PS, Hart TC, Michalec MD, Ryu OH, Simmons D, Hong S, Wright JT (2004) Mutation in kallikrein 4 causes autosomal recessive hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 41:545–549
Hart TC, Hart PS, Gorry MC, Michalec MD, Ryu OH, Uygur C, Ozdemir D, Firatli S, Aren G, Firatli E (2003) Novel ENAM mutation responsible for autosomal recessive amelogenesis imperfecta and localised enamel defects. J Med Genet 40:900–906
Horer J, Blum R, Feick P, Nastainczyk W, Schulz I (1999) A comparative study of rat and human Tmp21 (p23) reveals the pseudogene-like features of human Tmp21-II. DNA Seq 10:121–126
Horie M, Okutomi K, Taniguchi Y, Ohbuchi Y, Suzuki M, Takahashi E-i (1998) Isolation and characterization of a new member of the human Ly6 gene family (LY6H). Genomics 53:365–368
Hu CC, Fukae M, Uchida T, Qian Q, Zhang CH, Ryu OH, Tanabe T, Yamakoshi Y, Murakami C, Dohi N, Shimizu M, Simmer JP (1997) Cloning and characterization of porcine enamelin mRNAs. J Dent Res 76:1720–1729
Hu JC, Sun X, Zhang C, Liu S, Bartlett JD, Simmer JP (2002) Enamelysin and kallikrein-4 mRNA expression in developing mouse molars. Eur J Oral Sci 110:307–315
Hu JC, Zhang CH, Yang Y, Karrman-Mardh C, Forsman-Semb K, Simmer JP (2001) Cloning and characterization of the mouse and human enamelin genes. J Dent Res 80:898–902
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, Speed TP (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostat 4:249–264
Jang S-I, Kalinin A, Takahashi K, Marekov LN, Steinert PM (2005) Characterization of human epiplakin: RNAi-mediated epiplakin depletion leads to the disruption of keratin and vimentin IF networks. J Cell Sci 118:781–793
Kataoka K, Han S-i, Shioda S, Hirai M, Nishizawa M, Handa H (2002) MafA is a glucose-regulated and pancreatic beta-cell-specific transcriptional activator for the insulin gene. J Biol Chem 277:49903–49910
Kim J-W, Simmer JP, Lin BPL, Seymen F, Bartlett JD, Hu JCC (2006) Mutational analysis of candidate genes in 24 amelogenesis imperfecta families. Eur J Oral Sci 114:3–12
Kong X, Murphy K, Raj T, He C, White PS, Matise TC (2004) A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 75:1143–1148
Lagerstrom M, Dahl N, Nakahori Y, Nakagome Y, Backman B, Landegren U, Pettersson U (1991) A deletion in the amelogenin gene (AMG) causes X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1). Genomics 10:971–975
Lewis TB, Wood S, Michaelis EK, DuPont BR, Leach RJ (1996) Localization of a gene for a glutamate binding subunit of a NMDA receptor (GRINA) to 8q24. Genomics 32:131–133
Llano E, Pendas AM, Knauper V, Sorsa T, Salo T, Salido E, Murphy G, Simmer JP, Bartlett JD, Lopez-Otin C (1997) Identification and structural and functional characterization of human enamelysin (MMP-20). Biochemistry 36:15101–15108
Luo W, Wen X, Wang HJ, MacDougall M, Snead ML, Paine ML (2004) In vivo overexpression of Tuftelin in the enamel organic matrix. Cells Tiss Organs 177:212–220
Nagano T, Oida S, Ando H, Gomi K, Arai T, Fukae M (2003) Relative levels of mRNA encoding enamel proteins in enamel organ epithelia and odontoblasts. J Dent Res 82:982–986
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998) PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63:259–266
Ohishi K, Inoue N, Maeda Y, Takeda J, Riezman H, Kinoshita T (2000) Gaa1p and Gpi8p are components of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) transamidase that mediates attachment of GPI to proteins. Mol Biol Cell 11:1523–1533
Ozdemir D, Hart PS, Ryu OH, Choi SJ, Ozdemir-Karatas M, Firatli E, Piesco N, Hart TC (2005) MMP20 active-site mutation in hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. J Dent Res 84:1031–1035
Paine ML, Wang H-J, Luo W, Krebsbach PH, Snead ML (2003) A Transgenic animal model resembling amelogenesis imperfecta related to ameloblastin overexpression. J Biol Chem 278:19447–19452
Paine ML, White SN, Luo W, Fong H, Sarikaya M, Snead ML (2001) Regulated gene expression dictates enamel structure and tooth function. Mat Biol 20:273–292
Papagerakis P, MacDougall M, Hotton D, Bailleul-Forestier I, Oboeuf M, Berdal A (2003) Expression of amelogenin in odontoblasts. Bone 32:228–240
Platenik J, Kuramoto N, Yoneda Y (2000) Molecular mechanisms associated with long-term consolidation of the NMDA signals. Life Sci 67:335–364
Price JA, Bowden DW, Wright JT, Pettenati MJ, Hart TC (1998) Identification of a mutation in DLX3 associated with tricho-dento-osseous (TDO) syndrome. Hum Molec Genet 7:563–569
Price JA, Wright JT, Walker SJ, Crawford PJM, Aldred MJ, Hart TC (1999) Tricho-dento-osseous syndrome and amelogenesis imperfecta with taurodontism are genetically distinct conditions. Clin Genet 56:35–40
Raiborg C, Rusten TE, Stenmark H (2003) Protein sorting into multivesicular endosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:446–455
Rajpar MH, Harley K, Laing C, Davies RM, Dixon MJ (2001) Mutation of the gene encoding the enamel-specific protein, enamelin, causes autosomal-dominant amelogenesis imperfecta. Hum Mol Genet 10:1673–1677
Schuler GD (1997) Sequence Mapping by Electronic PCR. Genome Res 7:541–550
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:Article 3
Snead ML, Luo W, Lau EC, Slavkin HC (1988) Spatial- and temporal-restricted pattern for amelogenin gene expression during mouse molar tooth organogenesis. Development 104:77–85
Sobel E, Lange K (1996) Descent graphs in pedigree analysis: applications to haplotyping, location scores, and marker-sharing statistics. Am J Hum Genet 58:1323–1337
Solban N, Jia H-P, Richard S, Tremblay S, Devlin AM, Peng J, Gossard F, Guo D-F, Morel G, Hamet P, Lewanczuk R, Tremblay J (2000) HCaRG, a novel calcium-regulated gene coding for a nuclear protein, is potentially involved in the regulation of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 275:32234–32243
Stephanopoulos G, Garefalaki ME, Lyroudia K (2005) Genes and related proteins involved in amelogenesis imperfecta. J Dent Res 84:1117–1126
Sundell S (1986) Hereditary amelogenesis imperfecta. An epidemiological, genetic and clinical study in a Swedish child population. Swed Dent J Suppl 31:1–38
Witkop CJ (1976) Clinical aspects of dental anomalies. Int Dent J 26:378–390
Wright JT, Daly B, Simmons D, Hong S, Hart SP, Hart TC, Atsawasuwan P, Yamauchi M (2006) Human enamel phenotype associated with amelogenesis imperfecta and a kallikrein-4 (g.2142G > A) proteinase mutation. Eur J Oral Sci 114:13–17
Wright JT, Hall K, Yamauchi M (1997) The protein composition of normal and developmentally defective enamel. Ciba Found Symp 205:85–99
Zhou S, Zawel L, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1998) Characterization of Human FAST-1, a TGF[beta] and Activin Signal Transducer. Mol Cell 2:121–127
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants DE14102 (P.I.P.) and DE06988 (M.L.S.) from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Genotyping services were provided by the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR). CIDR is fully funded through a federal contract from the National Institutes of Health to The Johns Hopkins University, contract number N01-HG-65403. This investigation was conducted in a facility constructed with support from Research Facilities Improvement Program Grant Number C06 (RR10600-01, CA62528-01, RR14514-01) from the National Center for Research Resources, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendoza, G., Pemberton, T.J., Lee, K. et al. A new locus for autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta on chromosome 8q24.3. Hum Genet 120, 653–662 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0246-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0246-6