Abstract
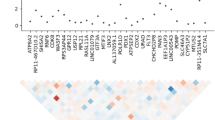
Autism affects more males than females and is associated with disturbances of the serotonin system. The integrin β3 (ITGB3) and serotonin transporter (SLC6A4) genes were both recently identified as male quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for serotonin levels and alleles of each have been associated with autism. Here, we use publicly available genomic resources to determine whether regulation of expression level could be the mechanism behind association between serotonin level and noncoding variation in ITGB3. We also examine whether ITGB3 might interact with SLC6A4 to contribute to autism susceptibility. Using murine and human expression data, we observe that ITGB3 and SLC6A4 expression levels are correlated (0.38<r<0.78). Moreover, genetic variation in ITGB3 is associated with expression of both ITGB3 (P=0.012) and SLC6A4 (P=0.008) in unrelated CEPH individuals. We also show preliminary evidence that genotypes at the ITGB3 and SLC6A4 loci may interact to affect autism susceptibility (P=0.033).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson RK, Wright HH, Carpenter R, Brennan W, Lumpuy O, Cole E, Young SR (1989) Elevated blood serotonin in autistic probands and their first-degree relatives. J Autism Dev Disord 19:397–407
Bradley SL, Dodelzon K, Sandhu HK, Philibert RA (2005) Relationship of serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms and haplotypes to mRNA transcription. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 136:58–61
Cook E, Leventhal B (1996) The serotonin system in autism. Curr Opin Pediatr 8:348–354
Cook EH, Leventhal BL, Heller W, Metz J, Wainwright M, Freedman DX (1990) Autistic children and their first-degree relatives: relationships between serotonin and norepinephrine levels and intelligence. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2:268–274
Coutinho AM, Oliveira G, Sousa I, Morgadinho T, Fesel C, Macedo TR, Bento C, Martins M, Marques C, Ataide A, Miguel TS, Borges L, Vicente AM (2005) Epistatic effects in hyperserotonemia and autism. American Society of Human Genetics
Devlin B, Cook EH, Coon H, Dawson G, Grigorenko EL, McMahon W, Minshew N, Pauls D, Smith M, Spence MA, Rodier PM, Stodgell C, Schellenberg GD (2005) Autism and the serotonin transporter: the long and short of it. Mol Psychiatry 10(12):1110–1116
Gordon C, State R, Nelson J, Hamburger S, Rapoport J (1993) A double-blind comparison of clomipramine, desipramine, and placebo in the treatment of autistic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:441–447
Hanna GL, Himle JA, Curtis GC, Koram DQ, Weele JVV, Leventhal BL, Cook EH, Jr (1998) Serotonin transporter and seasonal variation in blood serotonin in families with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:102–111
Hapke S, Gawaz M, Dehne K, Kohler J, Marshall JF, Graeff H, Schmitt M, Reuning U, Lengyel E (2001) beta(3)A-integrin downregulates the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (u-PAR) through a PEA3/ets transcriptional silencing element in the u-PAR promoter. Mol Cell Biol 21:2118–2132
Heils A, Teufel A, Petri S, Stoeber G, Riederer P, Bengel D, Lesch KP (1996) Allelic variation of human serotonin transporter gene expression. J Neurochem 66:2621–2624
Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, Zagursky K, Novotny S, Wasserman S, Iyengar R (2004) A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 30(3):582–589
Kim S-J, Cox N, Courchesne R, Lord C, Corsello C, Akshoomoff N, Guter S, Leventhal B, Courchesne E, Cook E (2002) Transmission disequilibrium mapping in the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) region in autistic disorder. Mol Psychiatry 7:278–288
Kuperman S, Beeghly JH, Burns TL, Tsai LY (1985) Serotonin relationships of autistic probands and their first-degree relatives. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 24:186–190
Leventhal BL, Cook EH Jr, Morford M, Ravitz A, Freedman DX (1990) Relationships of whole blood serotonin and plasma norepinephrine within families. J Autism Dev Disord 20:499–511
Lindemann S, Tolley ND, Eyre JR, Kraiss LW, Mahoney TM, Weyrich AS (2001) Integrins regulate the intracellular distribution of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in platelets. A checkpoint for translational control. J Biol Chem 276:33947–33951
Lord C, Rutter M, Goode S, Heemsbergen J, Jordan H, Mawhood L, Schopler E (1989) Autism diagnostic observation schedule: a standardized observation of communicative and social behavior. J Autism Dev Disord 19:185–212
Lord C, Rutter M, Le Couteur A (1994) Autism diagnostic interview—revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 24:659–685
Lu T, Pan Y, Kao SY, Li C, Kohane I, Chan J, Yankner BA (2004) Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature 429:883–891
Morley M, Molony CM, Weber TM, Devlin JL, Ewens KG, Spielman RS, Cheung VG (2004) Genetic analysis of genome-wide variation in human gene expression. Nature 430:743–747
Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC (2003) Genetic power calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 19:149–150
Riikonen T, Westermarck J, Koivisto L, Broberg A, Kahari VM, Heino J (1995) Integrin alpha 2 beta 1 is a positive regulator of collagenase (MMP-1) and collagen alpha 1(I) gene expression. J Biol Chem 270:13548–13552
Schain RJ, Freedman DX (1961) Studies on 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in autistic and other mentally retarded children. J Pediatr 58:315–320
Trefilov A, Berard J, Krawczak M, Schmidtke J (2000) Natal dispersal in rhesus macaques is related to serotonin transporter gene promoter variation. Behav Genet 30:295–301
Wassink TH, Brzustowicz LM, Bartlett CW, Szatmari P (2004) The search for autism disease genes. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 10:272–283
Weiss LA, Abney M, Cook EH, Ober C (2005a) Sex-specific genetic architecture of whole blood serotonin levels. Am J Hum Genet 76:33–41
Weiss LA, Abney M, Parry R, Scanu AM, Cook EH Jr, Ober C (2005b) Variation in ITGB3 has sex-specific associations with plasma lipoprotein(a) and whole blood serotonin levels in a population-based sample. Hum Genet 117(1):81–87
Weiss LA, Kosova G, Delahanty RJ, Jiang L, Cook EH Jr, Ober C, Sutcliffe JS (2006) Variation in ITGB3 is associated with whole blood serotonin level and autism susceptibility. Eur J Hum Genet (in press)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the help of Dr. Nancy Cox and Dr. Conrad Gilliam for helpful discussions and comments on this manuscript and Mariam Bramah-Lawani, Kathy Hennessy, Natasha Phillips, and Rebecca Anderson for technical assistance. This research was supported by the University of Chicago Clinical Research Center (NIH grant M01 RR00055) and by NIH grants R01 HL72414 to C.O. and U19 HD35482 to E.C. LAW was supported by a National Science Foundation graduate research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, L.A., Ober, C. & Cook, E.H. ITGB3 shows genetic and expression interaction with SLC6A4. Hum Genet 120, 93–100 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0196-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0196-z