Abstract
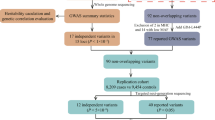
We studied patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD) from an isolated population in the Netherlands aiming to map gene(s) involved in PD susceptibility. A total of 109 parkinsonism patients were independently ascertained, of whom 62 presented late-onset, idiopathic PD. Genealogical research showed that 45 index cases with idiopathic PD were linked to a common ancestor, indicating familiar clustering among the patients. This strong familial clustering was highly significant (P=0.005) when compared to random controls from the same population. We performed a genome wide scan using 382 polymorphic markers in 44 distantly related PD patients plus 112 unaffected first-degree relatives and spouses. Our genome wide association analysis (DISLAMB) revealed evidence of association at a nominal P-value<0.01 for markers D2S2333, D4S405, D9S158, D13S153. Other regions on chromosomes 3p, 4q, 14q, 17p and 17q were found at a significance level of P<0.05. In a follow-up study, we investigated all the positive regions using a denser marker set and a larger sample (total of 630 individuals including all late-onset PD patients). The strongest evidence for association remained for the 9q and 14q region. A significant association was found for marker D9S1838 (OR=2.0, 95% CI 1.1–3.5, P=0.014) and D14S65 (OR=3.2, 95% CI 1.7–6.1, P<0.001). Moreover, a common haplotype with excess of sharing among late-onset PD cases was observed on both regions. Our results suggest the existence of two loci influencing PD susceptibility on chromosome 9q and 14q.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulchenko YS, Bertoli-Avella AM, van Duijn CM (2005) A method for pooling alleles from different genotyping experiments. Ann Hum Genet 69:233–238
Aulchenko YS, Heutink P, Mackay I, Bertoli-Avella AM, Pullen J, Vaessen N, Rademaker TA, Sandkuijl LA, Cardon L, Oostra B, van Duijn CM (2004) Linkage disequilibrium in young genetically isolated Dutch population. Eur J Hum Genet 12:527–534
Boichard D (2002) PEDIG: a FORTRAN package for pedigree analysis studied for large populations. In: Proceeding of the 7th World Congr. Genet. Appl. Livest. Prod., In Montpellier, France
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Dekker MC, van Swieten JC, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Snijders PJ, Boeren E, Hofman A, Breteler MM, Heutink P, Oostra BA, van Duijn CM (2003) A clinical-genetic study of Parkinson’s disease in a genetically isolated community. J Neurol 250:1056–1062
DeStefano AL, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Lazzarini AM, Maher NE, Saint-Hilaire M, Feldman RG, Guttman M, Watts RL, Suchowersky O, Lafontaine AL, Labelle N, Lew MF, Waters CH, Growdon JH, Singer C, Currie LJ, Wooten GF, Vieregge P, Pramstaller PP, Klein C, Hubble JP, Stacy M, Montgomery E, MacDonald ME, Gusella JF, Myers RH (2001) Genome-wide scan for Parkinson’s disease: the GenePD Study. Neurology 57:1124–1116
Gasser T (2001) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 248:833–840
Gasser T, Muller-Myhsok B, Wszolek ZK, Oehlmann R, Calne DB, Bonifati V, Bereznai B, Fabrizio E, Vieregge P, Horstmann RD (1998) A susceptibility locus for Parkinson’s disease maps to chromosome 2p13. Nat Genet 18:262–265
Hicks AA, Petursson H, Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Johannsdottir HS, Sainz J, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K, Sveinbjornsdottir S (2002) A susceptibility gene for late-onset idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 52:549–555
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Lang AE, Lozano AM (1998) Parkinson’s disease. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 339:1044–1053
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452
Li N, Stephens M (2003) Modeling linkage disequilibrium and identifying recombination hotspots using single-nucleotide polymorphism data. Genetics 165:2213–2233
Lotharius J, Brundin P (2002) Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: dopamine, vesicles and alpha-synuclein. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:932–942
Marder K, Tang MX, Mejia H, Alfaro B, Cote L, Louis E, Groves J, Mayeux R (1996) Risk of Parkinson’s disease among first-degree relatives: a community-based study. Neurology 47:155–160
Martinez M, Brice A, Vaughan JR, Zimprich A, Breteler MM, Meco G, Filla A, Farrer MJ, Betard C, Hardy J, De Michele G, Bonifati V, Oostra B, Gasser T, Wood NW, Durr A (2004) Genome-wide scan linkage analysis for Parkinson’s disease: the European genetic study of Parkinson’s disease. J Med Genet 41:900–907
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Nakamura S, Matsumoto T, Yada S, Hirahashi M, Suekane H, Yao T, Goda K, Iida M (2005) Overexpression of caspase recruitment domain (CARD) membrane-associated guanylate kinase 1 (CARMA1) and CARD9 in primary gastric B-cell lymphoma. Cancer 104:1885–1893
Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, van der Brug M, de Munain AL, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martinez JR, Nicholl D, Carrera IM, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Marti-Masso JF, Perez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singleton AB (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44:595–600
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Rudolph A, Shults C, Conneally PM, Foroud T (2002) Genome screen to identify susceptibility genes for parkinson disease in a sample without parkin mutations. Am J Hum Genet 71:124–135
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Murrell J, Rudolph A, Shults CW, Conneally PM, Foroud T (2003a) Genome-wide linkage analysis and evidence of gene-by-gene interactions in a sample of 362 multiplex Parkinson disease families. Hum Mol Genet 12:2599–2608
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Rudolph A, Shults C, Conneally PM, Foroud T (2003b) Significant linkage of Parkinson disease to chromosome 2q36–37. Am J Hum Genet 72:1053–1057
Pardo LM, MacKay I, Oostra B, van Duijn CM, Aulchenko YS (2005) The effect of genetic drift in a young genetically isolated population. Ann Hum Genet 69:288–295
Peltonen L, Palotie A, Lange K (2000) Use of population isolates for mapping complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 1:182–190
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH, Jr., Goetz CG, Small GW, Masterman D, Mastaglia F, Laing NG, Stajich JM, Slotterbeck B, Booze MW, Ribble RC, Rampersaud E, West SG, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Roses AD, Haines JL, Scott BL, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA (2001) Complete genomic screen in Parkinson disease: evidence for multiple genes. JAMA 286:2239–2244
Service SK, Lang DW, Freimer NB, Sandkuijl LA (1999) Linkage-disequilibrium mapping of disease genes by reconstruction of ancestral haplotypes in founder populations. Am J Hum Genet 64:1728–1738
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Sveinbjornsdottir S, Hicks AA, Jonsson T, Petursson H, Gugmundsson G, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K (2000) Familial aggregation of Parkinson’s disease in Iceland. N Engl J Med 343:1765–1770
Tan KO, Fu NY, Sukumaran SK, Chan SL, Kang JH, Poon KL, Chen BS, Yu VC (2005) MAP-1 is a mitochondrial effector of Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14623–14628
Terwilliger JD (1995) A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am J Hum Genet 56:777–787
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, the Centre for Medical Systems Biology, and a grant from the Internationaal Parkinson Fonds (B.A.O). Petra Veraart and Hilda Kornman are acknowledged for their contribution to the genealogical research, Erwin Wauters and Florencia Gosso for their help in genotyping and Tom de Vries Lentsch for the artwork. We are grateful to all patients and their relatives, general practitioners, neurologists and nursing home physicians for making this study possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertoli-Avella, A.M., Dekker, M.C., Aulchenko, Y.S. et al. Evidence for novel loci for late-onset Parkinson’s disease in a genetic isolate from the Netherlands. Hum Genet 119, 51–60 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0108-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0108-7