Abstract.
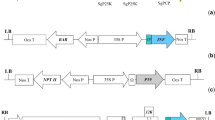
The nuclear gene PsaD encodes an abundant chloroplast protein located on the stromal side of the Photosystem I complex. We have cloned and sequenced a genomic fragment containing the PsaD gene from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sequence comparison with its cDNA revealed that the PsaD ORF contains no introns. Thus, the regulatory sequences required for high-level expression of PsaD must lie in the flanking promoter and untranslated regions. We used this genomic fragment to construct a vector that allows for high-level expression of endogenous and exogenous genes, as well as cDNAs that could not be expressed from existing vectors. It is also possible to use the PsaD transit sequence to target the expressed protein to the chloroplast compartment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, .N., Rochaix, .JD. The flanking regions of PsaD drive efficient gene expression in the nucleus of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii . Mol Gen Genomics 265, 888–894 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100485
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380100485