Abstract
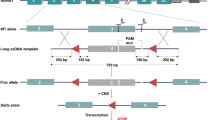
The C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II consists of tandem repeats of the consensus heptapeptide YSPTSPS. Deletion studies in tissue culture cells have indicated that the CTD plays an essential role in transcription, although the nature of this essential function remains unclear. About half of the CTD can be deleted without affecting the viability of cells in tissue culture. Paradoxically, the dispensable CTD repeats are precisely conserved among all mammals whose CTD sequences are known. To determine whether the mammalian CTD is important in transcription during mouse development, we developed a gene targeting approach to introduce deletions into the CTD coding region of mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. To maintain a functional Rpo2-1 gene, the neo marker in the targeting vector was positioned outside of the Rpo2-1 transcribed region, 1.2 kb from the site of the CTD deletion. G418-resistant clones were screened for co-integration of the CTD deletion, and the resulting ES lines were used to create germline chimeric mice. Stable heterozygous lines were established and mated to produce animals homozygous for the CTD deletion. We show here that mice homozygous for a deletion of thirteen of the 52 heptapeptide repeats are smaller than wild-type littermates and have a high rate of neonatal lethality. Surviving adults, although small, appear morphologically normal and are fertile. This result suggests that the CTD plays a role in regulating growth during mammalian development. The gene targeting approach described here should be useful for making further deletions in the CTD and may be of general applicability where it is desirable to engineer specific mutations in the germline of mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 August 1998 / Accepted: 15 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litingtung, Y., Lawler, A., Sebald, S. et al. Growth retardation and neonatal lethality in mice with a homozygous deletion in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Mol Gen Genet 261, 100–105 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050946
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050946