Abstract
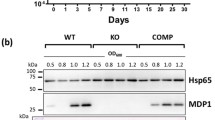
The aerobic saprophyte Mycobacterium smegmatis, like its pathogenic counterpart M. tuberculosis, has the ability to adapt to anaerobiosis by shifting down to a dormant state. Here, we report the identification and molecular genetic characterisation of the first dormancy-induced protein in M. smegmatis. Comparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of protein extracts of aerobically growing and dormant anaerobic M. smegmatis cultures revealed the upregulation of a 27-kDa protein in the dormant state. Peptide sequencing showed that the induced protein is a homologue of the histone-like protein Hlp, predicted by the M. tuberculosis genome project. The corresponding hlp gene was cloned from M. smegmatis and sequenced. Disruption of the hlp gene eliminated the histone-like protein but did not affect the viability of the dormant culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 June 1998 / Accepted: 22 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B., Murugasu-Oei, B. & Dick, T. Upregulation of a histone-like protein in dormant Mycobacterium smegmatis . Mol Gen Genet 260, 475–479 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050919
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050919