Abstract
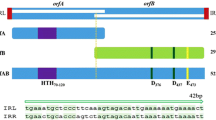
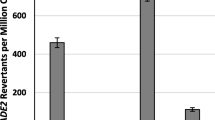
The transposable element IS801, isolated from plasmid pMMC7105 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola, transposes in Escherichia coli to plasmid targets, expressing a relatively relaxed target specificity. The target sequences are tetramers with homology with the left terminus (GAAC) of the transposing unit, the alternative targets being GAAC, GGAC, CAAG, and CGAC. In the areas flanking IS801 in 13 different locations, no similarities other than the target tetramer were observed. The transposase is physically and functionally separable from the transposing unit since transposition of constructs carrying marker genes occurs with the transposase expressed in trans. The IS801 transposase shows amino acid sequence homology to the transposases of the E. coli elements IS91 and IS1294. These tranposases contain conserved amino acid motifs found in the replicases of certain plasmids that replicate as rolling circles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 March 1998 / Accepted: 15 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richter, G., Björklöf, K., Romantschuk, M. et al. Insertion specificity and trans-activation of IS801. Mol Gen Genet 260, 381–387 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050907
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050907