Abstract
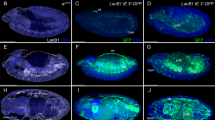
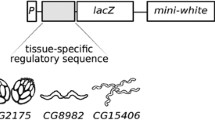
The Drosophila vitelline membrane protein gene VM32E is expressed according to a precise temporal and spatial program in the follicle cells. Results from germ line transformation experiments using different fragments of the −465/−39 VM32E region fused to the hsp/lacZ reporter gene revealed that the region −348/−39 is sufficient to confer the wild-type expression pattern. Within this segment, distinct cis-regulatory elements control VM32E expression in ventral and dorsal follicle cells. The region between −135/−113 is essential for expression of the VM32E gene in the ventral columnar follicle cells. Expression in the dorsal domain requires the two regions −348/−254 and −118/−39. Furthermore, the region −253/−119 appears to contain a negative element that represses gene activity in anterior centripetal cells. We suggest that the expression of the VM32E gene throughout the follicular epithelium is controlled by specific cis-regulatory elements acting in distinct spatial domains and following a precise developmental program.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 October 1996 / Accepted: 14 November 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavaliere, V., Spanò, S., Andrenacci, D. et al. Regulatory elements in the promoter of the vitelline membrane gene VM32E of Drosophila melanogaster direct gene expression in distinct domains of the follicular epithelium. Mol Gen Genet 254, 231–237 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050411
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050411