Abstract
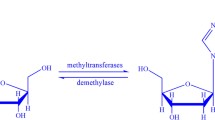
DNA N6-methyladenine is a non-canonical DNA modification that occurs in different eukaryotes at low levels and it has been identified as an extremely important function of life. Moreover, about 0.2% of adenines are marked by DNA N6-methyladenine in the rice genome, higher than in most of the other species. Therefore, the identification of them has become a very important area of study, especially in biological research. Despite the few computational tools employed to address this problem, there still requires a lot of efforts to improve their performance results. In this study, we treat DNA sequences by the continuous bags of nucleobases, including sub-word information of its biological words, which then serve as features to be fed into a support vector machine algorithm to identify them. Our model which uses this hybrid approach could identify DNA N6-methyladenine sites with achieved a jackknife test sensitivity of 86.48%, specificity of 89.09%, accuracy of 87.78%, and MCC of 0.756. Compared to the state-of-the-art predictor as well as the other methods, our proposed model is able to yield superior performance in all the metrics. Moreover, this study provides a basis for further research that can enrich a field of applying natural language-processing techniques in biological sequences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar S, Hayat M (2018) iMethyl-STTNC: identification of N 6-methyladenosine sites by extending the idea of SAAC into Chou’s PseAAC to formulate RNA sequences. J Theor Biol 455:205–211
Althaus IW, Chou JJ, Gonzales AJ, Deibel MR, Chou KC, Kezdy FJ, Romero DL, Aristoff PA, Tarpley WG, Reusser F (1993a) Steady-state kinetic studies with the non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor U-87201E. J Biol Chem 268:6119–6124
Althaus IW, Gonzales AJ, Chou JJ, Romero DL, Deibel MR, Chou KC, Kezdy FJ, Resnick L, Busso ME, So AG (1993b) The quinoline U-78036 is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem 268:14875–14880
Asgari E, Mofrad MRK (2015) Continuous distributed representation of biological sequences for deep proteomics and genomics. PLoS One 10:e0141287
Asgari E, McHardy AC, Mofrad MRK (2019) Probabilistic variable-length segmentation of protein sequences for discriminative motif discovery (DiMotif) and sequence embedding (ProtVecX). Sci Rep 9:3577
Bojanowski P, Grave E, Joulin A, Mikolov T (2017) Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist 5:135–146
Bradley AP (1997) The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit 30:1145–1159
Cai Y-D, Feng K-Y, Lu W-C, Chou K-C (2006) Using LogitBoost classifier to predict protein structural classes. J Theor Biol 238:172–176
Cai L, Huang T, Su J, Zhang X, Chen W, Zhang F, He L, Chou K-C (2018) Implications of newly identified brain eQTL genes and their interactors in schizophrenia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 12:433–442
Cao D-S, Xu Q-S, Liang Y-Z (2013) propy: a tool to generate various modes of Chou’s PseAAC. Bioinformatics 29:960–962
Chandra A, Sharma A, Dehzangi A, Ranganathan S, Jokhan A, Chou K-C, Tsunoda T (2018) PhoglyStruct: prediction of phosphoglycerylated lysine residues using structural properties of amino acids. Sci Rep 8:17923
Chang C-C, Lin C-J (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2:27
Chen W, Lei T-Y, Jin D-C, Lin H, Chou K-C (2014) PseKNC: a flexible web server for generating pseudo K-tuple nucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 456:53–60
Chen W, Feng P, Ding H, Lin H, Chou K-C (2015) iRNA-Methyl: identifying N 6-methyladenosine sites using pseudo nucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 490:26–33
Chen W, Ding H, Zhou X, Lin H, Chou K-C (2018) iRNA(m6A)-PseDNC: identifying N 6-methyladenosine sites using pseudo dinucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 561–562:59–65
Chen W, Lv H, Nie F, Lin H (2019) i6mA-Pred: Identifying DNA N 6-methyladenine sites in the rice genome. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz015
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2017) pLoc-mPlant: predict subcellular localization of multi-location plant proteins by incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Mol BioSyst 13:1722–1727
Cheng X, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2018) pLoc-mEuk: predict subcellular localization of multi-label eukaryotic proteins by extracting the key GO information into general PseAAC. Genomics 110:50–58
Chou KC (1989) Graphic rules in steady and non-steady state enzyme kinetics. J Biol Chem 264:12074–12079
Chou K-C (1990) Applications of graph theory to enzyme kinetics and protein folding kinetics: steady and non-steady-state systems. Biophys Chem 35:1–24
Chou K-C (2001a) Using subsite coupling to predict signal peptides. Protein Eng 14:75–79
Chou KC (2001b) Prediction of protein cellular attributes using pseudo-amino acid composition. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 43:246–255
Chou KC (2001c) Prediction of protein signal sequences and their cleavage sites. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 42:136–139
Chou K-C (2011) Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 273:236–247
Chou K-C (2015) Impacts of bioinformatics to medicinal chemistry. Med Chem 11:218–234
Chou K-C (2017) An unprecedented revolution in medicinal chemistry driven by the Progress of Biological science. Curr Top Med Chem 17:2337–2358
Chou K-C, Elrod DW (2002) Bioinformatical analysis of G-protein-coupled receptors. J Proteome Res 1:429–433
Chou KC, Forsén S (1980) Graphical rules for enzyme-catalysed rate laws. Biochem J 187:829
Chou K-C, Shen H-B (2009) Recent advances in developing web-servers for predicting protein attributes. Nat Sci 1:63
Chou KC, Jiang SP, Liu WM, Fee CH (1979) Graph theory of enzyme kinetics: 1. Steady-state reaction system
Chou K-C, Maggiora GM, Mao B (1989) Quasi-continuum models of twist-like and accordion-like low-frequency motions in DNA. Biophys J 56:295–305
Du P, Wang X, Xu C, Gao Y (2012) PseAAC-Builder: a cross-platform stand-alone program for generating various special Chou’s pseudo-amino acid compositions. Anal Biochem 425:117–119
Du P, Gu S, Jiao Y (2014) PseAAC-general: fast building various modes of general form of chou’s pseudo-amino acid composition for large-scale protein datasets. Int J Mol Sci 15:3495
Fang G, Munera D, Friedman DI, Mandlik A, Chao MC, Banerjee O, Feng Z, Losic B, Mahajan MC, Jabado OJ, Deikus G, Clark TA, Luong K, Murray IA, Davis BM, Keren-Paz A, Chess A, Roberts RJ, Korlach J, Turner SW, Kumar V, Waldor MK, Schadt EE (2012) Genome-wide mapping of methylated adenine residues in pathogenic Escherichia coli using single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 30:1232
Feng P-M, Chen W, Lin H, Chou K-C (2013) iRSpot-PseDNC: identify recombination spots with pseudo dinucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e68
Feng P, Yang H, Ding H, Lin H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2019) iDNA6 mA-PseKNC: identifying DNA N 6-methyladenosine sites by incorporating nucleotide physicochemical properties into PseKNC. Genomics 111:96–102
Flusberg BA, Webster DR, Lee JH, Travers KJ, Olivares EC, Clark TA, Korlach J, Turner SW (2010) Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nat Methods 7:461
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152
Fu Y, Luo G-Z, Chen K, Deng X, Yu M, Han D, Hao Z, Liu J, Lu X, Doré Louis C, Weng X, Ji Q, Mets L, He C (2015) N 6-methyldeoxyadenosine marks active transcription start sites in chlamydomonas. Cell 161:879–892
Greer Eric L, Blanco Mario A, Gu L, Sendinc E, Liu J, Aristizábal-Corrales D, Hsu C-H, Aravind L, He C, Shi Y (2015) DNA methylation on N 6-adenine in C. elegans. Cell 161:868–878
Habibi M, Weber L, Neves M, Wiegandt DL, Leser U (2017) Deep learning with word embeddings improves biomedical named entity recognition. Bioinformatics 33:i37–i48
Hamid M-N, Friedberg I (2018) Identifying antimicrobial peptides using word embedding with deep recurrent neural networks. Bioinformatics:bty937-bty937
Hu L, Huang T, Shi X, Lu W-C, Cai Y-D, Chou K-C (2011) Predicting functions of proteins in mouse based on weighted protein-protein interaction network and protein hybrid properties. PLoS One 6:e14556
Jia J, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou K-C (2016) pSuc-Lys: predict lysine succinylation sites in proteins with PseAAC and ensemble random forest approach. J Theor Biol 394:223–230
Jia J, Li X, Qiu W, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2019) iPPI-PseAAC(CGR): identify protein-protein interactions by incorporating chaos game representation into PseAAC. J Theor Biol 460:195–203
Jones PL, Jan Veenstra GC, Wade PA, Vermaak D, Kass SU, Landsberger N, Strouboulis J, Wolffe AP (1998) Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat Genet 19:187
Joulin A, Grave E, Bojanowski P, Mikolov T (2017) Bag of tricks for efficient text classification. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 2, Short Papers, pp 427–431
Khan YD, Jamil M, Hussain W, Rasool N, Khan SA, Chou K-C (2019) pSSbond-PseAAC: prediction of disulfide bonding sites by integration of PseAAC and statistical moments. J Theor Biol 463:47–55
Kuo-Chen C (2010) Graphic rule for drug metabolism systems. Curr Drug Metab 11:369–378
Lacks S, Greenberg B (1977) Complementary specificity of restriction endonucleases of Diplococcus pneumoniae with respect to DNA methylation. J Mol Biol 114:153–168
Le NQK, Ou YY (2016a) Incorporating efficient radial basis function networks and significant amino acid pairs for predicting GTP binding sites in transport proteins. BMC Bioinf 17:183
Le NQK, Ou YY (2016b) Prediction of FAD binding sites in electron transport proteins according to efficient radial basis function networks and significant amino acid pairs. BMC Bioinf 17:298
Le NQK, Ho QT, Ou YY (2017) Incorporating deep learning with convolutional neural networks and position specific scoring matrices for identifying electron transport proteins. J Comput Chem 38:2000–2006
Le NQK, Ho QT, Ou YY (2018) Classifying the molecular functions of Rab GTPases in membrane trafficking using deep convolutional neural networks. Anal Biochem 555:33–41
Le NQK, Yapp EKY, Ho QT, Nagasundaram N, Ou YY, Yeh HY (2019) iEnhancer-5Step: identifying enhancers using hidden information of DNA sequences via Chou’s 5-step rule and word embedding. Anal Biochem 571:53–61
Lin H, Deng E-Z, Ding H, Chen W, Chou K-C (2014) iPro54-PseKNC: a sequence-based predictor for identifying sigma-54 promoters in prokaryote with pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 42:12961–12972
Liu F, Chen J, Fang L, Wang X, Liu B, Chou K-C (2015) Pse-in-One: a web server for generating various modes of pseudo components of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W65–W71
Liu Z, Xiao X, Yu D-J, Jia J, Qiu W-R, Chou K-C (2016) pRNAm-PC: predicting N 6-methyladenosine sites in RNA sequences via physical–chemical properties. Anal Biochem 497:60–67
Liu B, Wu H, Chou K-C (2017) Pse-in-One 20: an improved package of web servers for generating various modes of pseudo components of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences. Nat Sci 9:67
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. ICLR Workshop
Öztürk H, Ozkirimli E, Özgür A (2018) A novel methodology on distributed representations of proteins using their interacting ligands. Bioinformatics 34:i295–i303
Qiu W-R, Xiao X, Chou K-C (2014) iRSpot-TNCPseAAC: identify recombination spots with trinucleotide composition and pseudo amino acid components. Int J Mol Sci 15:1746
Qiu W-R, Xiao X, Lin W-Z, Chou K-C (2015) iUbiq-Lys: prediction of lysine ubiquitination sites in proteins by extracting sequence evolution information via a gray system model. J Biomol Struct Dyn 33:1731–1742
Qiu W-R, Xiao X, Xu Z-C, Chou K-C (2016) iPhos-PseEn: identifying phosphorylation sites in proteins by fusing different pseudo components into an ensemble classifier. Oncotarget 7:51270
Qiu W-R, Sun B-Q, Xiao X, Xu Z-C, Jia J-H, Chou K-C (2018) iKcr-PseEns: identify lysine crotonylation sites in histone proteins with pseudo components and ensemble classifier. Genomics 110:239–246
Rahman MS, Aktar U, Jani MR, Shatabda S (2019) iPro70-FMWin: identifying Sigma70 promoters using multiple windowing and minimal features. Mol Genet Genom 294:69–84
Smith ZD, Meissner A (2013) DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet 14:204
Song J, Li F, Takemoto K, Haffari G, Akutsu T, Chou K-C, Webb GI (2018) PREvaIL, an integrative approach for inferring catalytic residues using sequence, structural, and network features in a machine-learning framework. J Theor Biol 443:125–137
Tahir M, Hayat M, Khan SA (2019) iNuc-ext-PseTNC: an efficient ensemble model for identification of nucleosome positioning by extending the concept of Chou’s PseAAC to pseudo-tri-nucleotide composition. Mol Genet Genomics 294:199–210
Touzain F, Petit M-A, Schbath S, Karoui ME (2010) DNA motifs that sculpt the bacterial chromosome. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:15
Vang YS, Xie X (2017) HLA class I binding prediction via convolutional neural networks. Bioinformatics 33:2658–2665
Wu TP, Wang T, Seetin MG, Lai Y, Zhu S, Lin K, Liu Y, Byrum SD, Mackintosh SG, Zhong M, Tackett A, Wang G, Hon LS, Fang G, Swenberg JA, Xiao AZ (2016) DNA methylation on N 6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Nature 532:329
Xie H-L, Fu L, Nie X-D (2013) Using ensemble SVM to identify human GPCRs N-linked glycosylation sites based on the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Protein Eng Des Sel 26:735–742
Xu Y, Ding J, Wu L-Y, Chou K-C (2013a) iSNO-PseAAC: predict cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins by incorporating position specific amino acid propensity into pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS One 8:e55844
Xu Y, Shao X-J, Wu L-Y, Deng N-Y, Chou K-C (2013b) iSNO-AAPair: incorporating amino acid pairwise coupling into PseAAC for predicting cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins. PeerJ 1:e171
Xu Y, Wen X, Wen L-S, Wu L-Y, Deng N-Y, Chou K-C (2014) iNitro-tyr: prediction of nitrotyrosine sites in proteins with general pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS One 9:e105018
Yang X, Macdonald C, Ounis I (2018) Using word embeddings in twitter election classification. Inf Retr J 21:183–207
Zhang C-T, Chou K-C (1992) An optimization approach to predicting protein structural class from amino acid composition. Protein Sci 1:401–408
Zhang J, Zhao X, Sun P, Ma Z (2014) PSNO: predicting cysteine S-nitrosylation sites by incorporating various sequence-derived features into the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Int J Mol Sci 15:11204–11219
Zhang G, Huang H, Liu D, Cheng Y, Liu X, Zhang W, Yin R, Zhang D, Zhang P, Liu J, Li C, Liu B, Luo Y, Zhu Y, Zhang N, He S, He C, Wang H, Chen D (2015) N 6-methyladenine DNA modification in drosophila. Cell 161:893–906
Zhou G-P (2011) The disposition of the LZCC protein residues in wenxiang diagram provides new insights into the protein–protein interaction mechanism. J Theor Biol 284:142–148
Zhou GP, Deng MH (1984) An extension of Chou’s graphic rules for deriving enzyme kinetic equations to systems involving parallel reaction pathways. Biochemical Journal 222:169
Zhou C, Wang C, Liu H, Zhou Q, Liu Q, Guo Y, Peng T, Song J, Zhang J, Chen L, Zhao Y, Zeng Z, Zhou D-X (2018) Identification and analysis of adenine N 6-methylation sites in the rice genome. Nat Plants 4:554–563
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of NVIDIA Corporation with the donation of the Titan Xp GPU used for this research.
Funding
The author received no funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, N.Q.K. iN6-methylat (5-step): identifying DNA N6-methyladenine sites in rice genome using continuous bag of nucleobases via Chou’s 5-step rule. Mol Genet Genomics 294, 1173–1182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01570-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01570-y