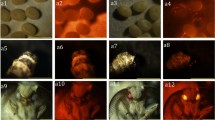
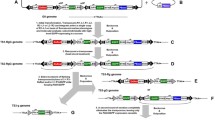
Abstract
Deletion of transposable elements post-genomic integration holds great promise for stability of the transgene in the host genome and has an essential role for the practical application of transgenic animals. In this study, a modified piggyBac vector that mediated deletion of the transposon sequence post-integration for transgene stability in the economically important silkworm Bombyx mori was constructed. The piggyBac vector architecture contains inversed terminal repeat sequences L1, L2 and R1, which can form L1/R1 and L2/R1 types of transposition cassettes. hsp70-PIG as the piggyBac transposase expression cassette for initial transposition, further remobilization and transgene stabilization test was transiently expressed in a helper vector or integrated into the modified vector to produce a transgenic silkworm. Shortening L2 increased the transformation frequency of L1/R1 into the silkworm genome compared to L2/R1. After the integration of L1/R1 into the genome, the remobilization of L2/R1 impaired the transposon structure and the resulting transgene linked with an impaired transposon was stable in the genome even in the presence of exogenously introduced transposase, whereas those flanked by the intact transposon were highly mobile in the genome. Our results demonstrated the feasibility of post-integration deletion of transposable elements to guarantee true transgene stabilization in silkworm. We suggest that the modified vector will be a useful resource for studies of transgenic silkworms and other piggyBac-transformed organisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg CA, Spradling AC (1991) Studies on the rate and site-specificity of P element transposition. Genetics 127:515–524
Consortium ISG (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1036–1045
Dafa’alla TH, Condon GC, Condon KC, Phillips CE, Morrison NI, Jin L, Epton MJ, Fu G, Alphey L (2006) Transposon-free insertions for insect genetic engineering. Nat Biotechnol 24:820–821
Fraser MJ Jr (2012) Insect transgenesis: current applications and future prospects. Annu Rev Entomol 57:267–289
Goldsmith MR, Shimada T, Abe H (2005) The genetics and genomics of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Annu Rev Entomol 50:71–100
Handler AM, Harrell RA 2nd (1999) Germline transformation of Drosophila melanogaster with the piggyBac transposon vector. Insect Mol Biol 8:449–457
Handler AM, Zimowska GJ, Horn C (2004) Post-integration stabilization of a transposon vector by terminal sequence deletion in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Biotechnol 22:1150–1154
Hino R, Tomita M, Yoshizato K (2006) The generation of germline transgenic silkworms for the production of biologically active recombinant fusion proteins of fibroin and human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 27:5715–5724
Horn C, Wimmer EA (2000) A versatile vector set for animal transgenesis. Dev Genes Evol 210:630–637
Iizuka T, Sezutsu H, Tatematsu K, Kobayashi I, Yonemura N, Uchino K, Nakajima K, Kojima K, Takabayashi C, Machii H, Yamada K, Kurihara H, Asakura T, Nakazawa Y, Miyawaki A, Karasawa S, Kobayashi H, Yamaguchi J, Kuwabara N, Nakamura T, Yoshii K, Tamura T (2013) Colored fluorescent silk made by transgenic silkworms. Adv Funct Mater 23:5232–5239
Jiang L, Cheng T, Zhao P, Yang Q, Wang G, Jin S, Lin P, Xiao Y, Xia Q (2012) Resistance to BmNPV via overexpression of an exogenous gene controlled by an inducible promoter and enhancer in transgenic silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS One 7:e41838
Jiang L, Zhao P, Cheng TC, Sun Q, Peng ZW, Dang YH, Wu XW, Wang GH, Jin SK, Lin P, Xia QY (2013) A transgenic animal with antiviral properties that might inhibit multiple stages of infection. Antiviral Res 98:171–173
Jiang L, Sun Q, Liu W, Guo H, Peng Z, Dang Y, Huang C, Zhao P, Xia Q (2014) Postintegration stability of the silkworm piggyBac transposon. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 50:18–23
Ma L, Xu H, Zhu J, Ma S, Liu Y, Jiang RJ, Xia Q, Li S (2011) Ras1(CA) overexpression in the posterior silk gland improves silk yield. Cell Res 21:934–943
Ma S, Zhang S, Wang F, Liu Y, Xu H, Liu C, Lin Y, Zhao P, Xia Q (2012) Highly efficient and specific genome editing in silkworm using custom TALENs. PLoS One 7:e45035
Ma S, Chang J, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhang J, Lu W, Gao J, Shi R, Zhao P, Xia Q (2014) CRISPR/Cas9 mediated multiplex genome editing and heritable mutagenesis of BmKu70 in Bombyx mori. Sci Rep 4:4489
Rubin GM, Spradling AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T, Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, Shirk P, Fraser M, Prudhomme JC, Couble P (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Teule F, Miao YG, Sohn BH, Kim YS, Hull JJ, Fraser MJ, Lewis RV, Jarvis DL (2012) Silkworms transformed with chimeric silkworm/spider silk genes spin composite silk fibers with improved mechanical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:923–928
Thibault ST, Singer MA, Miyazaki WY, Milash B, Dompe NA, Singh CM, Buchholz R, Demsky M, Fawcett R, Francis-Lang HL, Ryner L, Cheung LM, Chong A, Erickson C, Fisher WW, Greer K, Hartouni SR, Howie E, Jakkula L, Joo D, Killpack K, Laufer A, Mazzotta J, Smith RD, Stevens LM, Stuber C, Tan LR, Ventura R, Woo A, Zakrajsek I, Zhao L, Chen F, Swimmer C, Kopczynski C, Duyk G, Winberg ML, Margolis J (2004) A complementary transposon tool kit for Drosophila melanogaster using P and piggyBac. Nat Genet 36:283–287
Thomas JL, Da Rocha M, Besse A, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G (2002) 3xP3-EGFP marker facilitates screening for transgenic silkworm Bombyx mori L. from the embryonic stage onwards. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:247–253
Tomita M (2011) Transgenic silkworms that weave recombinant proteins into silk cocoons. Biotechnol Lett 33:645–654
Uchino K, Sezutsu H, Imamura M, Kobayashi I, Tatematsu K, Iizuka T, Yonemura N, Mita K, Tamura T (2008) Construction of a piggyBac-based enhancer trap system for the analysis of gene function in silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1165–1173
Wang F, Ma S, Xu H, Duan J, Wang Y, Ding H, Liu Y, Wang X, Zhao P, Xia Q (2013a) High-efficiency system for construction and evaluation of customized TALENs for silkworm genome editing. Mol Genet Genomics 288:683–690
Wang F, Xu H, Yuan L, Ma S, Wang Y, Duan X, Duan J, Xiang Z, Xia Q (2013b) An optimized sericin-1 expression system for mass-producing recombinant proteins in the middle silk glands of transgenic silkworms. Transgenic Res 22:925–938
Wang F, Xu H, Wang Y, Wang R, Yuan L, Ding H, Song C, Ma S, Peng Z, Zhao P, Xia Q (2014) Advanced silk material spun by a transgenic silkworm promotes cell proliferation for biomedical application. Acta Biomater 10:4947–4955
Xia Q, Zhou Z, Lu C, Cheng D, Dai F, Li B, Zhao P, Zha X, Cheng T, Chai C, Pan G, Xu J, Liu C, Lin Y, Qian J, Hou Y, Wu Z, Li G, Pan M, Li C, Shen Y, Lan X, Yuan L, Li T, Xu H, Yang G, Wan Y, Zhu Y, Yu M, Shen W, Wu D, Xiang Z, Yu J, Wang J, Li R, Shi J, Li H, Li G, Su J, Wang X, Li G, Zhang Z, Wu Q, Li J, Zhang Q, Wei N, Xu J, Sun H, Dong L, Liu D, Zhao S, Zhao X, Meng Q, Lan F, Huang X, Li Y, Fang L, Li C, Li D, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Huang Y, Xi Y, Qi Q, He D, Huang H, Zhang X, Wang Z, Li W, Cao Y, Yu Y, Yu H, Li J, Ye J, Chen H, Zhou Y, Liu B, Wang J, Ye J, Ji H, Li S, Ni P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Mao B, Wang W, Ye C, Li S, Wang J, Wong GK, Yang H (2004) A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 306:1937–1940
Xia Q, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Li D, Xuan Z, Li Z, Dai F, Li Y, Cheng D, Li R, Cheng T, Jiang T, Becquet C, Xu X, Liu C, Zha X, Fan W, Lin Y, Shen Y, Jiang L, Jensen J, Hellmann I, Tang S, Zhao P, Xu H, Yu C, Zhang G, Li J, Cao J, Liu S, He N, Zhou Y, Liu H, Zhao J, Ye C, Du Z, Pan G, Zhao A, Shao H, Zeng W, Wu P, Li C, Pan M, Li J, Yin X, Li D, Wang J, Zheng H, Wang W, Zhang X, Li S, Yang H, Lu C, Nielsen R, Zhou Z, Wang J, Xiang Z, Wang J (2009) Complete resequencing of 40 genomes reveals domestication events and genes in silkworm (Bombyx). Science 326:433–436
Xia Q, Li S, Feng Q (2013) Advances in silkworm studies accelerated by the genome sequencing of Bombyx mori. Annu Rev Entomol 59:513–536
Xu HF, Xia QY, Liu C, Cheng TC, Zhao P, Duan J, Zha XF, Liu SP (2006) Identification and characterization of piggyBac-like elements in the genome of domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori. Mol Genet Genomics 276:31–40
Zhao A, Zhao T, Zhang Y, Xia Q, Lu C, Zhou Z, Xiang Z, Nakagaki M (2010) New and highly efficient expression systems for expressing selectively foreign protein in the silk glands of transgenic silkworm. Transgenic Res 19:29–44
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, 2012CB114600), National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863 program, 2011AA100306), 2362014xk06 and doctoral innovation fund of southwest university (kb2011008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communiacated by: S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Wang, R., Wang, Y. et al. Remobilizing deleted piggyBac vector post-integration for transgene stability in silkworm. Mol Genet Genomics 290, 1181–1189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0982-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0982-6