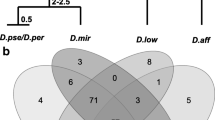
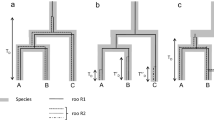
Abstract
A PCR screening approach was used to search for sequences homologous to a previously described hAT transposon found in Drosophila simulans and Drosophila sechellia, named here as hosimary. In this study, 52 Drosophilidae species were analyzed and these sequences seem to be restricted to some species of the melanogaster group and Zaprionus indianus. These species present variable number of copies and most of those appear to be putatively encoding. The high hosimary sequences similarity among different species and the patchy distribution presented by this transposon strongly support the hypothesis that hosimary was horizontally transferred between the melanogaster group species and Z. indianus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida L, Carareto CM (2006) Sequence heterogeneity and phylogenetic relationships between the copia retrotransposon in Drosophila species of the repleta and melanogaster groups. Genet Sel Evol 38:535–550
Arensburger P, Kim YJ, Orsetti J, Aluvihare C, O’Brochta DA, Atkinson PW (2005) An active transposable element, Herves, from the African malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Genetics 169:697–708
Bartolomé C, Bello X, Maside X (2009) Widespread evidence for horizontal transfer of transposable elements across Drosophila genomes. Genome Biol. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-r22
Biémont C, Vieira C (2006) Junk DNA as an evolutionary force. Nature 443:521–524
Boer JG, Yazawa R, Davidson WS, Koop BF (2007) Bursts and horizontal evolution of DNA transposons in the speciation of pseudotetraploid salmonids. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-422 8:422
Brunet F, Godin F, Bazin C, Capy P (1999) Phylogenetic analysis of Mos1-Like transposable elements in the Drosophilidae. J Mol Evol 49:760–768
Calvi BR, Hong TJ, Findley SD, Gelbart WM (1991) Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of inverted repeat transposons in Drosophila and plants: hobo, Activator, and Tam3. Cell 66:465–471
Capy P, Bazin C, Higuet D, Langin T (1998) Dynamics and evolution of transposable elements. Landes Bioscience, Austin, Texas
Clark AG, Eisen MB, Smith DR, Bergman CM, Oliver B, Markow TA et al (2007) Evolution of genes and genomes on the Drosophila phylogeny. Nature 450:203–218
Coates CJ, Jonhson KM, Perkins HD, Howells AJ, O’Brochta DA, Atkinson PW (1996) The hermit transposable element of the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina, belongs to the hAT family of transposable elements. Genetica 97:23–31
Daniels SB, Chovnick A, Boussy IA (1990) Distribution of hobo transposable elements in the genus Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 7:589–606
David J, Lemeunier F, Tsacas L, Yassin A (2007) The historical discovery of the nine species in the Drosophila melanogaster species subgroup. Genetics 177:1969–1973
Diao X, Freeling M, Lisch D (2006) Horizontal transfer of a plant transposon. PLoS Biology 4:119–128
Finnegan DJ (1989) Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5:103–107
Grumbling G, Strelets V (2006) FlyBase: anatomical data, images and queries. Nucleic Acids Res 34:484–488
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol 22:160–174
Hehl R, Nacken WK, Krause A, Saedler H, Sommer H (1991) Structural analysis of Tam3, a transposable element from Antirrhinum majus, reveal homologies to the Ac element from maize. Plant Mol Biol 16:369–371
Herédia FO, Loreto ELS, Valente VLS (2004) Complex evolution of gypsy in Drosophilid species. Mol Biol Evol 21:1–12
Hickman AB, Perez ZN, Zhou LQ, Musingarimi P, Ghirlando R, Hinshaw JE, Craig NL, Dyda F (2005) Molecular architecture of a eukaryotic DNA transposase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:715–721
Hotopp JC, Clark ME, Oliveira DC, Foster JM, Fischer P, Torres MC et al (2007) Widespread lateral gene transfer from intracellular bacteria to multicellular eukaryotes. Science 317:1753–1756
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2003) Molecular paleontology of transposable elements in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6569–6574
Kempken F, Windhofer F (2001) The hAT family: a versatile transposon group common to plants, fungi, animals, and man. Chromosoma 110:1–9
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (1997) Transposable elements as sources of variation in animals and plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7704–7711
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (2001) Transposable elements, parasitic DNA, and genome evolution. Evolution 55:1–24
Klasson L, Kambris Z, Cook PE, Walker T, Sinkins SP (2009) Horizontal gene transfer between Wolbachia and the mosquito Aedes aegypti. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-33
Lachaise D, Silvain JF (2004) How two Afrotropical endemics made two cosmopolitan human commensals: the Drosophila melanogaster–D. simulans paleogeographic riddle. Genetica 120:17–39
Lachaise D, David JR, Lemeunier F, Tsacas L, Ashburner M (1986) The reproductive relationships of Drosophila sechellia with D. mauritiana, D. simulans and D. melanogaster from the Afrotropical region. Evolution 40:262–271
Le Rouzic A, Boutin TS, Capy P (2007) Long-term evolution of transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19375–19380
Lerat E, Rizzon C, Biémont C (2003) Sequence divergence of transposable elements in the D. melanogaster genome. Genome Res 13:1889–1896
Loreto EL, Zaha A, Nichols C, Pollock JA, Valente VLS (1998) Characterization of a hypermutable strain of Drosophila simulans. Cell Mol Life Sci 54:1283–1290
Loreto EL, Carareto CMA, Capy P (2008) Revisiting horizontal transfer of transposable elements in Drosophila. Heredity 100:545–554
Ludwig A, Valente VLS, Loreto ELS (2008) Multiple invasions of Errantivirus in the genus Drosophila. Insect Mol Biol 17:113–124
Maruyama K, Hartl DL (1991) Evidence for interspecific transfer of the transposable element mariner between Drosophila and Zaprionus. J Mol Evol 33:514–524
Maside X, Assimacopoulos S, Charlesworth B (2005) Fixation of transposable elements in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genet Res 85:195–203
McClintock B (1947) Cytogenetic studies of maize and Neurospora. Carnegie Inst Washington Year Book 46:146–152
Michalak P, Noor MAF (2004) Association of Misexpression with Sterility in Hybrids of Drosophila simulans and D. mauritiana. J Mol Evol 59:277–282
Morton BR (1993) Chloroplast DNA codon use: evidence for selection at the psbA locus based on tRNA availability. J Mol Evol 37:273–280
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Nylander JAA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Uppsala
Ortiz M, Loreto EL (2009) Characterization of new hAT transposable elements in twelve Drosophila genomes. Genetica 135:67–75
Pace JK II, Gilbert C, Clark MS, Feschotte C (2008) Repeated horizontal transfer of a DNA transposon in mammals and other tetrapods. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17023–17028
Remsen J, O’Grady P (2002) Phylogeny of Drosophilinae (Diptera: Drosophilidae), with comments on combined analysis and character support. Mol Phylogenet Evol 24:249–264
Robe LJ (2008) Relações filogenéticas no gênero Drosophila (Diptera, Drosophilidae): uma abordagem molecular. PhD Thesis. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul
Robe LJ, Valente VLS, Budnik M, Loreto ELS (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the subgenus Drosophila (Diptera, Drosophilidae) with an emphasis on Neotropical species and groups: a nuclear versus mitochondrial gene approach. Mol Phylogenet Evol 36:623–640
Robert CE (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Roulin A, Piegu B, Wing RA, Panaud O (2008) Evidence of multiple horizontal transfers of the long terminal repeat retrotransposon RIRE1 within the genus Oryza. Plant J 53:950–959
Rozas J, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC, Messenguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Rubin E, Lithwick G, Levy AA (2001) Structure and evolution of the hAT transposon superfamily. Genetics 158:949–957
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sanchez-Gracia A, Maside X, Charlesworth B (2005) High rate of horizontal transfer of transposable elements in Drosophila. Trends Genet 21:200–203
Sassi AK, Herédia FO, Loreto ELS, Valente VLS, Rohde C (2005) Transposable elements P and gypsy in natural populations of Drosophila willistoni. Genet Mol Biol 28:734–739
Sharp PM, Li W-H (1989) On the rate of DNA sequence evolution in Drosophila. J Mol Evol 28:398–402
Silva JC, Kidwell MG (2000) Horizontal transfer and selection in the evolution of P element. Mol Biol Evol 17:1542–1557
Silva JC, Loreto EL, Clark JB (2004) Factors that affect the horizontal transfer of transposable elements. Curr Issues Mol Biol 6:57–72
Souames S, Bazin C, Bonnivard E, Higuet D (2003) Behavior of the hobo transposable element with regard to TPE repeats in transgenic lines of Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 20:2055–2066
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analyses package. Mol Biotechnol 5:233–241
Subramanian RA, Cathcart LA, Krafsur ES, Atkinson PW, O’Brochta DA (2009) Hermes transposon distribution and structure in Musca domestica. J Hered 100:473–480
Tamura K (1992) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitution when there are strong transition-transversion and G + C biases. Mol Biol Evol 9:678–687
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Vidal NM, Ludwig A, Loreto ELS (2009) Evolution of Tom, 297, 17.6 and rover retrotransposons in Drosophilidae species. Mol Genet Genomics Doi:10.1007/s00438-009-0468-0
Vieira C, Fablet M, Lerat E (2009) Infra- and transspecific Clues to understanding the dynamics of transposable elements. In: Lankenau DH, Volff JN (eds) Transposons and the dynamic genome. Springer, Berlin
Warren WD, Atkinson PW, O’Brochta DA (1994) The Hermes transposable element from the house fly, Musca domestica, is a short inverted repeat-type element of the hobo, Ac, and Tam3 (hAT) element family. Genet Res 64:87–97
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B et al (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Wright F (1990) The “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 87:23–29
Yassin A, Araripe LO, Capy P, Da Lage JL, Klaczko LB, Maisonhaute C, Ogereau D, David JR (2008) Grafting the molecular phylogenetic tree with morphological branches to reconstruct the evolutionary history of the genus Zaprionus (Díptera: Drosophilidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:903–915
Acknowledgments
To Dra. Claude Bazin for gently providing the Zola strain. To M.Sc. Nina Roth Mota and Dra. Lizandra Robe for the valuable help and critical comments which contributed significantly to the improvement of this manuscript. To M.Sc. Paloma Rubin for sequencing the DNA samples. This work was supported by grants from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Reuter.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deprá, M., Panzera, Y., Ludwig, A. et al. hosimary: a new hAT transposon group involved in horizontal transfer. Mol Genet Genomics 283, 451–459 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0531-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0531-x