Abstract
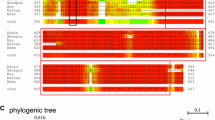
Mind bomb (Mib) facilitates Notch signaling pathway by promoting the endocytosis of Notch ligand. The zebrafish mib ta52b mutant has a defect in its ubiquitin ligase activity which is necessary to inhibit the neurogenesis, resulting in a neuronal hyperplasia. Several genes regulated in the mib ta52b mutant have been well established, however, there were relatively few reports about the transcriptome profile. To identify the genes differentially expressed in the mib ta52b mutant, genome-wide analysis was performed using serial analysis of gene expression. Three hundred and thirty-five transcripts were identified whose expressions were significantly altered in the mib ta52b mutant as compared with the wild-type. Interestingly, it was suggested that the mib ta52b mutation may affect not only neurogenesis but also mesoderm development. These results provide new insights into Notch signaling pathway.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Simpson P (1991) Choosing a cell fate: a view from the Notch locus. Trends Genet 7:403–408
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Brou C, Logeat F, Gupta N, Bessia C, Lebail O, Doedens JR, Cumano A, Roux P, Black RA, Israël A (2000) A novel proteolytic cleavage involved in Notch signaling: the role of the disintegrin-metalloprotease TACE. Mol Cell 5:207–216
Campos-Ortega JA (1988) Cellular interactions during early neurogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Neurosci 11:400–405
Charroux B, Pellizzoni L, Perkinson RA, Yong J, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (2000) Gemin4. A novel component of the SMN complex that is found in both gems and nucleoli. J Cell Biol 148:1177–1186
De Strooper B (2003) Aph-1, Pen-2, and nicastrin with presenilin generate an active gamma-secretase complex. Neuron 38:9–12
Fischer U, Liu Q, Dreyfuss G (1997) The SMN-SIP1 complex has an essential role in spliceosomal snRNP biogenesis. Cell 90:1023–1029
Fortini ME (2002) Gamma-secretase-mediated proteolysis in cell-surface-receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:673–684
Geling A, Plessy C, Rastegar S, Strähle U, Bally-Cuif L (2004) Her5 acts as a prepattern factor that blocks neurogenin1 and coe2 expression upstream of Notch to inhibit neurogenesis at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. Development 131:1993–2006
Greenwald I, Rubin GM (1992) Making a difference: the role of cell–cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell 68:271–281
Hegde A, Qiu NC, Qiu X, Ho SH, Tay KQ, George J, Ng FS, Govindarajan KR, Gong Z, Mathavan S, Jiang YJ (2008) Genomewide expression analysis in zebrafish mind bomb alleles with pancreas defects of different severity identifies putative notch responsive genes. PLoS ONE 3:e1479
Huovila AP, Turner AJ, Pelto-Huikko M, Kärkkäinen I, Ortiz RM (2005) Shedding light on ADAM metalloproteinases. Trends Biochem Sci 30:413–422
Hyatt BA, Yost HJ (1998) The left–right coordinator: the role of Vg1 in organizing left–right axis formation. Cell 93:37–46
Hyatt BA, Lohr JL, Yost HJ (1996) Initiation of vertebrate left–right axis formation by maternal Vg1. Nature 384:62–65
Isaka F, Shimizu C, Nakanishi S, Kageyama R (1996) Genetic mapping of four mouse bHLH genes related to Drosophila proneural gene atonal. Genomics 37:400–402
Itoh M, Kim CH, Palardy G, Oda T, Jiang YJ, Maust D, Yeo SY, Lorick K, Wright GJ, Ariza-McNaughton L, Weissman AM, Lewis J, Chandrasekharappa SC, Chitnis AB (2003) Mind bomb is a ubiquitin ligase that is essential for efficient activation of Notch signaling by Delta. Dev Cell 4:67–82
Jarriault S, Greenwald I (2005) Evidence for functional redundancy between C. elegans ADAM proteins SUP-17/Kuzbanian and ADM-4/TACE. Dev Biol 287:1–10
Jiang YJ, Brand M, Heisenberg CP, Beuchle D, Furutani-Seiki M, Kelsh RN, Warga RM, Granato M, Haffter P, Hammerschmidt M, Kane DA, Mullins MC, Odenthal J, van Eeden FJ, Nüsslein-Volhard C (1996) Mutations affecting neurogenesis and brain morphology in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development 123:205–216
Jiang YJ, Aerne BL, Smithers L, Haddon C, Ish-Horowicz D, Lewis J (2000) Notch signalling and the synchronization of the somite segmentation clock. Nature 408:475–479
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Lawson ND, Scheer N, Pham VN, Kim CH, Chitnis AB, Campos-Ortega JA, Weinstein BM (2001) Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 128:3675–3683
Lee S, Hwang J, Ulaszek J, Kim YC, Dong H, Kim HS, Seok JW, Suh BK, Yim SJ, Johnson D, Choe NH, Chang KT, Ryoo ZY, Tseng CC, Wickrema A, Wang SM (2007) Stable transcriptional status in the apoptotic erythroid genome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 359:556–562
Meister G, Hannus S, Plottner O, Baars T, Hartmann E, Fakan S, Laggerbauer B, Fischer U (2001) SMNrp is an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor required for the formation of the mature spliceosome. Embo J 20:2304–2314
Mueller T, Wullimann MF (2003) Anatomy of neurogenesis in the early zebrafish brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 140:137–155
Mumm JS, Kopan R (2000) Notch signaling: from the outside in. Dev Biol 228:151–165
Nam DK, Lee S, Zhou G, Cao X, Wang C, Clark T, Chen J, Rowley JD, Wang SM (2002) Oligo(dT) primer generates a high frequency of truncated cDNAs through internal poly(A) priming during reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6152–6156
Pellizzoni L, Kataoka N, Charroux B, Dreyfuss G (1998) A novel function for SMN, the spinal muscular atrophy disease gene product, in pre-mRNA splicing. Cell 95:615–624
Qiu X, Xu H, Haddon C, Lewis J, Jiang YJ (2004) Sequence and embryonic expression of three zebrafish fringe genes: lunatic fringe, radical fringe, and manic fringe. Dev Dyn 231:621–630
Ramsdell AF, Yost HJ (1999) Cardiac looping and the vertebrate left-right axis: antagonism of left-sided Vg1 activity by a right-sided ALK2-dependent BMP pathway. Development 126:5195–5205
Schier AF, Neuhauss SC, Harvey M, Malicki J, Solnica-Krezel L, Stainier DY, Zwartkruis F, Abdelilah S, Stemple DL, Rangini Z, Yang H, Driever W (1996) Mutations affecting the development of the embryonic zebrafish brain. Development 123:165–178
Selkoe D, Kopan R (2003) Notch and Presenilin: regulated intramembrane proteolysis links development and degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:565–597
Shpargel KB, Matera AG (2005) Gemin proteins are required for efficient assembly of Sm-class ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:17372–17377
Six E, Ndiaye D, Laabi Y, Brou C, Gupta-Rossi N, Israel A, Logeat F (2003) The Notch ligand Delta1 is sequentially cleaved by an ADAM protease and gamma-secretase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7638–7643
Taghert PH, Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1984) Cell determination and regulation during development of neuroblasts and neurones in grasshopper embryo. Nature 307:163–165
Thisse C, Thisse B, Schilling TF, Postlethwait JH (1993) Structure of the zebrafish snail1 gene and its expression in wild-type, spadetail and no tail mutant embryos. Development 119:1203–1215
Thisse B, Pflumio S, Fürthauer M, Loppin B, Heyer V, Degrave A, Woehl R, Lux A, Steffan T, Charbonnier XQ, Thisse C (2001) Expression of the zebrafish genome during embryogenesis (NIH R01 RR15402). ZFIN Direct Data Submission (http://zfin.org)
van Bergeijk J, Rydel-Konecke K, Grothe C, Claus P (2007) The spinal muscular atrophy gene product regulates neurite outgrowth: importance of the C terminus. FASEB J 21:1492–1502
van Eeden FJ, Granato M, Schach U, Brand M, Furutani-Seiki M, Haffter P, Hammerschmidt M, Heisenberg CP, Jiang YJ, Kane DA, Kelsh RN, Mullins MC, Odenthal J, Warga RM, Allende ML, Weinberg ES, Nüsslein-Volhard C (1996) Mutations affecting somite formation and patterning in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Development 123:153–164
Velculescu VE, Zhang L, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1995) Serial analysis of gene expression. Science 270:484–487
Wang W, Struhl G (2004) Drosophila epsin mediates a select endocytic pathway that DSL ligands must enter to activate Notch. Development 131:5367–5380
Wang W, Struhl G (2005) Distinct roles for mind bomb, neuralized and epsin in mediating DSL endocytosis and signaling in Drosophila. Development 132:2883–2894
Yeo SY, Kim M, Kim HS, Huh TL, Chitnis AB (2007) Fluorescent protein expression driven by her4 regulatory elements reveals the spatiotemporal pattern of Notch signaling in the nervous system of zebrafish embryos. Dev Biol 301:555–567
Zhang C, Li Q, Lim CH, Qiu X, Jiang YJ (2007) The characterization of zebrafish antimorphic mib alleles reveals that Mib and Mind bomb-2 (Mib2) function redundantly. Dev Biol 305:14–27
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Research grant from Ministry of Science and Technology (NBM2300812).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Becker.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
438_2008_395_MOESM1_ESM.doc
MOESM1 Confirm the mesoderm-specific expression of zgc:162968 using whole-mount in situ hybridization. Cross-section of the trunk somite shows that zgc:162968 is specifically expressed in somatic mesoderm (arrows). The sectioned level is indicated by black line in left panel. (DOC 1534 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, J., Kim, HS., Seok, JW. et al. Transcriptome analysis of the zebrafish mind bomb mutant. Mol Genet Genomics 281, 77–85 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0395-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0395-5