Abstract
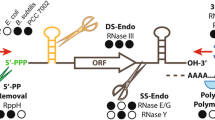
Light-responsive gene expression is crucial to photosynthesizing organisms. Here, we studied functions of cis-elements (AU-box and SD sequences) and a trans-acting factor (ribonuclease, RNase) in light-responsive expression in cyanobacteria. The results indicated that AU-rich nucleotides with an AU-box, UAAAUAAA, just upstream from an SD confer instability on the mRNA under darkness. An RNase E/G homologue, Slr1129, of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 was purified and confirmed capable of endoribonucleolytic cleavage at the AU- (or AG)-rich sequences in vitro. The cleavage depends on the primary target sequence and secondary structure of the mRNA. Complementation tests using Escherichia coli rne/rng mutants showed that Slr1129 fulfilled the functions of both the RNase E and RNase G. An analysis of systematic mutations in the AU-box and SD sequences showed that the cis-elements also affect significantly mRNA stability in light-responsive genes. These results strongly suggested that dark-induced mRNA instability involves RNase E/G-type cleavage at the AU-box and SD sequences in cyanobacteria. The mechanical impact and a possible common mechanism with RNases for light-responsive gene expression are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afonyushkin T, Vecerek B, Moll I, Blasi U, Kaberdin VR (2005) Both RNase E and RNase III control the stability of sodB mRNA upon translational inhibition by the small regulatory RNA RyhB. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1678–1689
Agrawal GK, Asayama M, Shirai M (1997) A novel bend of DNA CIT: changeable bending-center sites of an intrinsic curvature under temperature conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 147:139–145
Agrawal GK, Kato H, Asayama M, Shirai M (2001) An AU-box motif upstream of the SD sequence of light-dependent psbA transcripts confers mRNA instability in darkness in cyanobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 29:1835–1843
Agrawal GK, Asayama M, Shirai M (2003) Two distinct curved DNAs upstream of the light-responsive psbA gene in a cyanobacterium. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1817–1821
Asayama M (2006) Regulatory system for light-responsive gene expression in photosynthesizing bacteria: cis-elements and trans-acting factors in transcription and post-transcription. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:565–573
Asayama M, Tanaka K, Takahashi H, Sato A, Aida T, Shirai M (1996a) Cloning, sequencing and characterization of the gene encoding a principal sigma factor homolog from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa K-81. Gene 181:213–217
Asayama M, Suzuki H, Sato A, Aida T, Tanaka K, Takahashi H, Shirai M (1996b) The rpoD1 gene product is a principal sigma factor of RNA polymerase in Microcystis aeruginosa K-81. J Biochem (Tokyo) 120:752–758
Asayama M, Hayasaka Y, Kabasawa M, Shirai M, Ohyama A (1999) An intrinsic DNA curvature found in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa K-81 affects the promoter activity of rpoD1 encoding a principal sigma factor. J Biochem (Tokyo) 125:460–468
Asayama M, Kato H, Shibato J, Shirai M, Ohyama T (2002) The curved DNA structure in the 5′-upstream region of the light-responsive genes: its universality, binding factor and function for cyanobacterial psbA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4658–4666
Baginsky S, Gruissem W (2001) Chloroplast mRNA 3′-end nuclease complex. Methods Enzymol 342:408–419
Baginsky S, Gruissem W (2002) Endonucleolytic activation directs dark-induced chloroplast mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4527–4533
Baginsky S, Shteiman-Kotler A, Liveanu V, Yehudai-Resheff S, Bellaoui M, Settlage RE, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Schuster G, Gruissem W (2001) Chloroplast PNPase exists as a homo-multimer enzyme complex that is distinct from the Escherichia coli degradosome. RNA 7:1464–1475
Blum E, Py B, Carpousis AJ, Higgins CF (1997) Polyphosphate kinase is a component of the Escherichia coli RNA degradosome. Mol Microbiol 26:387–398
Braun F, Hajnsdorf E, Regnier P (1996) Polynucleotide phosphorylase is required for the rapid degradation of the RNase E-processed rpsO mRNA of Escherichia coli devoid of its 3′ hairpin. Mol Microbiol 19:997–1005
Callaghan AJ, Marcaida MJ, Stead JA, McDowall KJ, Scott WG, Luisi BF (2005) Structure of Escherichia coli RNase E catalytic domain and implications for RNA turnover. Nature 437:1187–1191
Carpousis AJ (2002) The Escherichia coli RNA degradosome: structure, function and relationship in other ribonucleolytic multienzyme complexes. Biochem Soc Trans 30:150–155
Carpousis AJ, Van Houwe G, Ehretsmann C, Krisch HM (1994) Copurification of E. coli RNAase E and PNPase: evidence for a specific association between two enzymes important in RNA processing and degradation. Cell 76:889–900
Carpousis AJ, Vanzo NF, Raynal LC (1999) mRNA degradation. A tale of poly(A) and multiprotein machines. Trends Genet 15:24–28
Cormack RS, Mackie GA (1992) Structural requirements for the processing of Escherichia coli 5S ribosomal RNA by RNase E in vitro. J Mol Biol 228:1078–1090
Drager RG, Girard-Bascou J, Choquet Y, Kindle KL, Stern DB (1998) In vivo evidence for 5′→3′ exoribonuclease degradation of an unstable chloroplast mRNA. Plant J 13:85–96
Ehretsmann CP, Carpousis AJ, Krisch HM (1992) Specificity of Escherichia coli endoribonuclease RNase E: in vivo and in vitro analysis of mutants in a bacteriophage T4 mRNA processing site. Genes Dev 6:149–159
Fritsch J, Rothfuchs R, Rauhut R, Klug G (1995) Identification of an mRNA element promoting rate-limiting cleavage of the polycistronic puf mRNA in Rhodobacter capsulatus by an enzyme similar to RNase E. Mol Microbiol 15:1017–1029
Geissmann TA, Touati D (2004) Hfq, a new chaperoning role: binding to messenger RNA determines access for small RNA regulator. EMBO J 23:396–405
Golden SS, Brusslan J, Haselkorn R (1987) Genetic engineering of the cyanobacterial chromosome. Methods Enzymol 153:215–231
Gutierrez RA, MacIntosh GC, Green PJ (1999) Current perspectives on mRNA stability in plants: multiple levels and mechanisms of control. Trends Plant Sci 4:429–438
Hager DA, Burgess RR (1980) Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem 109:76–86
Hayes R, Kudla J, Gruissem W (1999) Degrading chloroplast mRNA: the role of polyadenylation. Trends Biochem Sci 24:199–202
Heck C, Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Balzer A, Klug G (1999) RNase E enzymes from Rhodobacter capsulatus and Escherichia coli differ in context- and sequence-dependent in vivo cleavage within the polycistronic puf mRNA. J Bacteriol 181:7621–7625
Horlitz M, Klaff P (2000) Gene-specific trans-regulatory functions of magnesium for chloroplast mRNA stability in higher plants. J Biol Chem 275:35638–35645
Imamura S, Yoshihara S, Nakano S, Shiozaki N, Yamada A, Tanaka K, Takahashi H, Asayama M, Shirai M (2003a) Purification, characterization, and gene expression of all sigma factors of RNA polymerase in a cyanobacterium. J Mol Biol 325:857–872
Imamura S, Asayama M, Takahashi H, Tanaka K, Shirai M (2003b) Antagonistic dark/light-induced SigB/SigD, group 2 sigma factors, expression through redox potential and their roles in cyanobacteria. FEBS Lett 554:357–362
Imamura S, Asayama M, Shirai M (2004) In vitro transcription analysis by reconstituted cyanobacterial RNA polymerase: roles of group 1 and 2 sigma factors and a core subunit, RpoC2. Genes Cells 9:1175–1187
Imamura S, Tanaka K, Shirai M, Asayama M (2006) Growth phase-dependent activation of nitrogen-related genes by a control network of group 1 and group 2 sigma factors in a cyanobacterium. J Biol Chem 281:2668–2675
Inagawa T, Okamoto S, Wachi M, Ochi K (2003) RNase ES of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) can complement the rne and rng mutations in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1767–1771
Ito Y, Asayama M, Shirai M (2003) Light-responsive psbA transcription requires the −35 hexamer in the promoter and its proximal upstream element, UPE, in cyanobacteria. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1382–1390
Jager S, Fuhrmann O, Heck C, Hebermehl M, Schiltz E, Rauhut R, Klug G (2001) An mRNA degrading complex in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4581–4588
Jiang X, Belasco JG (2004) Catalytic activation of multimeric RNase E and RNase G by 5′-monophosphorylated RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9211–9216
Jiang X, Diwa A, Belasco JG (2000) Regions of RNase E important for 5′-end-dependent RNA cleavage and autoregulated synthesis. J Bacteriol 182:2468–2475
Kaberdin VR (2003) Probing the substrate specificity of Escherichia coli RNase E using a novel oligonucleotide-based assay. Nucleic Acids Res 31:4710–4716
Kaberdin VR, Bizebard T (2005) Characterization of Aquifex aeolicus RNase E/G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:382–392
Kaberdin VR, Miczak A, Jakobsen JS, Lin-Chao S, McDowall KJ, von Gabain A (1998) The endoribonucleolytic N-terminal half of Escherichia coli RNase E is evolutionarily conserved in Synechocystis sp. and other bacteria but not the C-terminal half, which is sufficient for degradosome assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11637–11642
Kawamoto H, Morita T, Shimizu A, Inada T, Aiba H (2005) Implication of membrane localization of target mRNA in the action of a small RNA: mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation of glucose transporter in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev 19:328–338
Khemici V, Toesca I, Poljak L, Vanzo NF, Carpousis AJ (2004) The RNase E of Escherichia coli has at least two binding sites for DEAD-box RNA helicases: Functional replacement of RhlB by RhlE. Mol Microbiol 54:1422–1430
Khemici V, Poljak L, Toesca I, Carpousis AJ (2005) Evidence in vivo that the DEAD-box RNA helicase RhlB facilitates the degradation of ribosome-free mRNA by RNase E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6913–6918
Kulkarni RD, Golden SS (1997) mRNA stability is regulated by a coding-region element and the unique 5′ untranslated leader sequences of the three Synechococcus psbA transcripts. Mol Microbiol 24:1131–1142
Kunkel TA (1985) Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:488–492
Lee K, Cohen SN (2003) A Streptomyces coelicolor functional orthologue of Escherichia coli RNase E shows shuffling of catalytic and PNPase-binding domains. Mol Microbiol 48:349–360
Lee K, Zhan X, Gao J, Qiu J, Feng Y, Meganathan R, Cohen SN, Georgiou G (2003) RraA. a protein inhibitor of RNase E activity that globally modulates RNA abundance in E. coli. Cell 114:623–634
Li R, Golden SS (1993) Enhancer activity of light-responsive regulatory elements in the untranslated leader regions of cyanobacterial psbA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11678–11682
Li R, Dickerson NS, Mueller UW, Golden SS (1995) Specific binding of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 proteins to the enhancer element of psbAII required for high-light-induced expression. J Bacteriol 177:508–516
Li Z, Pandit S, Deutscher MP (1999) RNase G (CafA protein) and RNase E are both required for the 5′ maturation of 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J 18:2878–2885
Liere K, Link G (1997) Chloroplast endoribonuclease p54 involved in RNA 3′-end processing is regulated by phosphorylation and redox state. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2403–2408
Lin-Chao S, Wong TT, McDowall KJ, Cohen SN (1994) Effects of nucleotide sequence on the specificity of rne-dependent and RNase E-mediated cleavages of RNA I encoded by the pBR322 plasmid. J Biol Chem 269:10797–10803
Mackie GA (1991) Specific endonucleolytic cleavage of the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20 of Escherichia coli requires the product of the ams gene in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol 173:2488–2497
Mackie GA (1992) Secondary structure of the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20. Implications for cleavage by ribonuclease E. J Biol Chem 267:1054–1061
Mackie GA (1998) Ribonuclease E is a 5′-end-dependent endonuclease. Nature 395:720–723
Mackie GA, Genereaux JL (1993) The role of RNA structure in determining RNase E-dependent cleavage sites in the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20 in vitro. J Mol Biol 234:998–1012
Mandel M, Higa A (1970) Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol 53:159–162
Marcaida MJ, Depristo MA, Chandran V, Carpousis AJ, Luisi BF (2006) The RNA degradosome: life in the fast lane of adaptive molecular evolution. Trends Biochem Sci 31:359–365
Marchand I, Nicholson AW, Dreyfus M (2001) Bacteriophage T7 protein kinase phosphorylates RNase E and stabilizes mRNAs synthesized by T7 RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol 42:767–776
McDowall KJ, Cohen SN (1996) The N-terminal domain of the rne gene product has RNase E activity and is non-overlapping with the arginine-rich RNA-binding site. J Mol Biol 255:349–355
McDowall KJ, Hernandez RG, Lin-Chao S, Cohen SN (1993) The ams-1 and rne-3071 temperature-sensitive mutations in the ams gene are in close proximity to each other and cause substitutions within a domain that resembles a product of the Escherichia coli mre locus. J Bacteriol 175:4245–4249
McDowall KJ, Lin-Chao S, Cohen SN (1994) A+U content rather than a particular nucleotide order determines the specificity of RNase E cleavage. J Biol Chem 269:10790–10796
McDowall KJ, Kaberdin VR, Wu SW, Cohen SN, Lin-Chao S (1995) Site-specific RNase E cleavage of oligonucleotides and inhibition by stem-loops. Nature 374:287–290
Miczak A, Kaberdin VR, Wei CL, Lin-Chao S (1996) Proteins associated with RNase E in a multicomponent ribonucleolytic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3865–3869
Morita T, Maki K, Aiba H (2005) RNase E-based ribonucleoprotein complexes: mechanical basis of mRNA destabilization mediated by bacterial noncoding RNAs. Genes Dev 19:2176–2186
Nickelsen J, Link G (1993) The 54 kDa RNA-binding protein from mustard chloroplasts mediates endonucleolytic transcript 3′ end formation in vitro. Plant J 3:537–544
Py B, Higgins CF, Krisch HM, Carpousis AJ (1996) A DEAD-box RNA helicase in the Escherichia coli RNA degradosome. Nature 381:169–172
Rippka R (1988) Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167:3–27
Ross J (1995) mRNA stability in mammalian cells. Microbiol Rev 59:423–450
Rott R, Zipor G, Portnoy V, Liveanu V, Schuster G (2003) RNA polyadenylation and degradation in cyanobacteria are similar to the chloroplast but different from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 278:15771–15777
Shen Y, Danon A, Christopher DA (2001) RNA binding-proteins interact specifically with the Arabidopsis chloroplast psbA mRNA 5′ untranslated region in a redox-dependent manner. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1071–1078
Shibato J, Asayama M, Shirai M (1998) Specific recognition of the cyanobacterial psbA promoter by RNA polymerases containing principal sigma factors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1442:296–303
Shibato J, Agrawal GK, Kato H, Asayama M, Shirai M (2002) The 5′-upstream cis-acting sequences of a cyanobacterial psbA gene: analysis of their roles in basal, light-dependent and circadian transcription. Mol Genet Genomics 267:684–694
Sim S, Kim KS, Lee Y (2002) 3′-end processing of precursor M1 RNA by the N-terminal half of RNase E. FEBS Lett 529:225–231
Söderbom F, Svard SG, Kirsebom LA (2005) RNase E cleavage in the 5′ leader of a tRNA precursor. J Mol Biol 352:22–27
Tock MR, Walsh AP, Carroll G, McDowall KJ (2000) The CafA protein required for the 5′-maturation of 16 S rRNA is a 5′-end-dependent ribonuclease that has context-dependent broad sequence specificity. J Biol Chem 275:8726–8732
Tomcsányi T, Apirion D (1985) Processing enzyme ribonuclease E specifically cleaves RNA I. An inhibitor of primer formation in plasmid DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol 185:713–720
Umitsuki G, Wachi M, Takada A, Hikichi T, Nagai K (2001) Involvement of RNase G in in vivo mRNA metabolism in Escherichia coli. Genes Cells 6:403–410
Vytvytska O, Moll I, Kaberdin VR, von Gabain A, Bläsi U (2000) Hfq (HF1) stimulates ompA mRNA decay by interfering with ribosome binding. Genes Dev 14:1109–1118
Wachi M, Umitsuki G, Shimizu M, Takada A, Nagai K (1999) Escherichia coli cafA gene encodes a novel RNase, designated as RNase G, involved in processing of the 5′ end of 16S rRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259:483–488
Yang J, Schuster G, Stern DB (1996) CSP41, a sequence-specific chloroplast mRNA binding protein, is an endoribonuclease. Plant Cell 8:1409–1420
Yehudai-Resheff S, Hirsh M, Schuster G (2001) Polynucleotide phosphorylase functions as both an exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase in spinach chloroplasts. Mol Cell Biol 21:5408–5416
Yoshimura T, Imamura S, Tanaka K, Shirai M, Asayama M (2007) Cooperation of group 2 σ factors, SigD and SigE for light-induced transcription in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. FEBS Lett 581:1495–1500
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants from Scientific Research on Priority Areas from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan to MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horie, Y., Ito, Y., Ono, M. et al. Dark-induced mRNA instability involves RNase E/G-type endoribonuclease cleavage at the AU-box and SD sequences in cyanobacteria. Mol Genet Genomics 278, 331–346 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0254-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0254-9