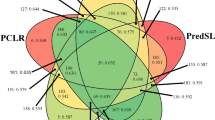
Abstract
A group of nuclear transcription factors, the Whirly proteins, were recently shown to be targeted also to chloroplasts and mitochondria. In order to find out whether other proteins might share this feature, an in silico-based screening of transcription factors from Arabidopsis and rice was carried out with the aim of identifying putative N-terminal chloroplast and mitochondrial targeting sequences. For this, the individual predictions of several independent programs were combined to a consensus prediction using a naïve Bayes method. This consensus prediction shows a higher specificity at a given sensitivity value than each of the single programs. In both species, transcription factors from a variety of protein families that possess putative N-terminal plastid or mitochondrial target peptides as well as nuclear localization sequences, were found. A search for homologues within members of the AP2/EREBP protein family revealed that target peptide-containing proteins are conserved among monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous species. Fusion of one of these proteins to GFP revealed, indeed, a dual targeting activity of this protein. We propose that dually targeted transcription factors might be involved in the communication between the nucleus and the organelles in plant cells. We further discuss how recent results on the physical interaction between the organelles and the nucleus could have significance for the regulation of the localization of these proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- At:
-
Arabidopsis thaliana
- cTP:
-
Chloroplast targeting peptide
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- mTP:
-
Mitochondrial targeting peptide
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization sequence
- Os:
-
Oryza sativa
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bae MS, Cho EJ, Choi EY, Park OK (2003) Analysis of the Arabidopsis nuclear proteome and its response to cold stress. Plant J 36:652–663
Bannai H, Tamada Y, Maruyama O, Nakai K, Miyano S (2002) Extensive feature detection of N-terminal protein sorting signals. Bioinformatics 18:298–305
Baumbusch LO, Thorstensen T, Krauss V, Fischer A, Naumann K, Assalkhou R, Schulz I, Reuter G, Aalen RB (2001) The Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains at least 29 active genes encoding SET domain proteins that can be assigned to four evolutionarily conserved classes. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4319–4333
Beck CF (2005) Signalling pathways from the chloroplast to the nucleus. Planta 222:743–756
Bodén M, Hawkins J (2005) Prediction of subcellular localization using sequence-biased recurrent networks. Bioinformatics 21:2279–2286
Boguta M, Hunter LA, Shen W-C, Gillman EC, Martin NC, Hopper AK (1994) Subcellular locations of MOD5 proteins: mapping of sequences sufficient for targeting to mitochondria and demonstration that mitochondrial and nuclear isoforms comingle in the cytosol. Mol Cell Biol 14:2298–2306
Bomsztyk K, Denisenko O, Ostrowski J (2004) hnRNP K: one protein multiple processes. BioEssays 26:629–638
Boyle B, Brisson N (2001) Repression of the defense gene PR-10a by the single-stranded DNA binding protein SEBF. Plant Cell 13:2525–2537
Bruce BD (2000) Chloroplast transit peptides: structure, function and evolution. Trends Cell Biol 10:440–447
Chen M, Tao Y, Lim J, Shaw A, Chory J (2005) Regulation of phytochrome B nuclear localization through light-dependent unmasking of nuclear localization signals. Curr Biol 15:637–642
Choi Y, Harada JJ, Goldberg RB, Fischer RL (2004) An invariant aspartic acid in the DNA glycosylase domain of DEMETER is necessary for transcriptional activation of the imprinted MEDEA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7481–7486
Claros MG, Vincens P (1996) Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem 241:779–786
Cokol M, Nair R, Rost B (2000) Finding nuclear localization signals. EMBO Rep 1:411–415
Cregan SP, Fortin A, MacLaurin JG, Callaghan SM, Cecconi F, Yu SW, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Park DS, Kroemer G, Slack RS (2002) Apoptosis-inducing factor is involved in the regulation of caspase-independent neuronal cell death. J Cell Biol 158:507–517
Curaba J, Herzog M, Vachon G (2003) GeBP, the first member of a new gene family in Arabidopsis, encoded a nuclear protein with DNA-binding activity and is regulated by KNAT1. Plant J 33:305–317
Davuluri RV, Sun H, Palaniswamy SK, Matthews N, Molina C, Kurtz M, Grotewold E (2003) AGRIS: Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an information resource of Arabidopsis cis-regulatory elements and transcription factors. BMC Bioinformatics 4:25
Desveaux D, Després C, Joyeux A, Subramaniam R, Brisson N (2000) PBF-2 is a novel single-stranded DNA binding factor implicated in PR-10a gene activation in potato. Plant Cell 12:1477–1489
Desveaux D, Subramaniam R, Despres C, Mess JN, Levesque C, Fobert PR, Dangl JL, Brisson N (2004) A "Whirly" transcription factor is required for salicylic acid-dependent disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 6:229–240
Ellis SR, Hopper AK, Martin NC (1989) Amino-terminal extension generated from an upstream AUG codon increases the efficiency of mitochondrial import of yeast N2,N2-dimethylguanosine-specific tRNA methyltransferases. Mol Cell Biol 9:1611–1620
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, von Heijne G (1999) ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci 8:978–984
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016
Guda C, Fahy E, Subramaniam S (2004) MITOPRED: a genome-scale method for prediction of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins. Bioinformatics 20:1785–1794
Hao D, Yamasaki K, Sarai A, Ohme-Takagi M (2002) Determinants in the sequence specific binding of two plant transcription factors, DBF1 and NtERF2, to the DRE and GCC motifs. Biochemistry 41:4202–4208
Harrison DJ, Langdale JA (2006) A step by step guide to phylogeny reconstruction. Plant J 45:561–572
Heazlewood JL, Tonti-Filippini J, Verboom RE, Millar H (2005) Combining experimental and predicted datasets for determination of the subcellular location of proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:598–609
Heidstra R, Welch D, Sheres B (2004) Mosaic analyses using marked activation and deletion clones to dissect Arabidopsis SCARECROW action in asymmetric cell division. Genes Dev 18:1964–1969
Horton P, Park K-J, Obayashi T, Nakai K (2006) Protein subcellular localization prediction with WoLF PSORT. In: Proceedings of the 4th annual Asia Pacific bioinformatics conference APBC06, Taipei, Taiwan, pp 39–48
Karniely S, Pines O (2005) Single translation—dual destination: mechanisms of dual protein targeting in eukaryotes. EMBO Rep 6:420–425
Kircher S, Gil P, Kozma-Bognár L, Fejes E, Speth V, Husselstein-Muller T, Bauer D, Adam E, Schäfer E, Nagy F (2002) Nucleocytoplasmic partitioning of the plant photoreceptors phytochrome A, B, C, D, and E is regulated differentially by light and exhibits a diurnal rhythm. Plant Cell 14:1541–1555
Koroleva OA, Tomlinson ML, Leader D, Shaw P, Doonan JH (2005) High-throughput protein localization in Arabidopsis using Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of GFP–ORF-fusions. Plant J 41:162–174
Krause K, Kilbienski I, Mulisch M, Rödiger A, Schäfer A, Krupinska K (2005) DNA-binding proteins of the Whirly family in Arabidopsis thaliana are targeted to the organelles. FEBS Lett 579:3707–3712
Krupinska K (2005) Fate and activities of plastids during leaf senescence. In: Wise RR, Hoober JK (eds) The structure and function of plastids. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 433–449
Kwok EY, Hanson MR (2004) Plastids and stromules interact with the nucleus and cell membrane in vascular plants. Plant Cell Rep 23:188–195
Liu L, White MJ, MacRae TH (1999) Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants. Functional domains, evolution and regulation. Eur J Biochem 262:247–257
Luo M, Orsi R, Patrucco E, Pancaldi SRC (1997) Multiple transcription start sites of the carrot dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene, and sub-cellular localization of the bifunctional protein. Plant Mol Biol 33:709–722
Magnani E, Sjölander K, Hake S (2004) From endonucleases to transcription factors: evolution of the AP2 DNA binding domain in plants. Plant Cell 16:2265–2277
Nakai K, Horton P (1999) PSORT: a program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem Sci 24:34–36
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140:411–432
Negrutiu I, Shillito RD, Potrykus I, Biasini G, Sala F (1987) Hybrid gene in the analysis of transformation conditions. I. Setting up a simple method for direct gene transfer in plant protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol 8:363–373
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak B, von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10:1–6
Nuhse TS, Stensballe A, Jensen ON, Peck SC (2003) Large-scale analysis of in vivo phosphorylated membrane proteins by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 2:1234–1243
Petsalaki EI, Bagos PG, Litou ZI, Hamodrakas SJ (2006) PredSL: a tool for the N-terminal sequence-based prediction of protein subcellular localization. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 4:48–55
Raynaud C, Sozzani R, Glab N, Domenichini S, Perennes C, Cella R, Kondorosi E, Bergouinoux C (2006) Two cell-cycle regulated SET-domain proteins interact with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:395–407
Richly E, Dietzmann A, Biehl A, Kurth J, Laloi C, Apel K, Salamini F, Leister D (2003) Covariations in the nuclear chloroplast transcriptome reveal a regulatory master-switch. EMBO Rep 4:491–498
Riechmann JL, Meyerowitz EM (1998) The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biol Chem 379:633–646
Ruchalski K, Mao H, Li Z, Wang Z, Gillers S, Wang Y, Mosser DD, Gabai V, Schwartz JH, Borkan SC (2006) Distinct hsp70 domains mediate apoptosis-inducing factor release and nuclear accumulation. J Biol Chem 281:7873–7880
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sakamoto K, Briggs WR (2002) Cellular and subcellular localization of phototropin 1. Plant Cell 14:1723–1735
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2002) DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:998–1009
Schein AI, Kissinger JC, Ungar LH (2001) Chloroplast transit peptide prediction: a peek behind the black box. Nucleic Acids Res 29:82
Schneider M, Bairoch A, Wu CH, Apweiler R (2005) Plant protein annotation in the UniProt Knowledgebase. Plant Physiol 138:59–66
Selga T, Selga M, Pavila V (2005) Death of mitochondria during programmed cell death of leaf mesophyll cells. Cell Biol Int 29:1050–1056
Shigyo M, Hasabe M, Ito M (2006) Molecular evolution of the AP2 subfamily. Gene 366:256–265
Silva-Filho MC (2003) One ticket for multiple destinations: dual targeting of proteins to distinct subcellular locations. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:589–595
Slupphaug G, Markussen F-H, Olsen LC, Aasland R, Aarsaether N, Bakke O, Krokan HE, Helland DE (1993) Nuclear and mitochondrial forms of human uracil-DNA glycosylase are encoded by the same gene. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2579–2584
Small I, Wintz H, Akashi K, Mireau M (1998) Two birds with one stone: genes that encode products targeted to two or more compartments. Plant Mol Biol 38:265–277
Small I, Peeters N, Legeai F, Lurin C (2004) Predotar: a tool for rapidly screening proteomes for N-terminal targeting sequences. Proteomics 4:1581–1590
Springer NM, Napoli CA, Selinger DA, Pandey R, Cone KC, Chandler VL, Kaeppler HF, Kaeppler SM (2003) Comparative analysis of SET domain proteins in maize and Arabidopsis reveals multiple duplications preceding the divergence of monocots and dicots. Plant Physiol 132:907–925
Strand A (2004) Plastid-to-nucleus signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:621–625
Stribinskis V, Heyman H-C, Ellis SR, Steffen MC, Martin NC (2005) Rpm2p, a component of yeast mitochondrial RNaseP, acts as a transcriptional activator in the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol 25:6546–6558
Sunderland PA, West CE, Waterworth WM, Bray CM (2004) Choice of a start codon in a single transcript determines DNA ligase 1 isoform production and intracellular targeting in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Soc Trans 32:614–616
Sunderland PA, West CE, Waterworth WM, Bray CM (2006) An evolutionarily conserved translation initiation mechanism regulates nuclear or mitochondrial targeting of DNA ligase 1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 47:356–367
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler M, Larochette N, Goodlett DR, Aebersold R, Siderovski DP, Penninger JM, Kroemer G (1999) Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397:441–446
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewiak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Wagner R, Pfannschmidt T (2006) Eukaryotic transcription factors in plastids—bioinformatic assessment and implications for the evolution of gene expression machineries in plants. Gene 381:62–70
Weigel D (1995) The APETALA2 domain is related to a novel type of DNA binding domain. Plant Cell 7:388–389
Wessler SR (2005) Homing into the origin of the AP2 DNA binding domain. Trends Plant Sci 10:54–56
Wissing S, Ludovico P, Herker E, Büttner S, Engelhardt SM, Decker T, Link A, Proksch A, Rodrigues F, Corte-Real M, Fröhlich K-U, Manns J, Candé C, Sigrist SJ, Kroemer G, Madeo F (2004) An AIF orthologue regulates apoptosis in yeast. J Cell Biol 166:969–974
Wolfe CL, Lou Y-C, Hopper AK, Martin NC (1994) Interplay of heterogenous transcriptional start sites and translational selection of AUGs dictate the production of mitochondrial and cytosolic/nuclear tRNA nucleotidyltransferase from the same gene in yeast. J Biol Chem 269:13361–13366
Wolfe CL, Hopper AK, Martin NC (1996) Mechanisms leading to and the consequences of altering the normal distribution of ATP (CTP):tRNA nucleotidyltransferase in yeast. J Biol Chem 271:4679–4686
Xiong Y, Liu T, Tian C, Sun S, Li J, Chen M (2005) Transcription factors in rice: a genome-wide comparative analysis between monocots and eudicots. Plant Mol Biol 59:191–203
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Mario Brosch and Isabell Kilbienski (University of Kiel) for stimulating discussions. Prof. Martin Huelskamp (University of Cologne) is thanked for providing the Arabidopsis cell culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. F. Lang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary meterial
438_2007_214_MOESM1_ESM.xls
S1: List of plastid proteins used as test set for chloroplast localization. The gene identifier, organism and function of each protein are given. (64 KB)
438_2007_214_MOESM2_ESM.xls
S2: List of mitochondrial proteins used as test set for mitochondrial localization. The gene identifier, organism and function of each protein are given. (35 KB)
438_2007_214_MOESM3_ESM.xls
S3: List of non-plastid and non-mitochondrial proteins used as control test set for non-organellar localization. The gene identifier, organism and function of each protein are given. (93 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwacke, R., Fischer, K., Ketelsen, B. et al. Comparative survey of plastid and mitochondrial targeting properties of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice. Mol Genet Genomics 277, 631–646 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0214-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0214-4