Abstract
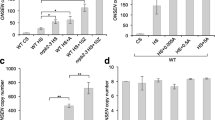
Transposable elements are major components of plant genomes. Their activity seems to be epigenetically regulated by gene silencing systems. Here we report epigenetic variation in the retrotransposon Tos17 activity in rice varieties. Of the two copies of Tos17 present in chromosome 7 (Tos17 chr.7) and chromosome 10 (Tos17 chr.10), Tos17 chr.7 is strongly activated by tissue culture in most varieties including Nipponbare except for Moritawase, despite the identity of the DNA sequences in Moritawase and Nipponbare. Tos17 chr.7 activity correlated with its methylation status, and Tos17 chr.7 in Moritawase was heavily methylated and activated by treatment of 5-azacytidine (5-azaC), a DNA methylation inhibitor. Although the original copies of Tos17 are methylated to some extent in all varieties examined, the transposed copies in calli mostly are not methylated. When plants were regenerated from calli, the degree of methylation of the Tos17 DNA increased gradually with the growth of plants, and a significant progress of DNA methylation occurred in the next generation after a completed reproductive cycle. With increasing DNA methylation, the transcription of transposed and original Tos17 copies driven by its own as well as by a flanking gene promoter were suppressed. We conclude that Tos17 DNA methylation controls the transpositional activity of Tos17, and modulates the activity of neighboring genes. Based on the analysis of the inactive Tos17 chr.10, we propose that another mechanism, called transcriptional interference, is involved in the control of Tos17 activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhya S, Gottesman M (1982) Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell 29:939–944
Barkan A, Martienssen RA (1991) Inactivation of maize transposon Mu suppresses a mutant phenotype by activating an outward-reading promoter near the end of Mu1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3502–3506
Bateman E, Paule MR (1988) Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell 54:985–992
Capy P, Gasperi G, Biemont C, Bazin C (2000) Stress and transposable elements: co-evolution or useful parasites?. Heredity 85:101–106
Chan SW, Zilberman D, Xie Z, Johansen LK, Carrington JC, Jacobsen SE (2004) RNA silencing genes control de novo DNA methylation. Science 303:1336
Cheng C, Motohashi R, Tsuchimoto S, Fukuta Y, Ohtsubo H, Ohtsubo E (2003) Polyphyletic origin of cultivated rice: based on the interspersion pattern of SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 20:67–75
Fedoroff N (1996) Epigenetic regulation of the maize Spm transposable element. In: Russo VEA et al (eds) Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, pp 575–592
Feschotte C, Jiang N, Wessler SR (2002) Plant transposable elements: where genetics meets genomics. Nat Rev Genet 3:329–341
Hagan CR, Sheffield RF, Rudin CM (2003) Human Alu element retrotransposition induced by genotoxic stress. Nat Genet 35:219–220
Hamilton A, Voinnet O, Chappell L, Baulcombe D (2002) Two classes of short interfering RNA in RNA silencing. EMBO J 21:4671–4679
Han JS, Szak ST, Boeke JD (2004) Transcriptional disruption by the L1 retrotransposon and implications for mammalian transcriptomes. Nature 429:268–274
Hirochika H (1993) Activation of tobacco retrotransposons during tissue culture. EMBO J 12:2521–2528
Hirochika H, Otsuki H, Yoshikawa M, Otsuki Y, Sugimoto K, Takeda S (1996a) Autonomous transposition of the tobacco retrotransposon Tto1 in rice. Plant Cell 8:725–734
Hirochika H, Sugimoto K, Otsuki Y, Tsugawa H, Kanda M (1996b) Autonomous Retrotransposons of rice involved in mutations induced by tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7783–7788
Hirochika H, Okamoto H, Kakutani T (2000) Silencing of retrotransposons in arabidopsis and reactivation by the ddm1 mutation. Plant Cell 12:357–369
Hirochika H, Guiderdoni E, An G, Hsing Y, Eun MY, Han C, Upadhyaya N, Ramachandran S, Zhang Q, Pereira A, Sundaresan V, Leung H (2004) Rice mutant resources for gene discovery. Plant Mol Biol 54:325–334
International human genome sequencing consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Jiang N, Bao Z, Zhang X, Hirochika H, Eddy SR, Mccouch SR, Wessler SR (2003) An active DNA transposon family in rice. Nature 421:163–167
Kanno T, Huettel B, Mette MF, Aufsatz W, Jaligot E, Daxinger L, Kreil DP, Matzke M, Matzke AJ (2005) Atypical RNA polymerase subunits required for RNA-directed DNA methylation. Nat Genet 37:761–765
Kashkush K, Feldman M, Levy AA (2003) Transcriptional activation of retrotransposons alters the expression of adjacent genes in wheat. Nat Genet 33:102–106
Kato M, Miura A, Bender J, Jacobsen SE, Kakutani T (2003) Role of CG and non-CG methylation in immobilization of transposons in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 13:421–426
Kazazian HH Jr (2004) Mobile elements: drivers of genome evolution. Science 303: 1626–1632
Kiger AA, Gigliotti S, Fuller MT (1999) Developmental genetics of the essential Drosophila nucleoporin nup154: allelic differences due to an outward-directed promoter in the P-element 3’ end. Genetics 153:799–812
Kikuchi K, Terauchi K, Wada M, Hirano HY (2003) The plant MITE mPing is mobilized in anther culture. Nature 421:167–170
Komatsu M, Shimamoto K, Kyozuka J (2003) Two-step regulation and continuous retrotransposition of the rice LINE-type retrotransposon Karma. Plant Cell 15:1934–1944
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Lindroth AM, Cao X, Jackson JP, Zilberman D, Mccallum CM, Henikoff S, Jacobsen SE (2001) Requirement of CHROMOMETHYLASE3 for maintenance of CpXpG methylation. Science 292:2077–2080
Lippman Z, Gendrel AV, Black M, Vaughn MW, Dedhia N, Mccombie WR, Lavine K, Mittal V, May B, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC, Doerge RW, Colot V, Martienssen R (2004) Role of transposable elements in heterochromatin and epigenetic control. Nature 430:471–476
Martienssen RA (1996) Epigenetic silencing of Mu transposable elements in maize. In: Russo VEA et al (eds) Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 593–608
Martienssen R (1998) Transposons, DNA methylation and gene control. Trends Genet 14:263–264
Martienssen RA, Colot DV (2001) DNA methylation and epigenetic inheritance in plants and filamentous fungi. Science 293:1070–1074
McCarthy EM, Liu J, Lizhi G, McDonald JF (2002) Long terminal repeat retrotransposons of Oryza sativa. Genome Biol 3:research 0053.1–0053.11
McClintock B (1984) The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 226:792–801
Melayah D, Bonnivard E, Chalhoub B, Audeon C, Grandbastien MA (2001) The mobility of the tobacco Tnt1 retrotransposon correlates with its transcriptional activation by fungal factors. Plant J 28:159–168
Meyers BC, Tingey SV, Organte MM (2001) Abundance, distribution, and transcriptional activity of repetitive elements in the maize genome. Genome Res 11:1660–1676
Miura A, Yonebayashi S, Watanabe K, Toyama T, Shimada H, Kakutani T (2001) Mobilization of transposons by a mutation abolishing full DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Nature 411:212–214
Miyao A, Tanaka K, Murata K, Sawaki H, Takeda S, Abe K, Shinozuka Y, Onosato K, Hirochika H (2003) Target site specificity of the Tos17 retrotransposon shows a preference for insertion within genes and against insertion in retrotransposon-rich regions of the genome. Plant Cell 15:1771–1780
Nakazaki T, Okumoto Y, Horibata A, Yamahira S, Teraishi M, Nishida H, Inoue H, Tanisaka T (2003) Mobilization of a transposon in the rice genome. Nature 421:170–172
Okamoto H, Hirochika H (2001) Silencing of transposable elements in plants. Trends Plant Sci 6:527–534
Proudfoot NJ (1986) Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature 322:562–565
Rabinowicz PD, Palmer LE, May BP, Hemann MT, Iowe SW, Mccombie WR, Martienssen RA (2003) Genes and transposons are differentially methylated in plants, but not in mammals. Genome Res 13:2658–2664
Soppe WJ, Jasencakova Z, Houben A, Kakutani T, Meister A, Huang MS, Jacobsen SE, Schubert I, Fransz PF (2002) DNA methylation controls histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and heterochromatin assembly in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21:6549–6559
Scholes DT, Kenny AE, Gamache ER, Mou Z, Curcio MJ (2003) Activation of a LTR-retrotransposon by telomere erosion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15736–15741
Sijen T, Plasterk RH (2003) Transposon silencing in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line by natural RNAi. Nature 426:310–314
Slotkin RK, Freeling M, Lisch D (2005) Heritable transposon silencing initiated by a naturally occurring transposon inverted duplication. Nat Genet 37:641–644
Sugimoto K, Takeda S, Hirochika H (2000) MYB-related transcription factor NtMYB2 induced by wounding and elicitors is a regulator of the tobacco retrotransposon Tto1 and defense-related genes. Plant Cell 12:2511–2528
Takeda S, Sugimoto K, Otsuki H, Hirochika H (1998) Transcriptional activation of the tobacco retrotransposon Tto1 by wounding and methyl jasmonate. Plant Mol Biol 36:365–376
Takeda S, Sugimoto K, Otsuki H, Hirochika H (1999) A 13-bp cis-regulatory element in the LTR promoter of the tobacco retrotransposon Tto1 is involved in responsiveness to tissue culture, wounding, methyl jasmonate and fungal elicitors. Plant J 18:383–393
Tariq M, Saze H, Probst AV, Lichota J, Habu Y, Paszkowski J (2003) Erasure of CpG methylation in Arabidopsis alters patterns of histone H3 methylation in heterochromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8823–8827
Yamazaki M, Tsugawa H, Miyao A, Yano M, Wu J, Yamamoto S, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T, Hirochika H (2001) The rice retrotransposon Tos17 prefers low-copy-number sequences as integration targets. Mol Genet Genomics 265:336–344
Zilberman D, Cao X, Jacobsen SE (2003) ARGONAUTE4 control of locus-specific siRNA accumulation and DNA and histone methylation. Science 299:716–719
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Akio Miyao for supplying the tissue-culture derived R1 seeds and technical assistance. Dr. Muneo Yamazaki is gratefully acknowledged for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.-A. Grandbastien
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Daigen, M. & Hirochika, H. Epigenetic regulation of the rice retrotransposon Tos17 . Mol Genet Genomics 276, 378–390 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0141-9