Abstract
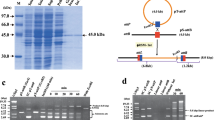
This study evaluated the ability of five serine phage integrases, from phages A118, U153, Bxb1, φFC1, and φRV1, to mediate recombination in mammalian cells. Two types of recombination were investigated, including the ability of an integrase to mediate recombination between its own phage att sites in the context of a mammalian cell and the ability of an integrase to perform genomic integration pairing a phage att site with an endogenous mammalian sequence. We demonstrated that the A118 integrase mediated precise intra-molecular recombination of a plasmid containing its attB and attP sites at a frequency of ∼ 50% in human cells. The closely related U153 integrase also performed efficient recombination in human cells on a plasmid containing the attB and attP sites of A118. The integrases from phages Bxb1, φFC1, and φRV1 carried out such recombination at their attB and attP sites at frequencies ranging from 11 to 75%. Furthermore, the A118 integrase mediated recombination between its attP site on a plasmid and pseudo attB sites in the human genome, i.e. native sequences with partial identity to attB. Fifteen such A118 pseudo att sites were analyzed, and a consensus recognition site was identified. The other integrases did not mediate integration at genomic sequences at a frequency above background. These site-specific integrases represent valuable new tools for manipulating eukaryotic genomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen BG, Weeks DL (2005) Transgenic Xenopus laevis embryos can be generated using φC31 integrase. Nat Methods 2:975–979
Barletta RG, Kim DD, Snapper SB, Bloom BR, Jacobs WR Jr (1992) Identification of expression signals of the mycobacteriophages Bxb1, L1 and TM4 using the Escherichia–Mycobacterium shuttle plasmids pYUB75 and pYUB76 designed to create translational fusions to the lacZ gene. J Gen Microbiol 138:23–30
Belteki G, Gertsenstein M, Ow DW, Nagy A (2003) Site-specific cassette exchange and germline transmission with mouse ES cells expressing φC31 integrase. Nat Biotechnol 21:321–324
Bertoni C, Jarrahian S, Wheeler TM, Li Y, Olivares EC, Calos MP, Rando TA (2006) Enhancement of plasmid-mediated gene therapy for muscular dystrophy by directed plasmid integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:419–424
Bibb LA, Hatfull GF (2002) Integration and excision of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis prophage-like element, φRV1. Mol Microbiol 45:1515–1526
Chalberg TW, Genise HL, Vollrath D, Calos MP (2005) φC31 integrase confers genomic integration and long-term transgene expression in rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:2140–2146
Chalberg TW, Portlock JL, Olivares EC, Thyagarajan B, Kirby PJ, Hillman RT, Hoelters J, Calos MP (2006) Integration specificity of phage φC31 integrase in the human genome. J Mol Biol 357:28–48
Christiansen B, Brondsted L, Vogensen FK, Hammer K (1996) A resolvase-like protein is required for the site-specific integration of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage TP901-1. J Bacteriol 178:5164–5173
Christiansen B, Johnsen MG, Stenby A, Vogensen FK, Hammer K (1994) Characterization of the lactococcal temperate phage TP901-1 and its site-specific integration. J Bacteriol 176:1069–1076
Cole ST, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon SV, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry CE 3rd, Tekaia F, Badcock K, Basham D, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Connor R, Davies R, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Hamlin N, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Jagels K, Krogh A, McLean J, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Osborne J, Quail MA, Rajandream MA, Rogers J, Rutter S, Seeger K, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston JE, Taylor K, Whitehead S, Barrell BG (1998) Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537–544
Ghosh P, Kim AI, Hatfull GF (2003) The orientation of mycobacteriophage Bxb1 integration is solely dependent on the central dinucleotide of attP and attB. Mol Cell 12:1101–1111
Groth AC, Olivares EC, Thyagarajan B, Calos MP (2000) A phage integrase directs efficient site-specific integration in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5995–6000
Groth AC, Fish M, Nusse R, Calos MP (2004) Construction of transgenic Drosophila by using the site-specific integrase from phage φC31. Genetics 166:1775–1782
Held PK, Olivares EC, Aguilar CP, Finegold M, Calos MP, Grompe M (2005) In vivo correction of murine hereditary tyrosinemia type I by φC31 integrase-mediated gene delivery. Mol Ther 11:399–408
Hendrix RW, Smith MC, Burns RN, Ford ME, Hatfull GF (1999) Evolutionary relationships among diverse bacteriophages and prophages: all the world’s a phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2192–2197
Hirt B (1967) Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cultures. J Mol Biol 26:365–369
Hodgson DA (2000) Generalized transduction of serotype 1/2 and serotype 4b strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol 35:312–323
Hollis RP, Stoll SM, Sclimenti CR, Lin J, Chen-Tsai Y, Calos MP (2003) Phage integrases for the construction and manipulation of transgenic mammals. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 1:79
Kim AI, Ghosh P, Aaron MA, Bibb LA, Jain S, Hatfull GF (2003) Mycobacteriophage Bxb1 integrates into the Mycobacterium smegmatis groEL1 gene. Mol Microbiol 50:463–473
Kuhstoss S, Rao RN (1991) Analysis of the integration function of the Streptomycete bacteriophage φC31. J Mol Biol 222:897–908
Landy A (1989) Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem 58:913–949
Lauer P, Chow MY, Loessner MJ, Portnoy DA, Calendar R (2002) Construction, characterization, and use of two Listeria monocytogenes site-specific phage integration vectors. J Bacteriol 184:4177–4186
Loessner MJ, Inman RB, Lauer P, Calendar R (2000) Complete nucleotide sequence, molecular analysis and genome structure of bacteriophage A118 of Listeria monocytogenes: implications for phage evolution. Mol Microbiol 35:324–340
Matsuura M, Noguchi T, Yamaguchi D, Aida T, Asayama M, Takahashi H, Shirai M (1996) The sre gene (ORF469) encodes a site-specific recombinase responsible for integration of the R4 phage genome. J Bacteriol 178:3374–3376
Mediavilla J, Jain S, Kriakov J, Ford ME, Duda RL, Jacobs WR Jr, Hendrix RW, Hatfull GF (2000) Genome organization and characterization of mycobacteriophage Bxb1. Mol Microbiol 38:955–970
O’Gorman S, Fox DT, Wahl GM (1991) Recombinase-mediated gene activation and site-specific integration in mammalian cells. Science 251:1351–1355
Olivares EC, Hollis RP, Calos MP (2001) Phage R4 integrase mediates site-specific integration in human cells. Gene 278:167–176
Olivares EC, HollisRP, Chalberg TW, Meuse L, Kay MA, Calos MP (2002) Site-specific genomic integration produces therapeutic factor IX levels in mice. Nat Biotechnol 20:1124–1128
Ortiz-Urda S, Thyagarajan B, Keene DR, Lin Q, Fang M, Calos MP, Khavari PA (2002) Stable nonviral genetic correction of inherited human skin disease. Nat Med 8:1166–1170
Ortiz-Urda S, Thyagarajan B, Keene DR, Lin Q, Calos MP, Khavari PA (2003) φC31 integrase-mediated nonviral genetic correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Gene Ther 14:923–928
Quenneville SP, Chapdelaine P, Rousseau J, Beaulieu J, Caron NJ, Skuk D, Mills P, Olivares EC, Calos MP, Tremblay JP (2004) Nucleofection of muscle-derived stem cells and myoblasts with φC31 integrase: stable expression of a full-length-dystrophin fusion gene by human myoblasts. Mol Ther 10:679–687
Rausch H, Lehmann M (1991) Structural analysis of the actinophage φC31 attachment site. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5187–5189
Sauer B (1994) Site-specific recombination: developments and applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 5:521–527
Sclimenti CR, Thyagarajan B, Calos MP (2001) Directed evolution of a recombinase for improved genomic integration at a native human sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 29:5044–5051
Smith MC, Thorpe HM (2002) Diversity in serine recombinases. Mol Microbiol 44:299–307
Sorrell DA, Kolb AF (2005) Targeted modification of mammalian genomes. Biotechnol Adv 23:431–469
Stark WM, Boocock MR, Sherratt DJ (1992) Catalysis by site-specific recombinases. Trends Genet 8:432–439
Stoll SM, Ginsburg DS, Calos MP (2002) Phage TP901-1 site-specific integrase functions in human cells. J Bacteriol 184:3657–3663
Thomason LC, Calendar R, Ow DW (2001) Gene insertion and replacement in Schizosaccharomyces pombe mediated by the Streptomyces bacteriophage φC31 site-specific recombination system. Mol Genet Genomics 265:1031–1038
Thorpe HM, Smith MC (1998) In vitro site-specific integration of bacteriophage DNA catalyzed by a recombinase of the resolvase/invertase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5505–5510
Thyagarajan B, Calos MP (2005) Site-specific integration for high-level protein production in mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol 308:99–106
Thyagarajan B, Olivares EC, Hollis RP, Ginsburg DS, Calos MP (2001) Site-specific genomic integration in mammalian cells mediated by phage φC31 integrase. Mol Cell Biol 21:3926–3934
Yang HY, Kim YW, Chang HI (2002) Construction of an integration-proficient vector based on the site-specific recombination mechanism of enterococcal temperate phage φFC1. J Bacteriol 184:1859–1864
Acknowledgements
We thank Rich Calendar for A118 and U153 phage DNA and W.R. Jacobs for Bxb1 phage DNA. This work was supported by NIH grants DK58187 and HL68112 to MPC. BT was supported by Poetic Genetics, LLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Aguilera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keravala, A., Groth, A.C., Jarrahian, S. et al. A diversity of serine phage integrases mediate site-specific recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Genet Genomics 276, 135–146 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0129-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0129-5